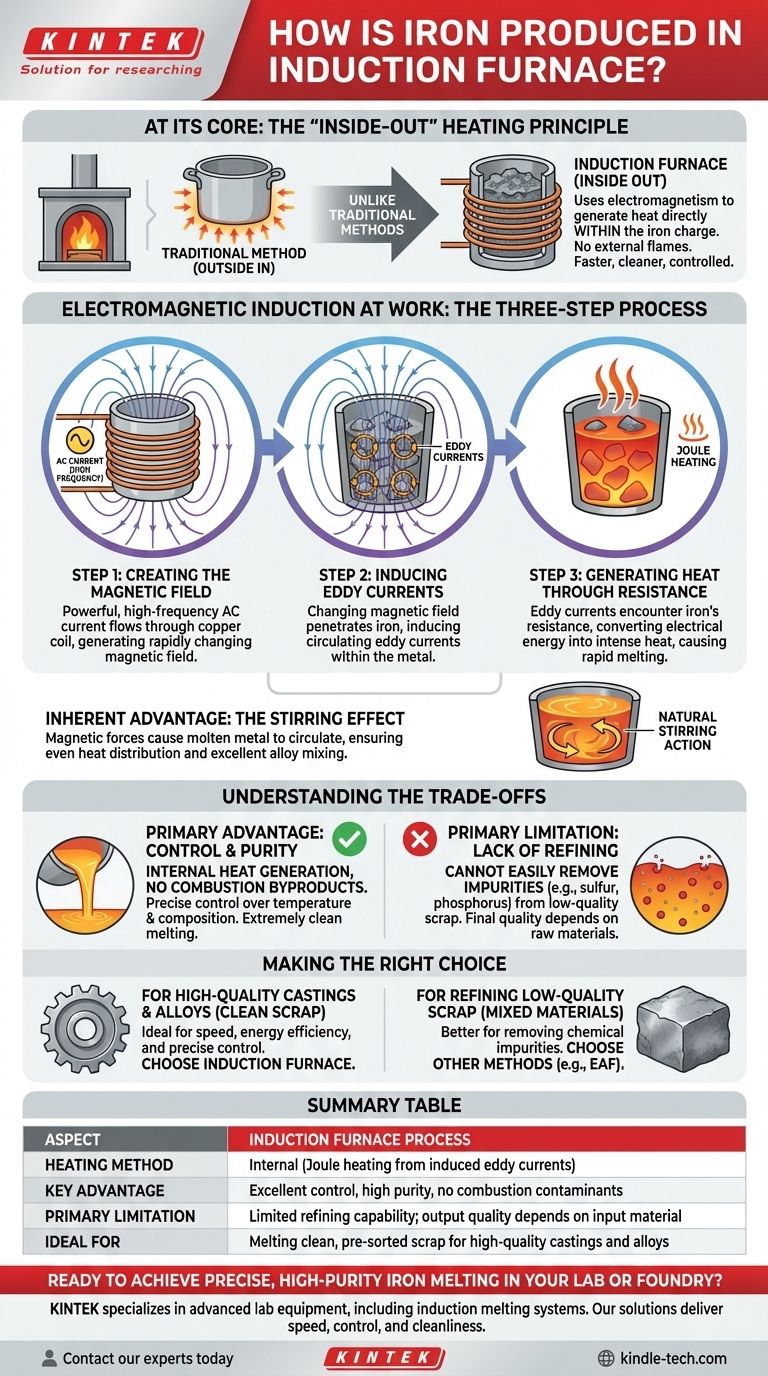
At its core, an induction furnace produces iron by turning the metal into its own heat source. It uses a powerful, rapidly changing magnetic field to induce strong electrical currents directly within the iron charge. The iron's natural resistance to these currents generates intense heat, causing it to melt quickly and efficiently without any external flames or heating elements.
The fundamental difference from traditional methods is that an induction furnace does not heat the iron from the outside in. Instead, it uses the principles of electromagnetism to generate heat from the inside out, leading to a faster, cleaner, and more controlled melting process.
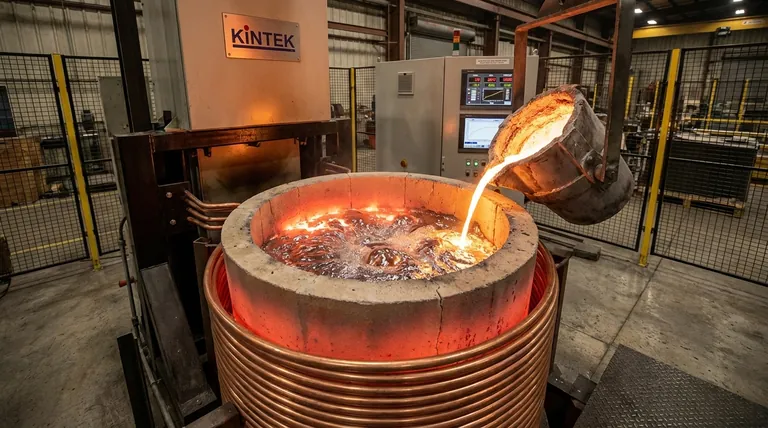

The Core Principle: Electromagnetic Induction at Work
To understand how an induction furnace operates, it's best to break the process down into three distinct physical steps. These steps happen almost instantaneously to create the heat required for melting.
Step 1: Creating the Magnetic Field
The process begins with a large, hollow copper coil that wraps around a crucible containing the iron charge (typically scrap metal or pig iron). A powerful, high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil. This flow of electricity generates a strong and rapidly fluctuating magnetic field in the space within and around the coil.
Step 2: Inducing Eddy Currents
This powerful magnetic field penetrates the crucible and passes directly through the electrically conductive pieces of iron inside. According to the laws of electromagnetic induction, this changing magnetic field induces smaller, circulating electrical currents within the iron itself. These are known as eddy currents.
Step 3: Generating Heat Through Resistance
This is the critical step where heat is created. As the induced eddy currents flow through the iron, they encounter the metal's inherent electrical resistance. This resistance converts the electrical energy of the currents into intense thermal energy, a phenomenon known as Joule heating. This heat is generated deep within the metal, causing it to melt rapidly and uniformly.
The Inherent Stirring Effect
A key advantage of this process is the natural stirring action created by the magnetic fields. The forces generated by the eddy currents cause the molten metal to circulate vigorously. This ensures an even distribution of heat and allows for excellent mixing when creating precise iron alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the induction furnace is not a universal solution. Its strengths in one area create limitations in another, which is a critical factor in its industrial application.
The Primary Advantage: Control and Purity
Because the heat is generated internally and there is no combustion of fuel, the melting process is extremely clean. There are no byproducts like ash or flue gases to contaminate the metal. This, combined with the stirring effect, gives operators precise control over the final temperature and chemical composition of the iron alloy.
The Primary Limitation: Lack of Refining
The clean nature of the process is also its main drawback. Induction furnaces are excellent at melting, but they are very poor at refining. They cannot easily remove undesirable impurities like sulfur and phosphorus from a low-quality scrap charge. The quality of the final product is therefore highly dependent on the quality of the raw materials put into it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use an induction furnace is based on the desired outcome and the quality of the starting materials.
- If your primary focus is melting clean, pre-sorted scrap to produce high-quality castings: The induction furnace is the ideal choice for its speed, energy efficiency, and precise control over the final product's composition.
- If your primary focus is refining large batches of low-quality or mixed scrap metal: Other methods, such as an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF), are more suitable due to their superior ability to remove chemical impurities during the melting process.
Ultimately, the induction furnace's brilliance lies in its elegant use of physics, treating the metal not as a passive material to be heated, but as an active component in its own electrical heating circuit.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Induction Furnace Process |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Internal (Joule heating from induced eddy currents) |
| Key Advantage | Excellent control, high purity, no combustion contaminants |
| Primary Limitation | Limited refining capability; output quality depends on input material |
| Ideal For | Melting clean, pre-sorted scrap for high-quality castings and alloys |
Ready to achieve precise, high-purity iron melting in your lab or foundry?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including induction melting systems. Our solutions deliver the speed, control, and cleanliness your processes demand.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our technology can enhance your melting operations and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?



















