In short, creating a lab-grown diamond typically takes several weeks to a few months. The exact duration depends on the method used and the desired size and quality of the final gemstone. This process is a remarkable acceleration of the billion-year timeline required for natural diamond formation beneath the Earth's crust.
While a natural diamond's value comes from its geological rarity, a lab-grown diamond's value comes from its technological purity. The controlled, rapid growth process allows for the creation of a chemically and physically identical gemstone without the variables and immense timescales of nature.

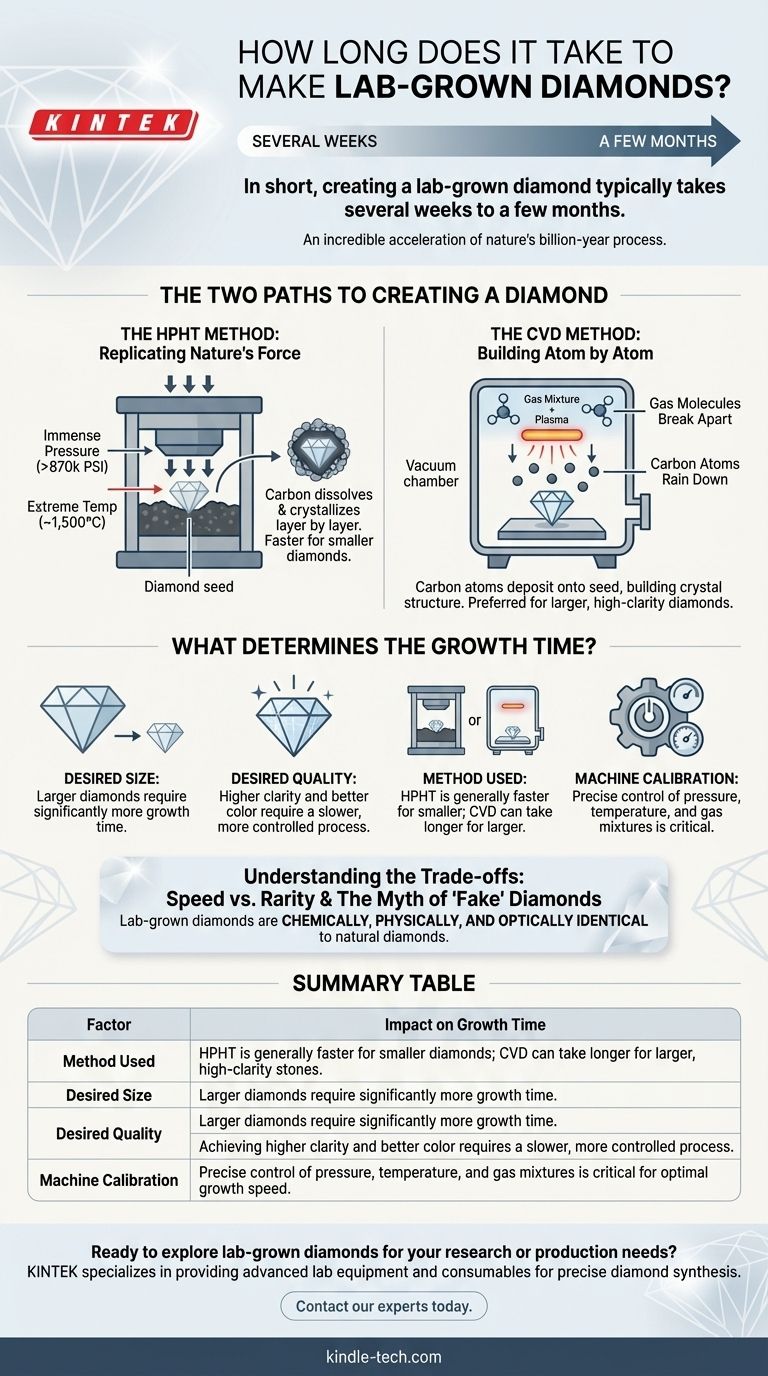
The Two Paths to Creating a Diamond
The creation of a lab-grown diamond is a highly sophisticated process that mimics the conditions of natural diamond formation, but on an exponentially faster schedule. The two dominant commercial methods are High Pressure/High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
The HPHT Method: Replicating Nature's Force
The HPHT method directly simulates the intense environment deep within the Earth where natural diamonds are born.
A small diamond "seed" is placed into a chamber with a source of pure carbon, like graphite. The chamber is then subjected to immense pressures (over 870,000 pounds per square inch) and extreme temperatures (around 1,500°C or 2,700°F).
Under these conditions, the carbon source dissolves and crystallizes onto the diamond seed, growing it layer by layer. This process is generally faster for producing collections of smaller diamonds.
The CVD Method: Building Atom by Atom
The CVD method is less about brute force and more about precision, often compared to a form of atomic 3D printing.
A diamond seed is placed inside a vacuum chamber filled with a carbon-rich gas, like methane. This gas is heated to a point where its molecules break apart, releasing carbon atoms.
These individual carbon atoms then "rain down" and deposit onto the diamond seed, meticulously building up the diamond's crystal structure. The CVD process can take longer but is often preferred for growing larger, high-clarity diamonds.
What Determines the Growth Time?
The primary factors influencing the creation timeline are the desired size and quality. Growing a larger, flawless, and colorless diamond requires more time and a more stable, controlled process than creating a smaller stone. The specific calibration of the machinery and the chosen method (HPHT vs. CVD) also play a significant role in the overall duration.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The speed of lab diamond creation introduces a different value proposition compared to natural diamonds. Understanding this is key to appreciating their role in the market.
Speed vs. Rarity
The core trade-off is technological efficiency versus geological rarity. Lab diamonds can be produced in a matter of weeks, while natural diamonds of similar quality are the result of a billion-year-plus natural process, making them finite and rare.
This speed does not imply lower quality. In fact, the controlled environment allows producers to aim for very high standards of clarity and color that are exceptionally rare in nature.
The Myth of "Fake" Diamonds
It is a critical error to confuse lab-grown diamonds with simulants like cubic zirconia or moissanite. As the reference materials confirm, lab-grown diamonds are chemically, physically, and optically identical to their natural counterparts.
They share the same crystal structure and carbon composition. The only difference is their origin: one is from a lab, the other is from the earth.
Post-Growth Treatments
Both lab-grown and natural diamonds can undergo post-growth treatments to enhance their color or clarity. For example, some HPHT-grown diamonds may be treated to improve their color. This transparency about origin and treatment is a hallmark of the lab-grown industry.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice between a lab-grown and a natural diamond depends entirely on what you value most.
- If your primary focus is maximizing size and quality for your budget: A lab-grown diamond is the logical choice, offering significant value.
- If your primary focus is a guaranteed and documented ethical origin: A lab-grown diamond provides a clear and transparent supply chain.
- If your primary focus is the romance and rarity of a geological antique: A natural diamond's billion-year history is its defining, unmatched characteristic.
Ultimately, the ability to create a perfect diamond in a matter of weeks is a testament to human ingenuity.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Growth Time |
|---|---|
| Method Used | HPHT is generally faster for smaller diamonds; CVD can take longer for larger, high-clarity stones. |
| Desired Size | Larger diamonds require significantly more growth time. |
| Desired Quality | Achieving higher clarity and better color requires a slower, more controlled process. |
| Machine Calibration | Precise control of pressure, temperature, and gas mixtures is critical for optimal growth speed. |
Ready to explore lab-grown diamonds for your research or production needs? KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables required for precise diamond synthesis. Whether you're developing new materials or scaling production, our expertise ensures you have the reliable tools for success. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- Which lab grown diamond process is best? Focus on Quality, Not the Method
- What are the limitations of diamonds? Beyond the Myth of Perfection
- What are the challenges of lab-grown diamonds? Navigating Value, Perception & Technical Limits
- What is the difference between MPCVD and HFCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- How do lab-grown diamonds compare to natural diamonds? Uncover the Truth About Origin, Price, and Value



















