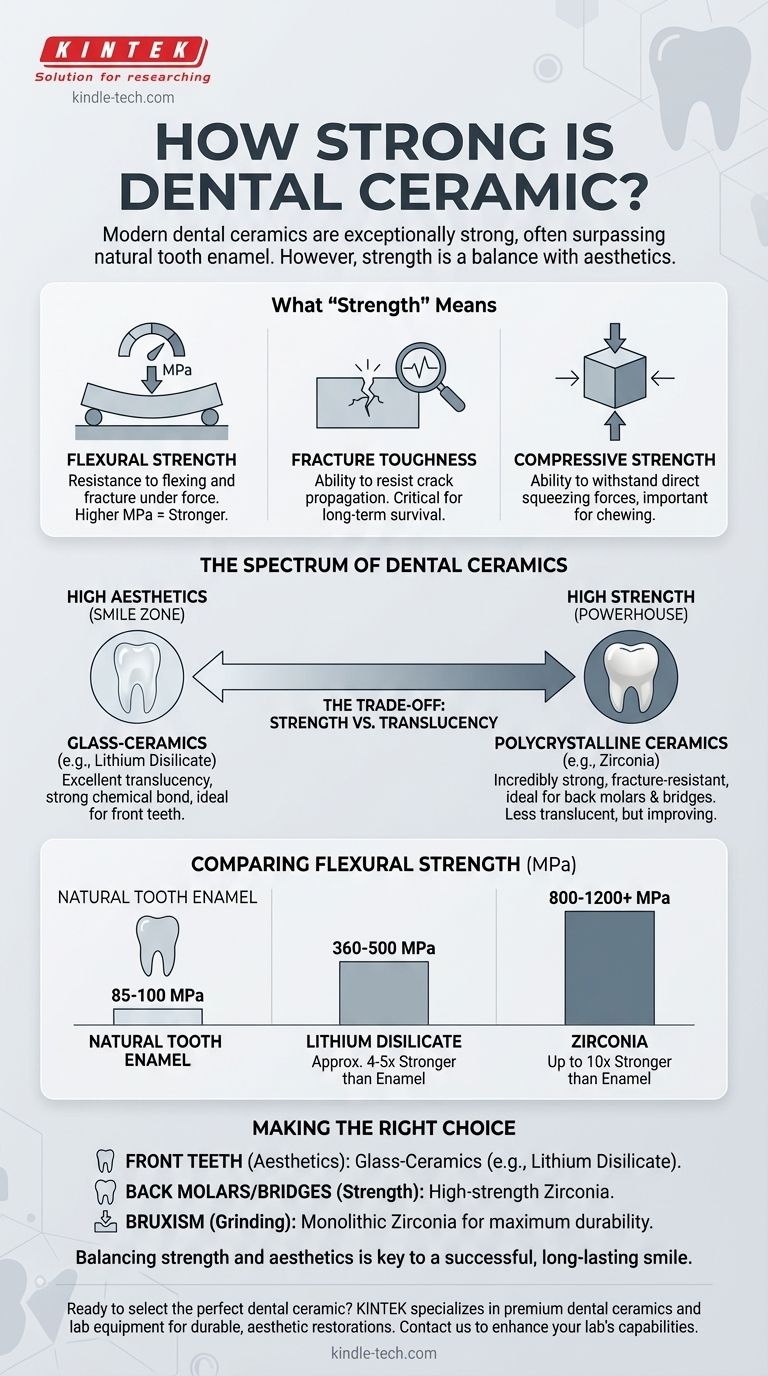
In short, modern dental ceramics are exceptionally strong. Many types are significantly stronger than natural tooth enamel, capable of withstanding the immense forces of chewing for many years. However, "strength" is not a single quality, and the best ceramic for a given situation depends on a crucial balance between durability and aesthetics.
The key takeaway is that dental ceramics exist on a spectrum. At one end, you have highly aesthetic, translucent glass-ceramics ideal for front teeth. At the other, you have ultra-strong, opaque zirconia engineered to withstand the powerful chewing forces on back molars. The "best" ceramic is the one that meets the specific demands of its location in your mouth.

What "Strength" Means for a Dental Restoration
When engineers and dentists discuss the strength of a ceramic, they are referring to several distinct mechanical properties. Understanding these helps clarify why one material is chosen over another.
Flexural Strength
Flexural strength is the most common metric used to compare dental materials. It measures how much force a material can endure before it flexes and fractures. It's measured in megapascals (MPa).
For context, a higher MPa value indicates a stronger, more fracture-resistant material.
Fracture Toughness
Fracture toughness measures a material's ability to resist the growth of a crack. This is critically important for long-term survival.
A material with high fracture toughness can tolerate tiny surface flaws without them propagating into a full-blown fracture, much like how ripstop nylon stops a small tear from spreading.
Compressive Strength
This measures a material's ability to withstand direct squeezing or pressing forces. All dental ceramics have extremely high compressive strength, making them well-suited for the vertical forces of chewing.
The Spectrum of Dental Ceramics
Not all ceramics are created equal. They are best understood as a family of materials, each optimized for different needs.
Glass-Ceramics (e.g., Lithium Disilicate)
These materials, like the popular brand E.max, contain a high concentration of glass, which gives them exceptional translucency and aesthetic properties. They are the go-to choice for restorations in the "smile zone."
Their chemical bond to the tooth structure is incredibly strong, which adds to the overall durability of the final restoration.
Polycrystalline Ceramics (e.g., Zirconia)
Zirconia is the powerhouse of the dental ceramic world. It is a crystalline material with virtually no glass in its structure, making it incredibly strong and resistant to fracture.
Originally, zirconia was very opaque, limiting its use to non-visible areas. However, modern "translucent" zirconia has greatly improved aesthetics, expanding its applications.
Comparing Ceramic Strength to Natural Teeth
Putting the numbers side-by-side reveals just how advanced these materials have become.
Natural Tooth Structure
A natural tooth is not uniformly strong. Enamel, the outer layer, has a flexural strength of around 85-100 MPa. Dentin, the layer beneath, is slightly tougher.
Lithium Disilicate (Glass-Ceramic)
Lithium disilicate has a flexural strength in the range of 360-500 MPa. This is approximately 4 to 5 times stronger than natural tooth enamel.
Zirconia (Polycrystalline Ceramic)
Zirconia boasts a flexural strength between 800 and 1,200 MPa, or even higher for some formulations. This makes it up to 10 times stronger than natural enamel and the most durable tooth-colored material available.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Strength vs. Aesthetics
Choosing a dental material is an exercise in balancing competing priorities. The strongest material is not always the best choice.
The Inverse Relationship
Generally, there is an inverse relationship between strength and translucency in ceramics. The more crystalline and stronger a material is (like zirconia), the more it tends to scatter light, making it more opaque. The more glass-like it is (like lithium disilicate), the more beautiful and natural it appears.
Location Dictates the Material
This trade-off is why material selection is so dependent on location. A front tooth veneer demands the highest level of aesthetics, making lithium disilicate the ideal choice. A three-tooth bridge replacing a molar requires maximum strength, making zirconia the clear winner.
The Dentist's Role is Critical
The inherent strength of a material is only part of the equation. The success of a ceramic restoration also depends heavily on the dentist’s design of the crown, the precision of the fit, and the quality of the bond to the underlying tooth. A perfectly executed restoration with a moderately strong material will outperform a poorly done restoration with the strongest material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Restoration
Your dentist will recommend a material based on your specific clinical needs, but understanding these principles will empower you to have a more informed discussion.
- If your primary focus is a front tooth (veneer or crown): A glass-ceramic like lithium disilicate is typically the best choice for its superior, natural-looking aesthetics.
- If your primary focus is a back molar or a multi-tooth bridge: High-strength zirconia is the standard of care due to its exceptional durability under heavy chewing forces.
- If you have a habit of grinding or clenching (bruxism): Your dentist will likely recommend monolithic zirconia, as it is the most fracture-resistant material available to withstand these intense forces.
Ultimately, knowing how to balance the need for strength against the desire for beauty is the key to a successful, long-lasting, and confident smile.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Tooth Enamel | 85-100 MPa | Natural outer layer of teeth | Reference point |
| Lithium Disilicate (Glass-Ceramic) | 360-500 MPa | High translucency, excellent aesthetics | Front teeth, veneers, single crowns |
| Zirconia (Polycrystalline) | 800-1200+ MPa | Maximum strength, fracture-resistant | Back molars, bridges, bruxism cases |
Ready to select the perfect dental ceramic for your laboratory needs? KINTEK specializes in premium dental ceramics and lab equipment, helping dental laboratories create durable, aesthetically perfect restorations. Our materials ensure your dental prosthetics meet the highest strength and beauty standards.
Contact our dental experts today to discuss how our ceramic solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and deliver superior results for your clients.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Precision Machined Yttria Stabilized Zirconia Ceramic Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What function do alumina ceramic plates serve as supports in the preparation of molecular sieve membranes?
- What are the two methods that can be used to prevent corrosion of a metal? Barrier vs. Sacrificial Protection Explained
- What are two disadvantages of metal? Understanding Corrosion and Weight Limitations
- How many types of hardening techniques are there? A Multi-Layered Security Strategy Explained
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection














