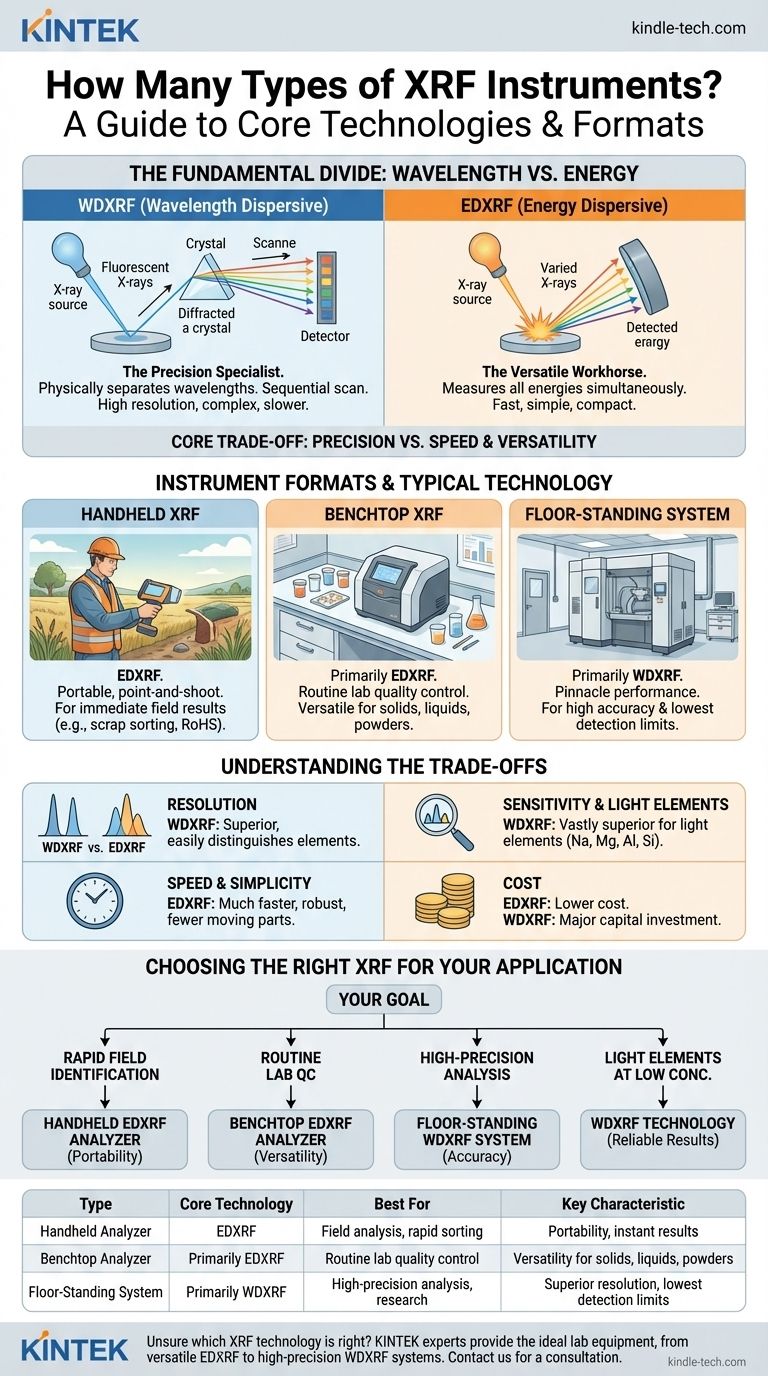
In essence, there are two fundamental types of X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectrometers, defined by how they separate and measure the X-ray signals. These are Wavelength Dispersive XRF (WDXRF) and Energy Dispersive XRF (EDXRF). All XRF instruments, from small handheld devices to large laboratory systems, are based on one of these two core technologies.
The choice between an XRF instrument is not about the number of "types," but about a core trade-off. You must decide between the ultimate precision and sensitivity of Wavelength Dispersive (WDXRF) systems and the speed, versatility, and cost-effectiveness of Energy Dispersive (EDXRF) systems.

The Fundamental Divide: Wavelength vs. Energy
The key difference between the two technologies lies in how they process the fluorescent X-rays that come from the sample after it has been excited. This single difference has massive implications for performance, cost, and application.
Energy Dispersive XRF (EDXRF): The Versatile Workhorse
An EDXRF system uses a detector that measures the energy of every X-ray photon it receives, all at once.
It processes the entire spectrum of emitted X-rays simultaneously. Think of it like listening to an orchestra and identifying each instrument's sound based on its unique pitch (energy) in a single moment.
This simultaneous collection makes EDXRF systems inherently fast, mechanically simple, and more compact.
Wavelength Dispersive XRF (WDXRF): The Precision Specialist
A WDXRF system physically separates the X-rays before they reach the detector. It uses a crystal that diffracts X-rays based on their specific wavelength.
The instrument then scans through these wavelengths one by one. This is like using a prism to split white light into a perfect rainbow and then precisely measuring the intensity of each individual color.
This sequential, high-resolution process gives WDXRF superior performance but makes the instruments larger, more complex, and slower.
A Closer Look at Instrument Formats
While the core technology is either ED or WD, XRF instruments come in several common physical forms. Most of these formats use EDXRF technology due to its simplicity and compactness.
Handheld XRF Analyzers
These are portable, battery-operated EDXRF devices designed for "point-and-shoot" analysis in the field.
Their primary use is for immediate, on-site results. Common applications include scrap metal sorting, alloy verification, environmental soil screening, and testing consumer products for restricted substances (RoHS).
Benchtop XRF Analyzers
These instruments are designed to sit on a laboratory bench. The vast majority are EDXRF, but some smaller WDXRF models exist.
They offer a significant performance improvement over handhelds and are ideal for routine quality control labs. They can analyze solids, liquids, powders, and films in a more controlled environment.
Floor-Standing Systems
These are large, high-power instruments that require a dedicated, climate-controlled room. They are almost exclusively WDXRF technology.
These systems represent the pinnacle of XRF performance. They are used in applications demanding the highest accuracy and the lowest possible detection limits, such as in cement plants, refineries, and advanced materials research.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Precision vs. Practicality
Choosing the right technology requires understanding its inherent compromises.
Resolution and Spectral Overlap
WDXRF provides much higher resolution, meaning it can easily distinguish between elements with very similar energy signatures (e.g., Arsenic and Lead, or Barium and Titanium).
EDXRF has lower resolution and can struggle with these overlaps, potentially requiring complex mathematical corrections that can affect accuracy.
Sensitivity and Detection Limits
WDXRF systems are generally more sensitive and offer lower limits of detection. This is especially true for light elements (like Sodium, Magnesium, Aluminum, and Silicon), where WDXRF is vastly superior.
Speed and Simplicity
EDXRF is significantly faster because it captures the entire elemental spectrum in seconds. The instruments have few or no moving parts, making them robust and easier to maintain.
WDXRF is slower because it must scan through each wavelength sequentially. The complex internal mechanics (goniometers and crystals) also require more expertise to operate and maintain.
Cost
There is a major difference in cost. Handheld and benchtop EDXRF systems can range from tens of thousands to low six-figure amounts. High-performance WDXRF systems are a major capital investment, often costing several hundred thousand dollars.
Choosing the Right XRF for Your Application
Your goal determines the correct instrument. The question is not "which is better," but "which is the right tool for the job."
- If your primary focus is rapid field identification and sorting: A handheld EDXRF analyzer is the definitive tool for its portability and instant results.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control in a lab setting: A benchtop EDXRF offers the best balance of performance, cost, and versatility for a wide range of sample types.
- If your primary focus is high-precision elemental analysis with the lowest possible detection limits: A floor-standing WDXRF system is the required standard for research-grade data.
- If you must accurately measure light elements (Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S) at low concentrations: WDXRF is often the only technology that can provide reliable results.
Understanding this core distinction between energy and wavelength dispersion empowers you to select not just an instrument, but the correct analytical strategy for your specific needs.
Summary Table:
| Instrument Type | Core Technology | Best For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Handheld Analyzer | EDXRF | Field analysis, rapid sorting | Portability, instant results |
| Benchtop Analyzer | Primarily EDXRF | Routine lab quality control | Versatility for solids, liquids, powders |
| Floor-Standing System | Primarily WDXRF | High-precision analysis, research | Superior resolution, lowest detection limits |
Unsure which XRF technology is right for your lab's specific needs? The experts at KINTEK can help. We specialize in providing the ideal lab equipment—from versatile EDXRF analyzers for quality control to high-precision WDXRF systems for research—to ensure accurate and efficient elemental analysis for your laboratory. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and let us help you make the right investment in analytical performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Thin-Layer Spectral Electrolysis Electrochemical Cell
- Laboratory Oscillating Orbital Shaker
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the necessary preparation steps before using a thin-layer spectroelectrochemical cell? A Guide to Reliable Results
- What general precautions should be taken when using a thin-layer spectroelectrochemical cell? Ensure Accurate Results and Equipment Safety
- For what types of systems, temperature ranges, and sealing configurations is the thin-layer spectroelectrochemical cell designed? Ideal for Aqueous and Non-Aqueous Analysis
- Which electrode types are compatible with thin-layer spectroelectrochemical cells? Optimize Your Hardware Fit
- What are the dimensions for thin-layer spectroelectrochemical cells? Optimize Your Lab's Optical Path Length
















