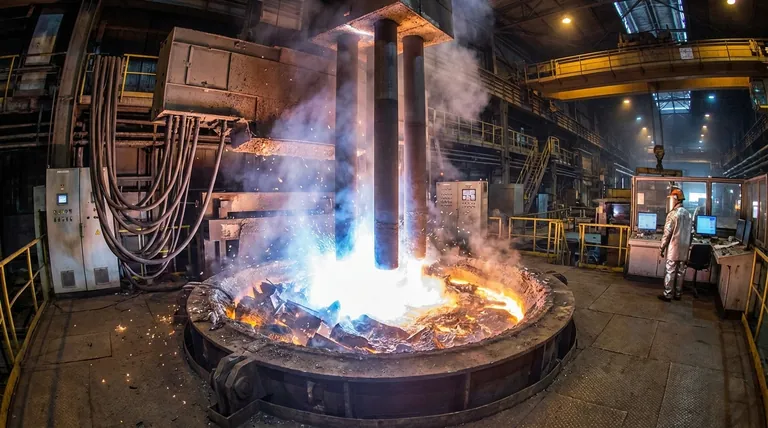
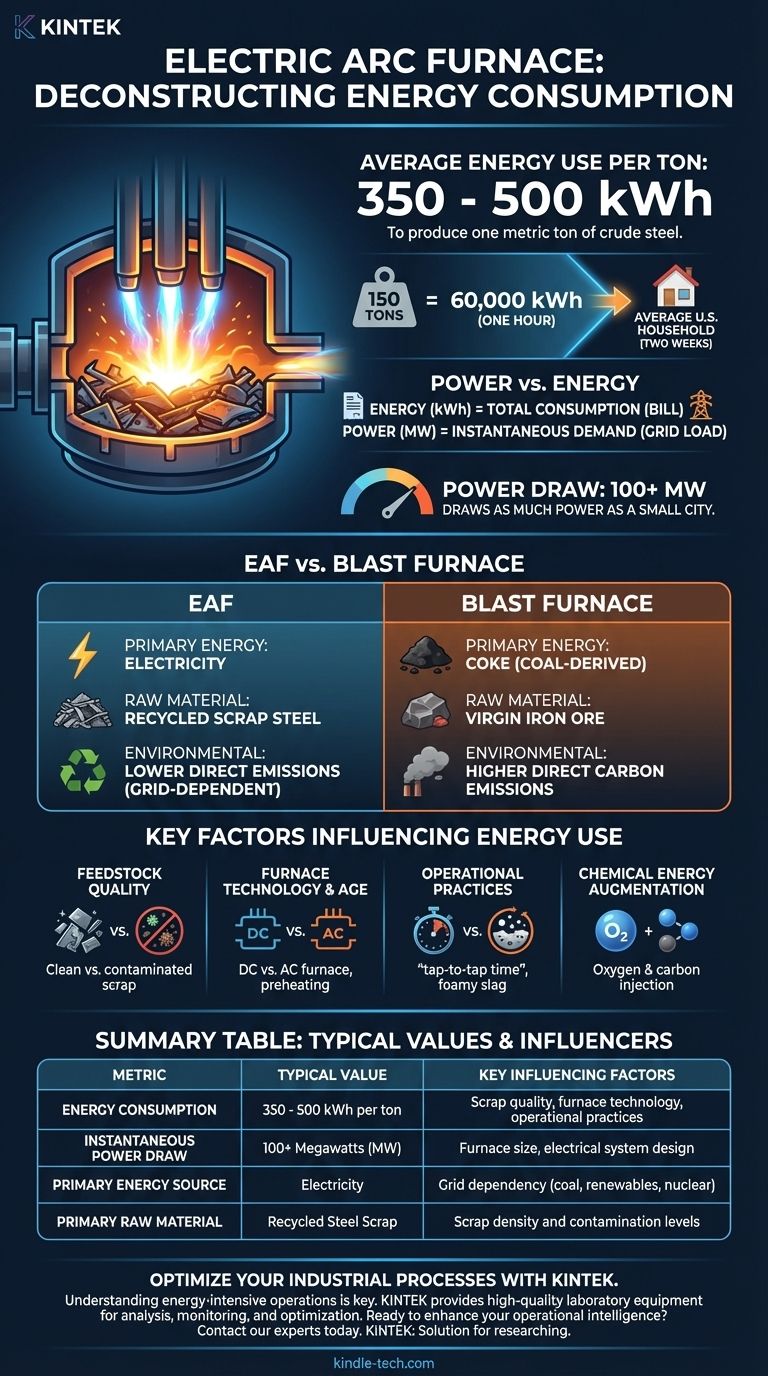
On average, a modern electric arc furnace (EAF) consumes between 350 and 500 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity to produce one metric ton of crude steel. The exact figure depends heavily on the furnace's age, the quality of the scrap metal being melted, and the efficiency of the plant's operational practices.
An electric arc furnace's electricity consumption is so immense that a single furnace can draw as much instantaneous power as a small city. Understanding this energy usage is not just about cost; it is the central challenge in a global effort to make steel production more sustainable.

Deconstructing EAF Energy Consumption
An electric arc furnace works by passing an enormous electrical current through graphite electrodes. This creates an arc of plasma—essentially a controlled lightning bolt—that can reach temperatures of over 3,000°C (5,400°F), melting the scrap steel charge in the furnace below.
The Core Numbers in Context
A typical consumption figure of 400 kWh per ton is a useful benchmark.
To put this in perspective, 400 kWh is enough electricity to power the average U.S. household for nearly two weeks. A furnace producing 150 tons of steel per "heat" (a single melting cycle) consumes 60,000 kWh in roughly an hour.
Power vs. Energy: A Critical Distinction
It is vital to distinguish between energy (kWh) and power (MW).
- Energy (kWh) is the total amount of electricity consumed over time. This is what determines the electricity bill.
- Power (MW) is the rate at which electricity is used at any given moment. This determines the load on the electrical grid.
An EAF is both an energy-intensive and a power-intensive device. A medium-sized furnace can have a power rating of 100 megawatts (MW) or more. This sudden, massive demand for power is why steel mills with EAFs are often located near dedicated power substations.
Key Factors Influencing Energy Use
Not all arc furnaces are created equal. The 350-500 kWh/ton range is wide because several variables can dramatically alter a furnace's efficiency.
Feedstock Quality
The type of metal fed into the furnace is a primary driver of energy use. Clean, dense, and heavy scrap metal melts predictably and efficiently.
Contaminated or light scrap (like shredded automobiles) has a lower density, requiring more energy to melt and often demanding a second or third charge to fill the furnace, which allows heat to escape.
Furnace Technology and Age
Modern EAFs incorporate numerous efficiency improvements. Direct current (DC) furnaces are generally more efficient than older alternating current (AC) furnaces.
Techniques like scrap preheating, where the hot off-gas from the furnace is used to heat the next batch of scrap, can reduce electrical consumption by 30-50 kWh/ton.
Operational Practices
The skill of the furnace crew is paramount. A key metric is "tap-to-tap time"—the total time for one complete melting cycle. Minimizing this time reduces heat loss and, therefore, energy waste.
Practices like creating a "foamy slag" layer on top of the molten steel act as an insulating blanket, trapping heat from the arc and transferring it more effectively to the metal bath.
Chemical Energy Augmentation
EAFs do not rely on electricity alone. They also function as chemical reactors.
By injecting oxygen and carbon into the furnace, operators trigger exothermic reactions that generate significant heat. This "chemical energy" reduces the required electrical energy, optimizing both cost and production speed.
Understanding the Trade-offs: EAF vs. Blast Furnace
The electric arc furnace represents one of two primary methods for steelmaking. Understanding its energy use requires comparing it to the alternative: the Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF), which processes molten iron from a blast furnace.
The Energy Source
An EAF's primary energy input is electricity. A blast furnace's primary energy input is coke, a fuel derived from coal. The BOF that refines the iron into steel uses the chemical energy from the hot metal itself, requiring very little external power.
The Raw Material
This is the most significant difference. EAFs almost exclusively use recycled steel scrap. The blast furnace/BOF route uses virgin iron ore. The EAF is fundamentally a recycling technology.
The Environmental Angle
Because it avoids the use of coke, the EAF process has drastically lower direct carbon emissions than the traditional blast furnace route.
However, the EAF's overall carbon footprint is tied to a region's power grid. If the furnace is powered by electricity from coal-fired plants, its lifecycle emissions are higher. If powered by renewables or nuclear, its footprint is exceptionally low.
How to Interpret This Data
How you use this information depends on your ultimate goal. Focus on the metric that matters most to your analysis.
- If your primary focus is cost analysis: The key metric is kWh per ton, as this directly translates to a major operational expense and is a primary target for efficiency improvements.
- If your primary focus is environmental impact: Consider both the furnace's electrical efficiency and the carbon intensity (gCO2/kWh) of the electrical grid supplying it.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Benchmark your tap-to-tap time, power-on time, and energy consumption against modern furnace standards, focusing on scrap quality and chemical energy use.
Ultimately, mastering the energy equation of an electric arc furnace is the key to producing steel in a more cost-effective and sustainable manner.
Summary Table:
| Metric | Typical Value | Key Influencing Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | 350 - 500 kWh per ton of steel | Scrap quality, furnace technology, operational practices |
| Instantaneous Power Draw | 100+ Megawatts (MW) | Furnace size, electrical system design |
| Primary Energy Source | Electricity | Grid dependency (coal, renewables, nuclear) |
| Primary Raw Material | Recycled Steel Scrap | Scrap density and contamination levels |
Optimize Your Industrial Processes with KINTEK
Understanding energy-intensive operations like arc furnace steelmaking is key to efficiency and sustainability. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables that help you analyze, monitor, and optimize your processes.
Whether you are involved in materials testing, quality control, or process development, our products support the precise measurements needed to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Ready to enhance your operational intelligence? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can meet your specific laboratory and industrial needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do I choose a tube furnace? A Guide to Matching Your Process Needs
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?



















