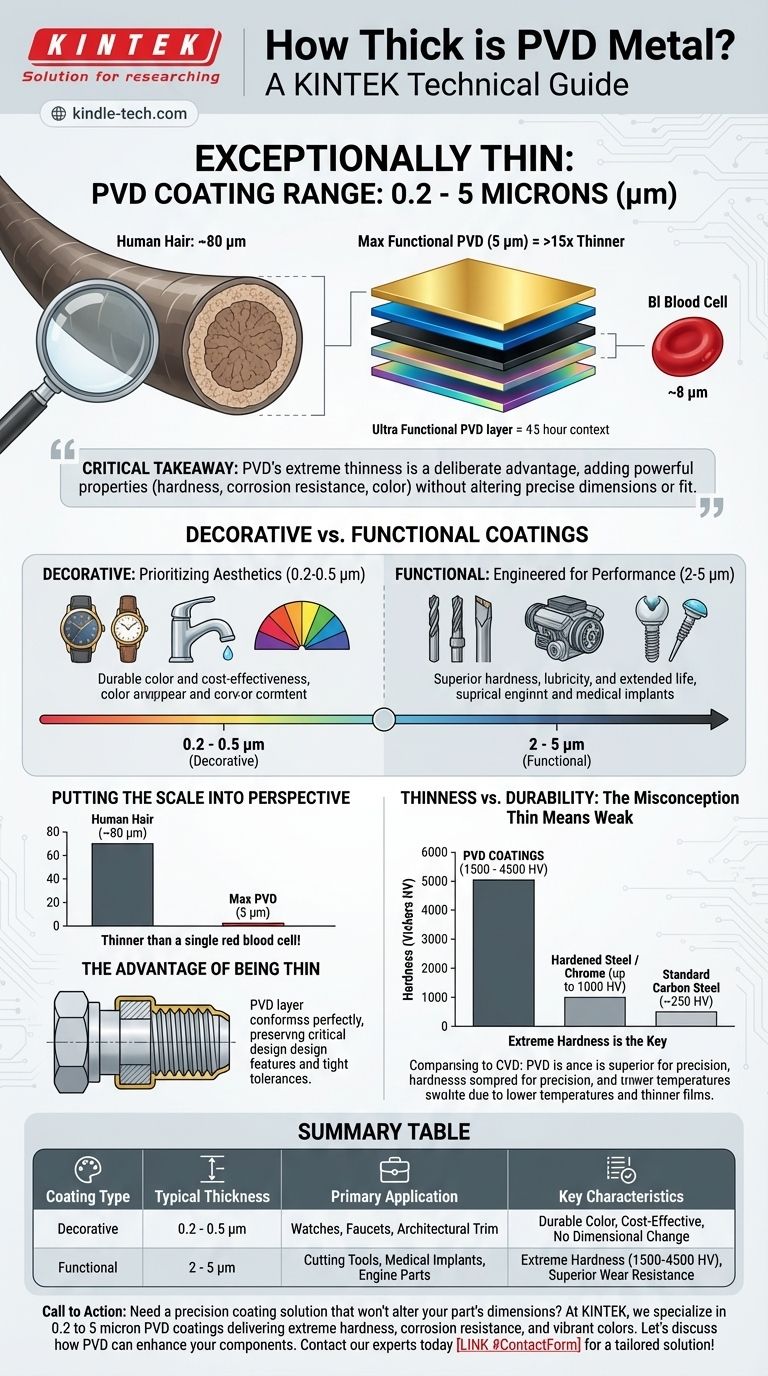
In practice, the thickness of a Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating is measured in microns and is exceptionally thin. A typical PVD coating ranges from 0.2 to 5 microns (µm), with the exact thickness being carefully controlled based on whether its purpose is purely decorative or functional. For context, a human hair is about 80 microns thick, meaning even the most robust PVD coatings are more than 15 times thinner.
The critical takeaway is that PVD's extreme thinness is a deliberate and significant advantage. It allows for the addition of powerful properties like extreme hardness, corrosion resistance, and vibrant color without altering the underlying part's precise dimensions or fit.

Why Thickness Varies: Decorative vs. Functional Coatings
The thickness of a PVD coating is not arbitrary; it is engineered to meet a specific goal. The primary distinction is between coatings designed for aesthetics and those designed for performance.
Decorative Coatings: Prioritizing Aesthetics
For products where the primary goal is achieving a specific color and premium finish—such as watches, faucets, or architectural trim—a thinner coating is used.
These decorative films typically fall in the 0.2 to 0.5 micron range. This is thick enough to provide a durable, consistent color but thin enough to be highly cost-effective and have no impact on the part's feel or texture.
Functional Coatings: Engineered for Performance
When the goal is to enhance a part's mechanical properties, a thicker and more robust coating is applied. These are common on cutting tools, engine components, and medical implants.
Functional coatings are typically in the 2 to 5 micron range. This added thickness provides superior hardness and lubricity, drastically increasing wear resistance, reducing friction, and extending the operational life of the component.
Putting the Scale into Perspective
Understanding the microscopic scale of PVD is key to appreciating its value in precision engineering.
How Thin is a Micron?
A micron (or micrometer) is one-millionth of a meter. To make this tangible:
- A single red blood cell is about 8 microns in diameter.
- A strand of human hair is around 80 microns thick.
- The thickest functional PVD coatings (5 µm) are still thinner than a single blood cell.
The Advantage of Being Thin
This microscopic thickness is PVD's greatest strength for engineered parts. Because the coating is so thin, it conforms perfectly to the substrate's surface.
This means that critical design features, thread profiles, and tight tolerances are completely preserved. The part's final dimensions are not meaningfully altered, which is a crucial factor in high-performance applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Thinness vs. Durability
A common question is how such a thin layer can provide any meaningful protection. The answer lies not in the thickness of the coating, but in the extreme hardness of the material being deposited.
The Misconception: "Thin Means Weak"
It's intuitive to assume that a thicker coating is always stronger. With PVD, this is not the case. The durability comes from the intrinsic properties of the ceramic materials, like Titanium Nitride or Zirconium Nitride, that are applied.
Extreme Hardness is the Key
PVD coatings have a Vickers hardness (HV) between 1500 and 4500 HV. For comparison:
- Standard carbon steels are around 250 HV.
- Hardened tool steels or chrome plating rarely exceed 1000 HV.
This means even a thin, 3-micron layer of PVD coating is significantly harder and more wear-resistant than the much thicker steel substrate it protects.
Comparison to Other Processes
Other coating processes, like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), often produce thicker films, typically between 5 and 10 microns. While also effective, the higher temperatures and greater thickness of CVD can sometimes alter a part's dimensions, making PVD the superior choice for components requiring the highest level of precision.
Choosing the Right Thickness for Your Project
The ideal PVD coating thickness is a direct function of your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics and color: A thinner, decorative coating in the 0.2 to 0.5 micron range will provide a durable, brilliant finish without unnecessary cost.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance and durability: A thicker, functional coating between 2 and 5 microns is necessary to provide the hardness required for demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is maintaining tight engineering tolerances: PVD is an ideal choice, as even its thickest functional coatings have a negligible impact on a component's final dimensions.
Ultimately, PVD allows you to add immense surface performance without sacrificing the precision of the underlying part.
Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Typical Thickness (Microns) | Primary Application | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decorative | 0.2 - 0.5 µm | Watches, Faucets, Architectural Trim | Durable color, cost-effective, no dimensional change |
| Functional | 2 - 5 µm | Cutting Tools, Medical Implants, Engine Parts | Extreme hardness (1500-4500 HV), superior wear resistance |
Need a precision coating solution that won't alter your part's dimensions?
At KINTEK, we specialize in applying PVD coatings that deliver extreme hardness, corrosion resistance, and vibrant colors with a thickness of just 0.2 to 5 microns. Whether your project requires a durable decorative finish or a high-performance functional coating, our expertise ensures optimal results for your laboratory or manufacturing needs.
Let's discuss how PVD can enhance your components. Contact our experts today for a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















