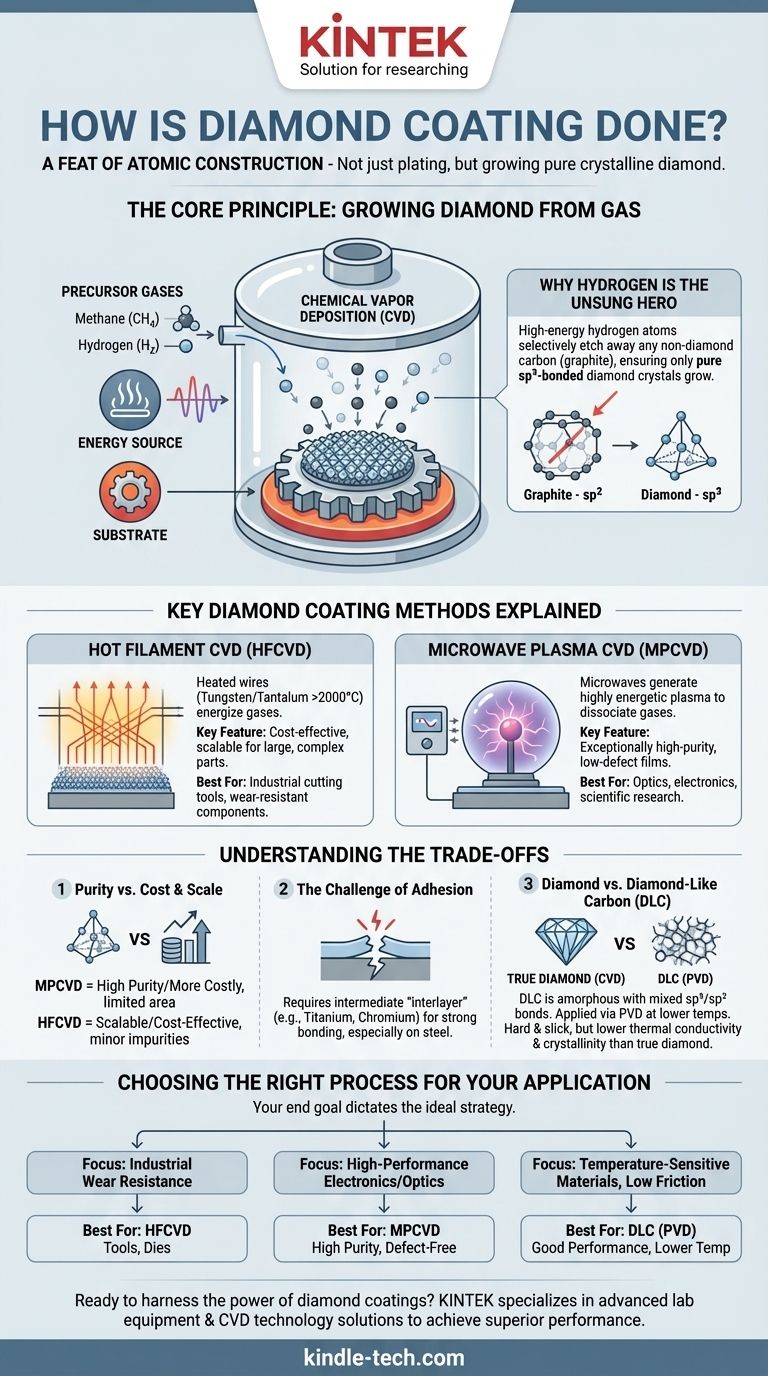
At its core, diamond coating is not a simple plating process but a feat of atomic construction. The primary method is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), a process where carbon-containing gases like methane are energized in a vacuum chamber, causing them to break apart and deposit carbon atoms onto a surface, meticulously growing a layer of pure, crystalline diamond.
The critical challenge in diamond coating isn't just depositing carbon, but ensuring it forms the ultra-hard diamond crystal structure instead of the soft, black graphite. The choice of method directly dictates the coating's purity, structure, and ultimate performance for a given application.
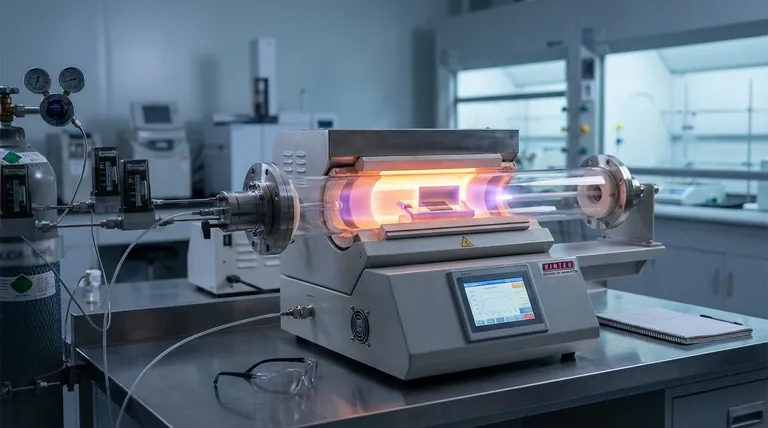

The Core Principle: Growing Diamond from Gas
To create a diamond film, you must provide the right ingredients and environment to replicate the conditions where diamond is more stable than its common counterpart, graphite. This is the central function of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
What is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)?
CVD is a process where a substrate (the part to be coated) is placed in a vacuum chamber and exposed to volatile precursor gases. These gases decompose on the heated substrate, causing the desired material—in this case, diamond—to deposit as a thin film.
The Essential Ingredients
The recipe for synthetic diamond film is surprisingly simple. It requires a carbon source, typically methane (CH₄), and an abundance of hydrogen gas (H₂). These gases are activated by a significant energy source.
Why Hydrogen is the Unsung Hero
While methane provides the carbon atoms, hydrogen is the crucial catalyst for quality. In the high-energy environment, hydrogen atoms selectively etch away any non-diamond carbon (graphite) that forms on the surface. This continuous cleaning action ensures that only the sp³-bonded diamond crystals are left to grow.
Key Diamond Coating Methods Explained
The specific method used to energize the gases determines the coating's characteristics and cost. Two CVD techniques dominate the field.
Hot Filament CVD (HFCVD)
In this method, a network of heated wires, or filaments (often made of tungsten or tantalum), is placed just above the substrate. The filaments are heated to over 2000°C, providing the thermal energy needed to break down the methane and hydrogen gas molecules.
HFCVD is valued for its ability to coat large, complex-shaped parts relatively economically, making it a workhorse for industrial applications like cutting tools and wear-resistant components.
Microwave Plasma CVD (MPCVD)
MPCVD uses microwaves to generate a highly energetic ball of plasma within the reaction chamber. This plasma efficiently dissociates the precursor gases into reactive atoms. The substrate is immersed in this plasma, allowing for uniform film growth.
This method is known for producing exceptionally high-purity, low-defect diamond films, making it the preferred choice for demanding applications in optics, electronics, and scientific research.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a diamond coating process involves balancing performance requirements with practical limitations. Understanding these compromises is key to a successful application.
Purity vs. Cost and Scale
MPCVD delivers superior diamond quality, but the equipment is more expensive and the process is typically limited to smaller areas. HFCVD is more scalable and cost-effective but can introduce minor impurities into the film from the filament itself.
The Challenge of Adhesion
Diamond does not bond easily to many materials, especially steels. Achieving strong adhesion often requires depositing an intermediate "interlayer" of a material like titanium or chromium to act as a glue between the substrate and the diamond film.
Diamond vs. Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC)
It is crucial to distinguish true diamond coatings from Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC). DLC is an amorphous film with a mix of diamond (sp³) and graphite (sp²) bonds. While very hard and slick, it does not possess the same supreme hardness, thermal conductivity, or crystalline structure of a true diamond film. DLC is often applied using Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) at lower temperatures.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Application
Your end goal dictates the ideal coating strategy. By matching the process to the performance needs, you can leverage the unique properties of diamond effectively.
- If your primary focus is industrial wear resistance (e.g., cutting tools, dies): HFCVD offers the most cost-effective path for coating large and complex parts where ultimate purity is secondary to hardness and durability.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics or optics: MPCVD is the necessary choice for its unmatched ability to produce the highly pure, uniform, and defect-free diamond films these applications demand.
- If you need hardness and low friction on a temperature-sensitive material: Consider DLC coatings applied via PVD, as they provide excellent performance and can be deposited at much lower temperatures than true diamond.
Ultimately, understanding how diamond is grown allows you to select the precise tool for your engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Hot Filament CVD (HFCVD) | Cost-effective, scalable for complex parts | Industrial tools, wear-resistant components |
| Microwave Plasma CVD (MPCVD) | High-purity, low-defect films | Electronics, optics, scientific research |
| Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) | Lower temperature application, good hardness | Temperature-sensitive materials, low friction needs |
Ready to harness the power of diamond coatings for your lab or industrial application? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for high-performance coatings. Our expertise in CVD technology can help you achieve superior hardness, wear resistance, and thermal management for your specific needs. Contact us today to discuss how our diamond coating solutions can enhance your project's performance and durability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of industrial CVD for solid boriding? Superior Process Control and Material Integrity
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision
- What role does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment play in the preparation of C/C composites? Expert Analysis



















