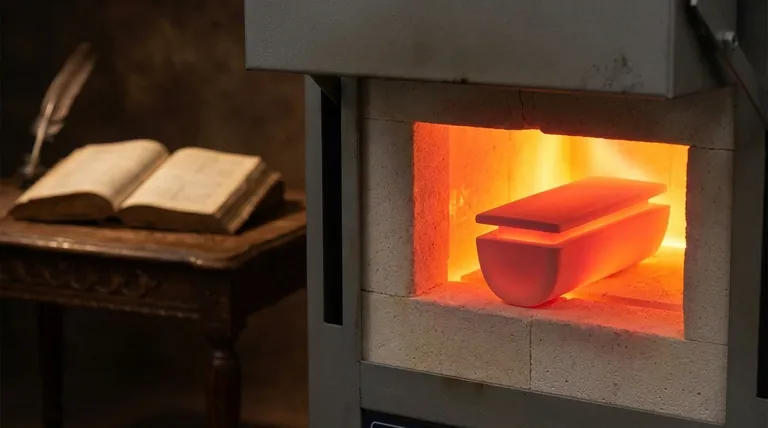
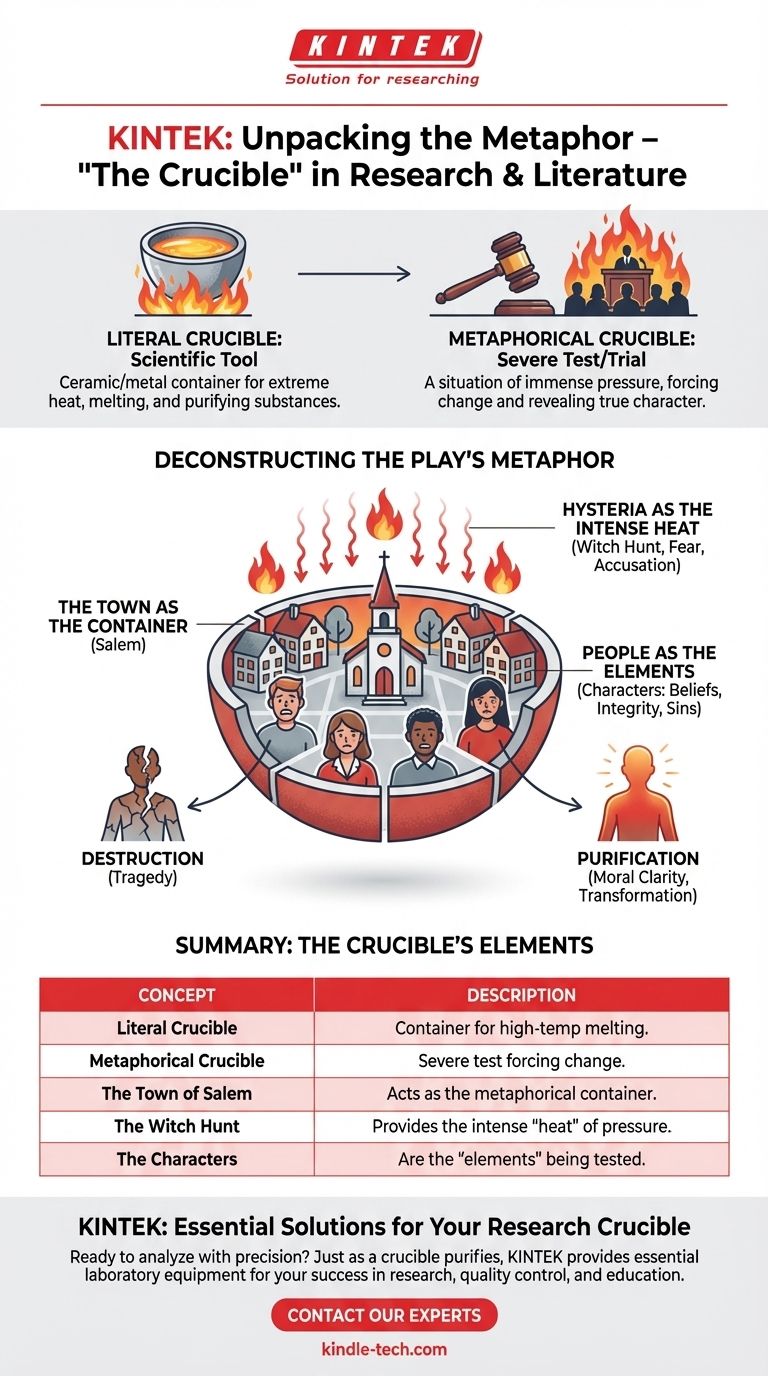
To be direct, your question points to a common confusion. A crucible, the physical tool used for melting substances at high temperatures, is not actually used within the famous play The Crucible by Arthur Miller. The title is a metaphor, referencing a severe test or trial where individuals are placed under immense pressure, forcing a change or revealing their true character.
The core of the matter is this: "The Crucible" uses the word not as a literal object, but as a powerful symbol. The entire town of Salem becomes a metaphorical crucible where the heat of hysteria and accusation tests the faith, integrity, and lives of its citizens.

Deconstructing the Term: Literal vs. Metaphorical
To fully grasp the title's meaning, we must first distinguish between the object and the idea it represents.
The Literal Meaning: A Scientific Tool
A crucible is a ceramic or metal container designed to withstand extreme heat. It's used in chemistry and metallurgy to melt down metals and other substances, separating impurities and creating something new from the raw elements.
The Metaphorical Meaning: A Severe Test
Because of its function, the word "crucible" has also come to mean a severe, searching test or trial. It describes a situation where concentrated forces interact to cause a change or a new creation. This is the definition that applies to the play.
How the Metaphor Works in the Play
Arthur Miller chose his title carefully. The events of the Salem witch trials serve as a perfect metaphorical crucible for the characters and the community.
The Town as the Container
The isolated, rigid, and religiously devout town of Salem itself is the container. The strict social and religious rules hold everyone together, much like the walls of a physical crucible.
Hysteria as the Intense Heat
The "heat" applied to this container is the mass hysteria of the witch hunt. Fueled by fear, personal grudges, and religious fervor, the accusations raise the temperature to an unbearable level.
People as the Elements Being Tested
Each character is an element placed into this heated environment. Their core beliefs, integrity, moral courage, and hidden sins are subjected to intense pressure. They are forced to "melt" under interrogation.
The Outcome: Purification or Destruction
As with a real crucible, the process has a transformative outcome. Some characters are destroyed, while others are purified. John Proctor, for example, is stripped of his pride and guilt, ultimately finding his "goodness" by refusing to confess to a lie, even at the cost of his life.
Understanding the Trade-offs of the Metaphor
While powerful, the metaphor has nuances that are important to recognize.
It Implies Inevitability
The metaphor suggests that once the "heat" is applied, the transformation is inevitable. This can overshadow the element of individual choice that Miller emphasizes, as characters like Proctor, Hale, and Elizabeth actively make decisions that seal their fate.
It Focuses on Purity
A crucible is used to burn away impurities. This framing suggests that characters like John Proctor are "purified" by their ordeal. While he achieves moral clarity, the process is one of utter destruction for him, his family, and the community. The outcome is tragedy, not just a refined product.
Making Sense of the Title for Your Goal
To apply this understanding, consider what aspect of the play you are focused on.
- If your primary focus is on social commentary: View the crucible as a societal event, where the heat of ideology and fear melts down justice and reason within the container of a rigid community.
- If your primary focus is on character analysis: See the crucible as a personal test, forcing each individual to confront their own flaws and decide what they are willing to sacrifice for their integrity.
- If your primary focus is on the historical allegory: Recognize that the play itself was a crucible for 1950s America, using the Salem witch trials to test the nation's conscience during the anti-communist "Red Scare."
Ultimately, the power of the title lies in its ability to capture the intense, transformative, and destructive pressure of a society turning on itself.
Summary Table:
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Literal Crucible | A container for melting substances at high temperatures. |
| Metaphorical Crucible | A severe test or trial that forces change or reveals true character. |
| The Town of Salem | Acts as the metaphorical container. |
| The Witch Hunt | Provides the intense 'heat' of pressure. |
| The Characters | Are the 'elements' being tested and transformed. |
Ready to analyze literature with precision? Just as a crucible is essential for purifying materials in the lab, KINTEK provides the essential equipment and consumables for your laboratory's success. Whether you're in research, quality control, or education, our reliable tools help you achieve accurate results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solutions for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What role does an Alumina Crucible play in the high-temperature solid-state synthesis of Na3OBr? Ensure Sample Purity
- Why is a high-purity alumina crucible preferred for high-temperature oxidation? Ensure Unmatched Data Integrity
- What is the function of alumina crucibles in Na3V2(PO4)2F3 synthesis? Ensure Purity in NVPF Production
- What are the advantages of high-purity alumina crucibles for molten ZnNaK//Cl salts? Ensure Experimental Purity
- Why is the use of high-purity alumina crucibles necessary for NMC powders? Ensure Purity in Cathode Synthesis



















