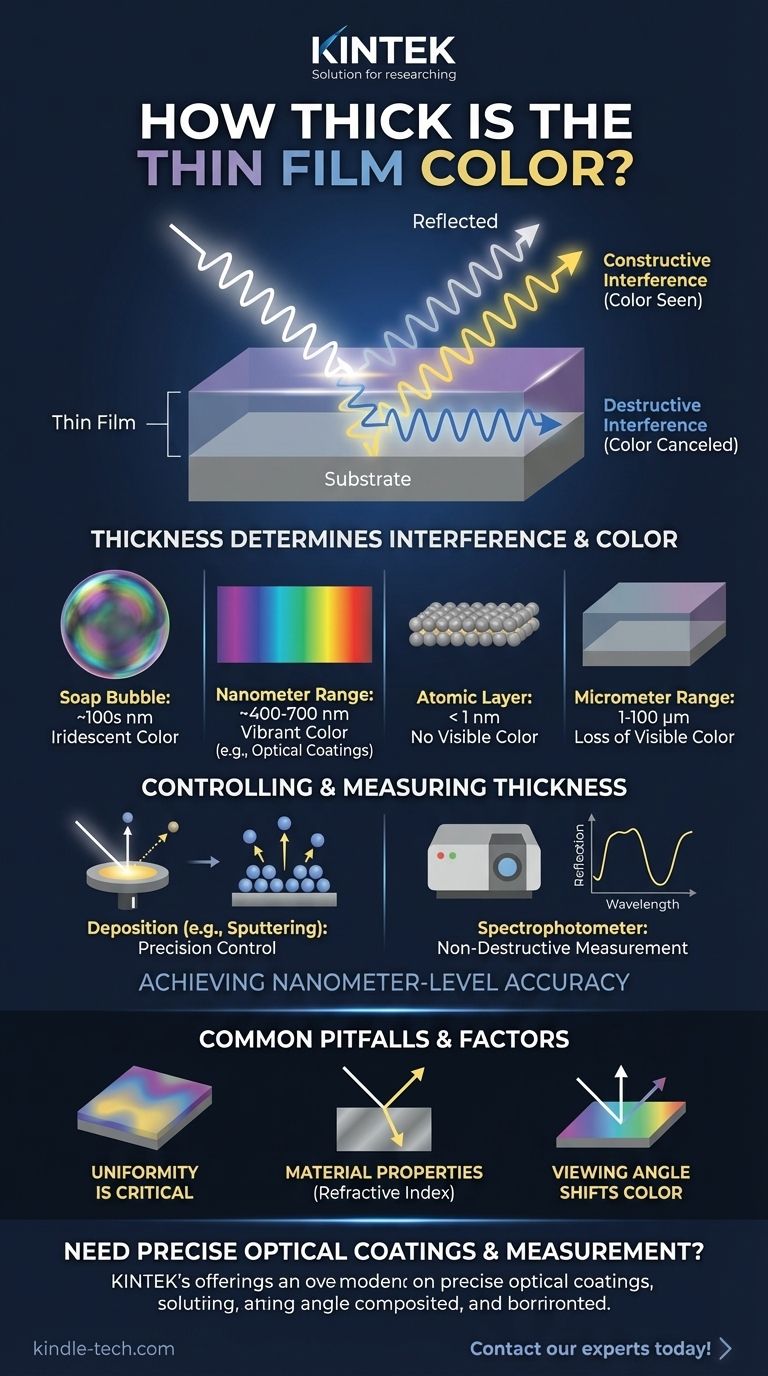
The color of a thin film is a direct result of its thickness. For visible, iridescent color effects, a thin film is typically only a few hundred nanometers thick—comparable to the thickness of a soap bubble. However, the technical definition of a "thin film" covers a much wider range, from a single layer of atoms (fractions of a nanometer) up to 100 micrometers.
The color you see in a thin film is not from pigment but from a physical phenomenon called thin-film interference. The film's thickness determines which wavelengths of light are reflected to your eye, creating a direct and controllable link between physical dimension and perceived color.

The Physics Behind the Color
To understand why thickness matters, you must first understand that the color isn't a chemical property. It's an optical effect created by the film's structure.
The Principle of Interference
When light hits a thin film, some of it reflects off the top surface. The rest of the light enters the film and reflects off the bottom surface.
These two reflected light waves then travel in the same direction and interfere with each other.
How Thickness Creates Color
The film's thickness dictates the path difference between these two reflected waves.
Based on this thickness, certain wavelengths (colors) of light are canceled out (destructive interference), while others are reinforced and amplified (constructive interference). The color you see is the wavelength that has been amplified.
The Soap Bubble Analogy
A soap bubble is the perfect example of this in action. Its walls are only a few hundred nanometers thick.
As gravity pulls the soap downwards, the top of the bubble becomes thinner than the bottom. This constantly changing thickness is why you see shifting bands of rainbow colors—each color corresponds to a specific thickness of the bubble's wall.
Defining the Scale of a Thin Film
While the color phenomenon happens at a specific scale, the term "thin film" is used across a broad range of applications and industries.
The Nanometer Range for Color
The most dramatic iridescent color effects occur when the film's thickness is on the same order of magnitude as the wavelengths of visible light (roughly 400-700 nanometers).
This is why films a few hundred nanometers thick produce vibrant, changing colors.
The Broader Micrometer Range
Technically, a layer of material can be considered a thin film even when it is several micrometers (µm) thick. Some definitions extend this up to 100 µm.
At these greater thicknesses, the interference effects for visible light become less apparent or disappear entirely.
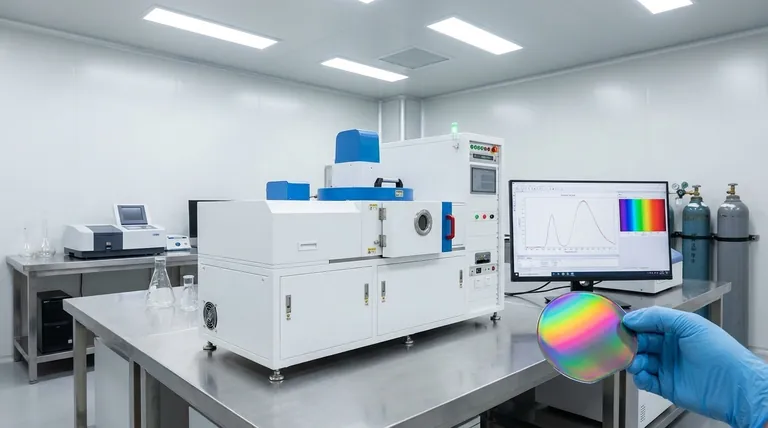
Controlling and Measuring Thickness
Creating a specific color is not an accident; it is an engineering process that requires immense precision.
The Deposition Process
Techniques like sputtering or chemical vapor deposition build the film one layer of atoms at a time.
The final thickness is precisely controlled by managing variables like the duration of the process, the energy used, and the rate of deposition. To achieve a target thickness, the process is run at a constant rate and then stopped.
Precision Measurement Tools
The thickness of these films is verified using non-destructive optical tools like spectrophotometers.
These instruments analyze how the film reflects light to calculate its thickness with high accuracy, often measuring layers between 0.3 and 60 µm.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Achieving the desired color effect with a thin film is more complex than just targeting a single thickness number.
Uniformity is Critical
If the thickness of the film is not perfectly uniform across a surface, you will see different colors in different areas. This can be a desired effect (like a soap bubble) or a critical manufacturing defect.
Material Properties Matter
The specific material used for the film is just as important as its thickness. The material's refractive index determines how much the light bends as it enters the film, which directly impacts the interference calculations.
Viewing Angle Can Shift Color
Because the path length of the light changes depending on the angle you view it from, the perceived color of an iridescent thin film can shift. This is a characteristic property of structural color and must be accounted for in its design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your objective determines how you should think about thin film thickness.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific, uniform color: You must precisely control the film's thickness to within a few nanometers during deposition.
- If your primary focus is understanding optical effects: Remember that color is a function of light interference, where the film's thickness dictates which wavelengths are constructively reinforced.
- If your primary focus is measuring an existing film: Use a non-destructive optical tool like a spectrophotometer to accurately determine its thickness based on its reflective properties.
Understanding this direct relationship between nanometer-scale thickness and visible color is the key to both creating and analyzing advanced optical coatings.
Summary Table:
| Film Thickness | Primary Effect | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| < 1 nm (atomic layer) | No visible color, functional layers | Electronic components |
| 100 - 700 nm | Vibrant iridescent color | Optical coatings, anti-reflective surfaces |
| 1 μm - 100 μm | Loss of visible color effects | Protective coatings, thick film circuits |
Need to create or analyze thin films with precise color effects? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced material deposition and measurement. Our spectrophotometers and deposition systems help you achieve nanometer-level thickness control for perfect optical coatings. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is the plasma CVD process? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the uses of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and sputter? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method


















