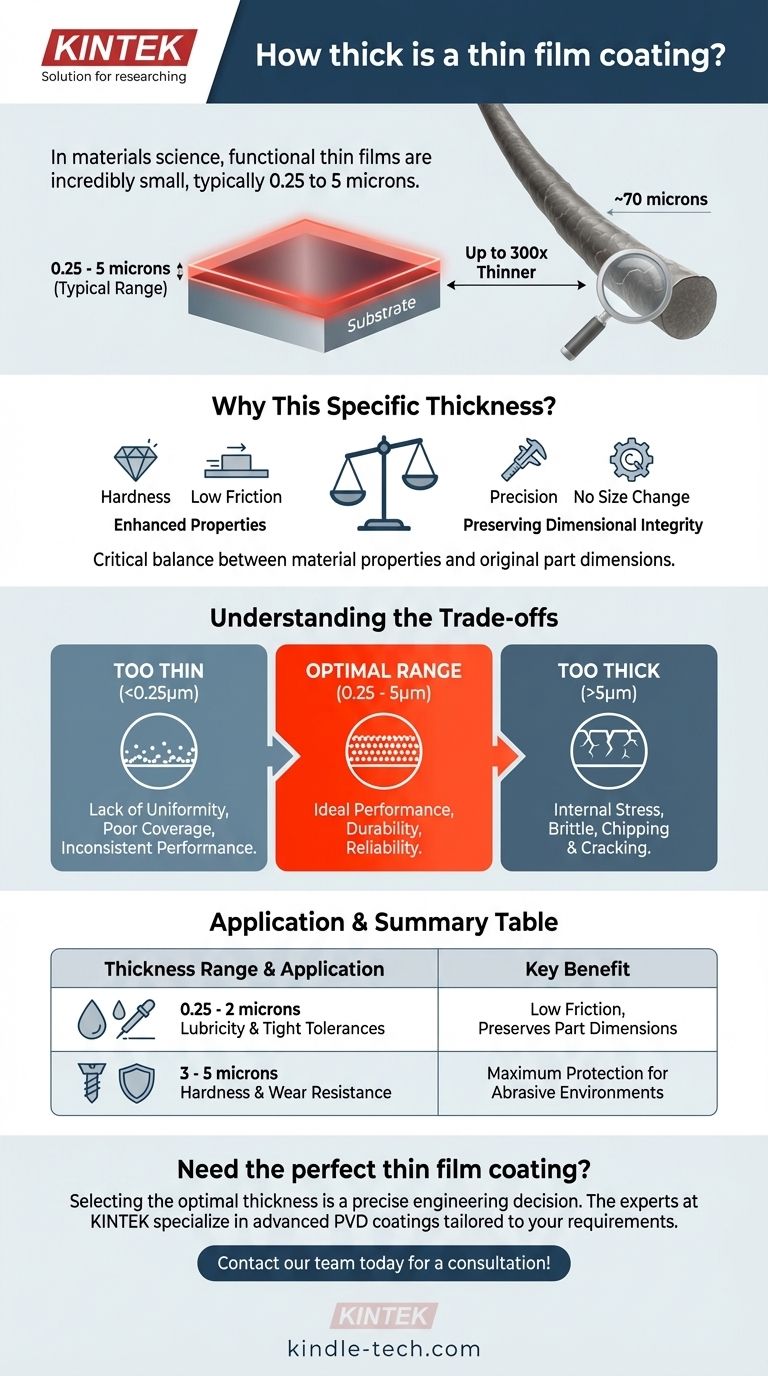
In the field of materials science, a thin film coating is defined by its incredibly small scale. The typical thickness for a functional or decorative thin film coating ranges from just 0.25 microns to 5 microns.
The thickness of a thin film is not an arbitrary measurement; it is a critical design parameter engineered to deliver specific performance benefits—like hardness or low friction—without altering the dimensional integrity of the underlying component.

Why This Specific Thickness?
The functional range of a thin film coating is a deliberate balance between achieving desired material properties and preserving the original part's precise dimensions.
Achieving Enhanced Properties
At this microscopic scale, coatings like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) films create a dense, highly-adherent layer. This structure is what provides significant improvements in hardness, wear resistance, chemical inertness, and lubricity (low friction).
Preserving Dimensional Integrity
A key reason for using thin films is that they do not meaningfully change the size or shape of the component. For precision parts like cutting tools, molds, or medical implants, even a tiny change in dimension can lead to failure.
A coating of a few microns adds a negligible amount to the overall dimensions, ensuring the part functions exactly as it was designed.
Visualizing the Scale
To put this into perspective, a single human hair is approximately 70 microns thick. The thickest typical thin film coating (5 microns) is still 14 times thinner than a human hair, while the thinnest (0.25 microns) is nearly 300 times thinner.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a thickness is a matter of engineering trade-offs. Moving outside the optimal range, either too thin or too thick, can compromise the coating's performance.
The Risk of Being Too Thin
A coating below approximately 0.25 microns may lack the uniformity and density to provide its intended benefit. It might not fully cover the surface asperities (microscopic peaks and valleys), leading to inconsistent performance and a shorter lifespan.
The Risk of Being Too Thick
As a coating's thickness increases beyond about 5 microns, internal stresses within the film can build up. This makes the coating more brittle and prone to chipping, cracking, or delamination under stress. Thicker coatings can also negatively impact the surface finish and dimensional tolerances of the part.
How to Apply This to Your Project
The ideal thickness for your component depends entirely on its primary performance goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: A thicker coating (e.g., 3-5 microns) provides more material to withstand abrasive wear, making it ideal for cutting tools or high-wear components.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction (lubricity): A thinner coating (e.g., 1-2 microns) is often sufficient to create an ultra-smooth, low-friction surface without risking brittleness.
- If your primary focus is maintaining tight dimensional tolerances: Always opt for the thinnest effective coating (e.g., 0.5-1.5 microns) to ensure the part's geometry remains virtually unchanged.
Ultimately, selecting the correct thin film thickness is a precise engineering decision, not an approximation.
Summary Table:
| Thickness Range | Primary Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 0.25 - 2 microns | Lubricity, Tight Tolerances | Low friction, preserves part dimensions |
| 3 - 5 microns | Hardness & Wear Resistance | Maximum protection for abrasive environments |
Need to specify the perfect thin film coating for your project?
Selecting the optimal thickness is a precise engineering decision that directly impacts your component's performance, durability, and lifespan. The experts at KINTEK specialize in applying advanced PVD coatings tailored to your specific requirements—whether you need maximum hardness for cutting tools or a low-friction layer for medical implants.
We provide the technical guidance and high-quality lab equipment to ensure your coating delivers the intended benefits without compromising your part's integrity.
Let's engineer the ideal solution for your application. Contact our team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Laboratory manual slicer
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- Is diamond coating permanent? The Truth About Its Long-Lasting Durability
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance


