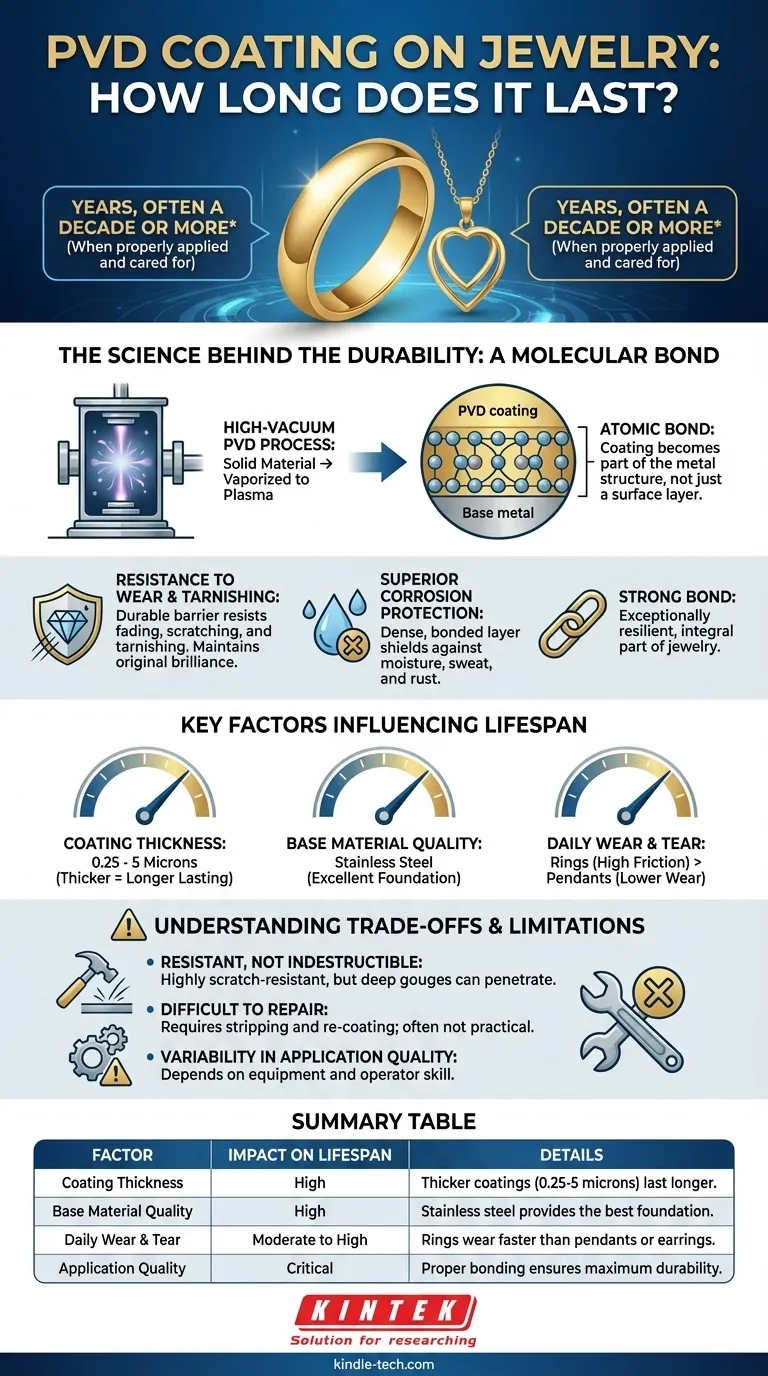
When properly applied and cared for, a PVD coating on jewelry can last for many years, often up to a decade or more. This remarkable lifespan is not a fixed guarantee but is highly dependent on the quality of the application, the thickness of the coating, and the daily wear the piece endures. Unlike traditional plating, PVD forms a much stronger bond with the base metal, making it exceptionally resilient.
The core reason for PVD's longevity isn't just the material coated on top, but the process itself. By forming a molecular bond between the coating and the base metal, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) creates a finish that is an integral part of the jewelry, not just a fragile surface layer.

The Science Behind PVD's Durability
To understand why PVD coatings last so long, it's essential to look at the process. It's fundamentally different from traditional electroplating, which simply "dips" a piece of jewelry in a solution of metal ions.
The Molecular Bond
The PVD process takes place in a high-vacuum environment where a solid coating material is vaporized into plasma. This vapor is then bonded to the jewelry at an atomic level.
This creates an atomic bond that is incredibly strong and durable. The coating doesn't just sit on the surface; it becomes a part of the metal's structure.
Resistance to Wear and Tarnishing
Because of this strong bond, the PVD layer is highly resistant to the daily factors that degrade jewelry. It provides a durable barrier that resists fading, scratching, and tarnishing.
This allows the piece to maintain its original brilliance and color for a significantly longer period than conventionally plated items.
Superior Corrosion Protection
The dense, bonded layer created by PVD is highly effective at protecting the base metal from corrosion. It acts as a shield against moisture, sweat, and other environmental elements that can cause rust or discoloration.
Key Factors Influencing PVD Lifespan
The "up to 10 years" figure is a benchmark, not a guarantee. Several critical factors determine where a specific piece will fall on that spectrum.
Coating Thickness
PVD coatings on jewelry typically range from 0.25 to 5 microns thick. For comparison, a human hair is about 70 microns.
While very thin, this range is significant. A thicker, well-applied coating will naturally offer more material to withstand wear and will last longer than a thinner one.
Quality of the Base Material
The PVD coating adheres best to a well-prepared, high-quality base material. Stainless steel is a common and excellent choice for PVD-coated jewelry because it provides a stable and durable foundation for the coating to bond with.
Daily Wear and Tear
How you wear the jewelry matters. A ring, which is constantly exposed to friction and impact, will show wear faster than a pendant or earrings. Constant exposure to harsh chemicals, abrasive surfaces, or extreme conditions can shorten the coating's lifespan.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While PVD is a superior technology, it's important to approach it with a clear understanding of its characteristics.
It Is Resistant, Not Indestructible
PVD coatings are exceptionally scratch-resistant, but they are not scratch-proof. A deep gouge from a sharp or highly abrasive object can still penetrate the coating and expose the base metal underneath.
Difficulty of Repair
Unlike traditional plating that can sometimes be touched up, repairing a damaged PVD coating is not practical. The process requires stripping the entire piece and re-coating it from scratch, which is often not a feasible or cost-effective option.
Variability in Application Quality
The term "PVD" describes a process, not a single standard of quality. The longevity and durability of the finish depend heavily on the equipment used and the skill of the operator. A poorly executed PVD application can fail much sooner than a properly bonded one.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding PVD allows you to select jewelry that aligns with your expectations for durability and style.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability for everyday wear: Seek out PVD jewelry with a quality base metal like stainless steel and inquire about the coating thickness if possible.
- If your primary focus is aesthetic variety and fashion: PVD is an excellent choice, offering a vast palette of colors (gold, rose gold, black, blue, rainbow) and finishes (matte, polished) that traditional metals cannot.
- If your primary focus is a long-term investment piece: Recognize that while PVD is highly durable, significant damage is difficult to repair, so it's best for pieces that won't be subjected to constant, heavy impact.
Ultimately, choosing PVD-coated jewelry is an investment in a modern technology that delivers resilient, long-lasting style.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Lifespan | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Thickness | High | Thicker coatings (0.25-5 microns) last longer. |
| Base Material Quality | High | Stainless steel provides the best foundation. |
| Daily Wear & Tear | Moderate to High | Rings wear faster than pendants or earrings. |
| Application Quality | Critical | Proper bonding ensures maximum durability. |
Need a PVD coating solution for your jewelry line?
KINTEK specializes in advanced PVD equipment and consumables for laboratories and manufacturers. Our technology ensures a strong molecular bond, superior scratch resistance, and vibrant color finishes that last. Enhance your product's durability and appeal—contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum lamination? Achieve a Flawless, Durable Finish on Complex Shapes
- What is hot press forging? Creating Complex, High-Strength Metal Components
- What is hot press moulding? Achieve Superior Density and Complex Shapes with Heat and Pressure
- What is hot press lamination? The Ultimate Guide to Strong, Durable Material Bonding
- What is the main function of hot press forming? Achieve Superior Strength & Precision in Manufacturing



















