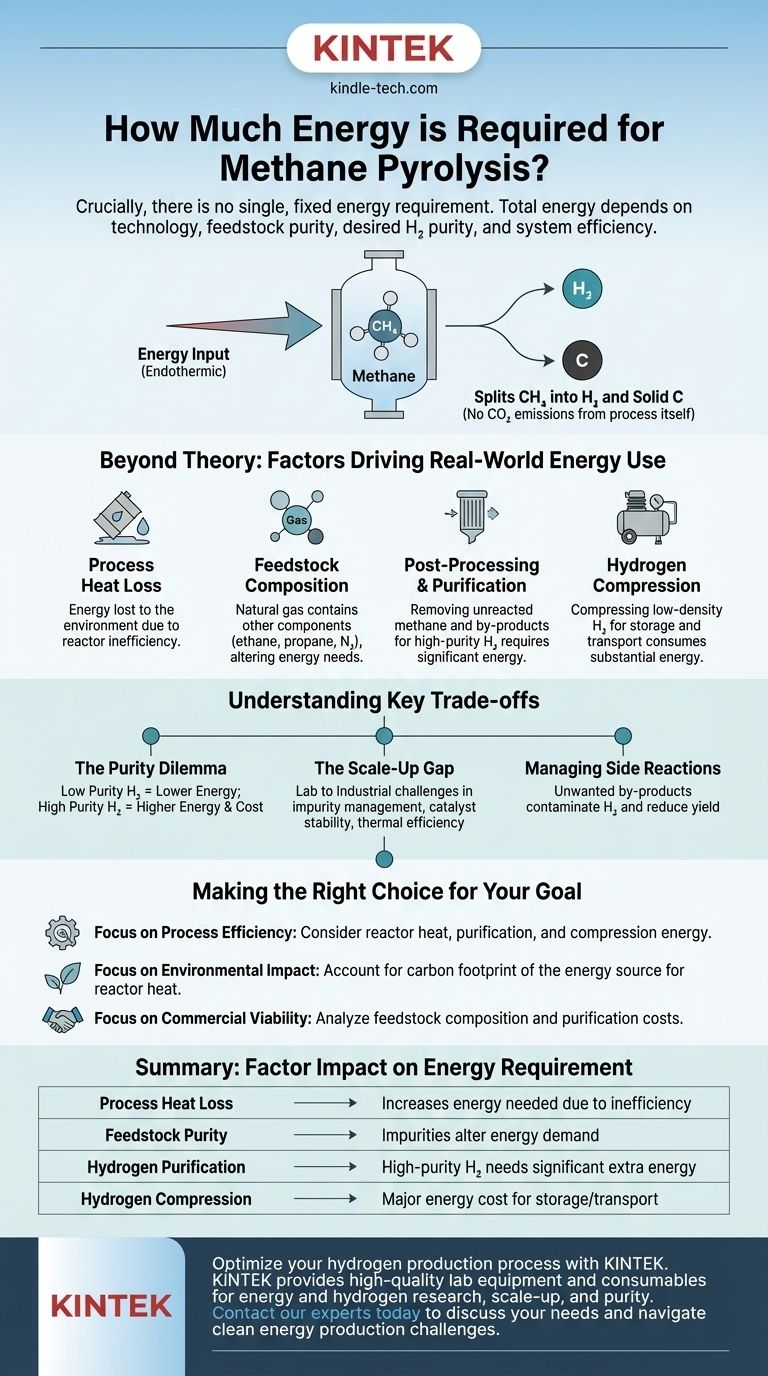
Crucially, there is no single, fixed energy requirement for methane pyrolysis. The total energy needed is highly variable, depending on the specific technology used, the purity of the natural gas feedstock, the desired purity of the final hydrogen product, and the efficiency of the overall system.
The theoretical energy needed to break methane's chemical bonds is only the starting point. The practical, real-world energy cost is significantly higher, driven by process heat loss, gas purification, and the energy-intensive step of hydrogen compression.
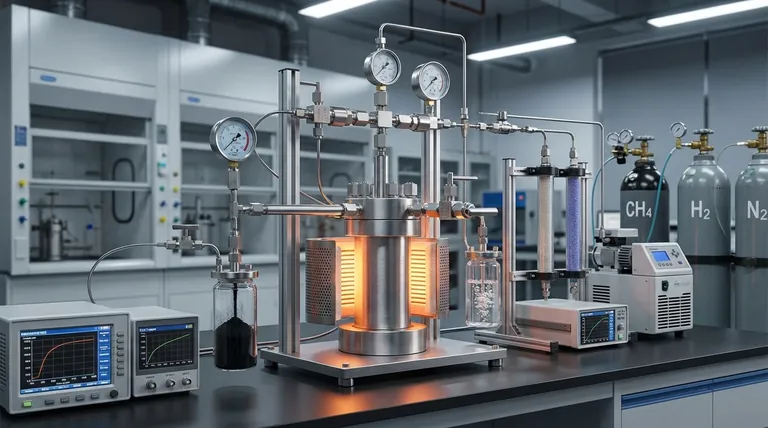

The Core Thermal Demand
Methane pyrolysis is an endothermic process, meaning it requires a continuous input of energy to function. This energy is used to heat methane (CH₄) to high temperatures, which breaks the strong chemical bonds between carbon and hydrogen atoms.
What the Energy Does
The primary goal of the energy input is to split the methane molecule into its constituent parts: hydrogen gas (H₂) and solid carbon (C). This is achieved without reacting the methane with oxygen, which is why the process itself does not produce CO₂ emissions.
Beyond Theory: Factors Driving Real-World Energy Use
The baseline thermal energy is just one piece of the puzzle. In any industrial application, several other factors add significant energy costs to the overall process.
Process Heat Loss
No industrial process is perfectly insulated. A portion of the thermal energy supplied to the reactor will inevitably be lost to the surrounding environment. This inefficiency means more energy must be supplied than is theoretically required just to make the reaction happen.
Feedstock Composition (Natural Gas vs. Methane)
While research often uses pure methane, industrial facilities use natural gas. Natural gas contains other components like ethane, propane, and nitrogen. These additional substances can influence the reaction, potentially requiring different operating temperatures or catalytic processes, thereby altering the energy demand.
Post-Processing and Purification
The gas stream leaving the reactor is not pure hydrogen. It contains unreacted methane and other hydrocarbon by-products. If high-purity hydrogen is the goal (e.g., for petrochemicals), this mixture must undergo energy-intensive purification and separation steps.
Hydrogen Compression
Hydrogen is the lightest element, meaning it has a very low density. To store or transport it effectively, the resulting hydrogen gas must be heavily compressed. This mechanical process consumes a substantial amount of electrical energy and is a major component of the total energy budget.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Evaluating methane pyrolysis requires understanding the practical challenges that directly impact its energy efficiency and economic viability.
The Purity Dilemma
The energy required to produce a mixed "dirty" hydrogen stream is far lower than what is needed for 99.9%+ pure hydrogen. The decision to pursue higher purity levels introduces significant energy and capital costs associated with advanced gas separation technologies.
The Scale-Up Gap
There is a notable gap between controlled laboratory experiments and large-scale industrial reality. Challenges related to managing impurities in natural gas, ensuring catalyst stability, and maintaining thermal efficiency become far more pronounced at an industrial scale.
Managing Side Reactions
Unwanted side reactions can produce other hydrocarbons or aromatic compounds. These by-products not only contaminate the hydrogen stream, making purification more difficult and energy-intensive, but also represent a loss of potential hydrogen yield from the feedstock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To assess the energy requirement for a specific application, you must look beyond the core reaction and consider the entire system.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Your analysis must account for the total energy input, including heat for the reactor, electricity for purification, and the significant energy consumed by hydrogen compression.
- If your primary focus is environmental impact: While the pyrolysis reaction is CO₂-free, you must consider the carbon footprint of the energy source used to heat the reactor. If natural gas is burned to generate this heat, the process will still have associated emissions.
- If your primary focus is commercial viability: A detailed analysis of your natural gas feedstock is critical. Its specific composition will determine the complexity and energy cost of the purification train required to meet your customer's hydrogen purity specifications.
Ultimately, understanding the true energy cost of methane pyrolysis requires a holistic view of the entire production chain, from the natural gas wellhead to the final compressed hydrogen product.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Energy Requirement |
|---|---|
| Process Heat Loss | Increases energy needed due to reactor inefficiency |
| Feedstock Purity | Impurities in natural gas can alter energy demand |
| Hydrogen Purification | High-purity H₂ requires significant additional energy |
| Hydrogen Compression | A major energy cost for storage and transport |
Optimize your hydrogen production process with KINTEK.
Understanding the complex energy dynamics of methane pyrolysis is key to developing an efficient and cost-effective operation. The right lab equipment is essential for accurate research, process development, and quality control.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables to support your energy and hydrogen research. Whether you are scaling up from lab to pilot or ensuring product purity, our solutions help you achieve reliable results and improve process efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your specific laboratory needs and help you navigate the challenges of clean energy production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature hydrothermal reactor? Enhance Iodine@Activated Carbon Cathode Synthesis
- How does a high-pressure reactor demonstrate its value in accelerated aging? Predict Catalyst Durability Fast
- What is the purpose of using high-purity argon gas in a high-pressure reactor? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Data
- Why are sealed laboratory reaction vessels necessary in the hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites? Ensure Purity and Yield
- What roles do autoclaves play in MFI zeolite synthesis? Master Hydrothermal Crystalline Growth



















