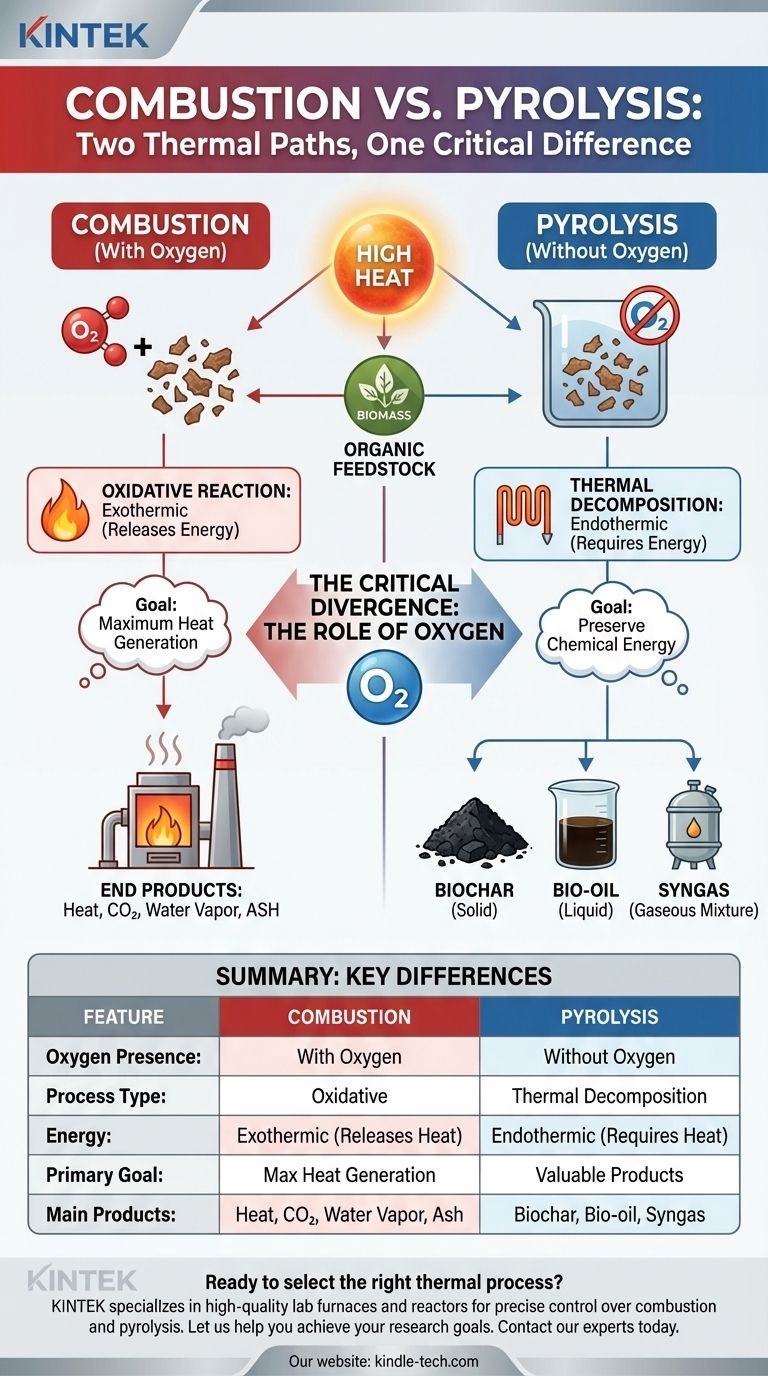
At their core, both combustion and pyrolysis are thermal decomposition processes that use high heat to break down organic materials. They represent two different paths for transforming matter with energy, starting from the same fundamental principle of applying heat to initiate a chemical change.
The crucial distinction is not the heat, but the air. Combustion is an oxidative process that occurs with oxygen, while pyrolysis is a non-oxidative process that occurs without it, fundamentally altering the reaction and its end products.

The Foundation: What Both Processes Share
While their outcomes are vastly different, combustion and pyrolysis begin from a shared starting point. Understanding this foundation is key to grasping their relationship.
High Heat as the Driving Force
Both processes rely on applying high temperatures to a feedstock, typically organic matter like biomass. This thermal energy is what breaks the complex chemical bonds within the material, initiating its transformation.
Transformation of the Feedstock
In both cases, a solid or liquid feedstock is converted into different states of matter. The original material is irreversibly broken down into simpler components.
Production of Gaseous Byproducts
Both combustion and pyrolysis release gases. However, the composition and utility of these gases are a primary point of divergence between the two methods.
The Critical Divergence: The Role of Oxygen
The presence or absence of oxygen is the single variable that determines whether the process is combustion or pyrolysis. This factor dictates the entire chemical pathway.
Combustion: An Oxidative Reaction
Combustion is an exothermic reaction, meaning it releases energy in the form of heat and light. It is defined by the rapid oxidation of a fuel source in the presence of an oxidizer, which is typically oxygen from the air. We commonly call this "burning."
The goal of combustion is to release the stored chemical energy of the fuel as quickly as possible.
Pyrolysis: A Thermal Reaction Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis is primarily an endothermic process, meaning it requires a constant input of energy to sustain the reaction. By heating material in a de-oxygenated environment, you prevent it from burning.
Instead of being released, the chemical energy is preserved and concentrated in the resulting products. Think of it as "baking" or "roasting" the material rather than burning it.
Comparing the End Products
The most practical difference between the two processes is what you are left with when the reaction is complete.
Combustion Yields Ash and Heat
The primary outputs of complete combustion are heat, carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor, and a low-energy solid residue known as ash. The fuel's potential has been fully spent to generate thermal energy.
Pyrolysis Yields Valuable, Energy-Dense Products
Pyrolysis breaks down material into three valuable outputs:
- Biochar: A stable, carbon-rich solid.
- Bio-oil: A liquid that can be refined into fuels.
- Syngas: A mixture of combustible gases.
These products retain a high percentage of the original feedstock's energy, making them useful for other applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the core difference allows you to select the right process based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is immediate and maximum heat generation: Combustion is the most direct and simple method for converting a fuel's chemical energy into thermal energy.
- If your primary focus is creating valuable, storable products from a feedstock: Pyrolysis is the necessary process to preserve chemical energy in the form of biochar, bio-oil, and syngas.
Ultimately, the choice between burning a material for heat or baking it for new products depends entirely on the presence of oxygen.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Combustion | Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Presence | With Oxygen | Without Oxygen |
| Process Type | Oxidative | Thermal Decomposition |
| Energy | Exothermic (Releases Heat) | Endothermic (Requires Heat) |
| Primary Goal | Maximum Heat Generation | Production of Valuable Products |
| Main Products | Heat, CO₂, Water Vapor, Ash | Biochar, Bio-oil, Syngas |
Ready to select the right thermal process for your lab's needs?
Whether your research focuses on energy generation or material transformation, having the right equipment is critical. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and reactors designed for precise control over combustion and pyrolysis processes. Our solutions ensure the accuracy and repeatability your experiments demand.
Let us help you achieve your research goals. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect equipment for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a laboratory furnace called? A Guide to Muffle and Tube Furnaces
- Why do we use a muffle furnace? For Pure, Precise, and Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What temperature do you fire alumina? Achieve Optimal Density and Strength
- What are the advantages and limitations of heat treatment? Tailor Material Properties for Peak Performance
- Is muffle furnace a vacuum? Choosing the Right High-Temperature Solution for Your Lab



















