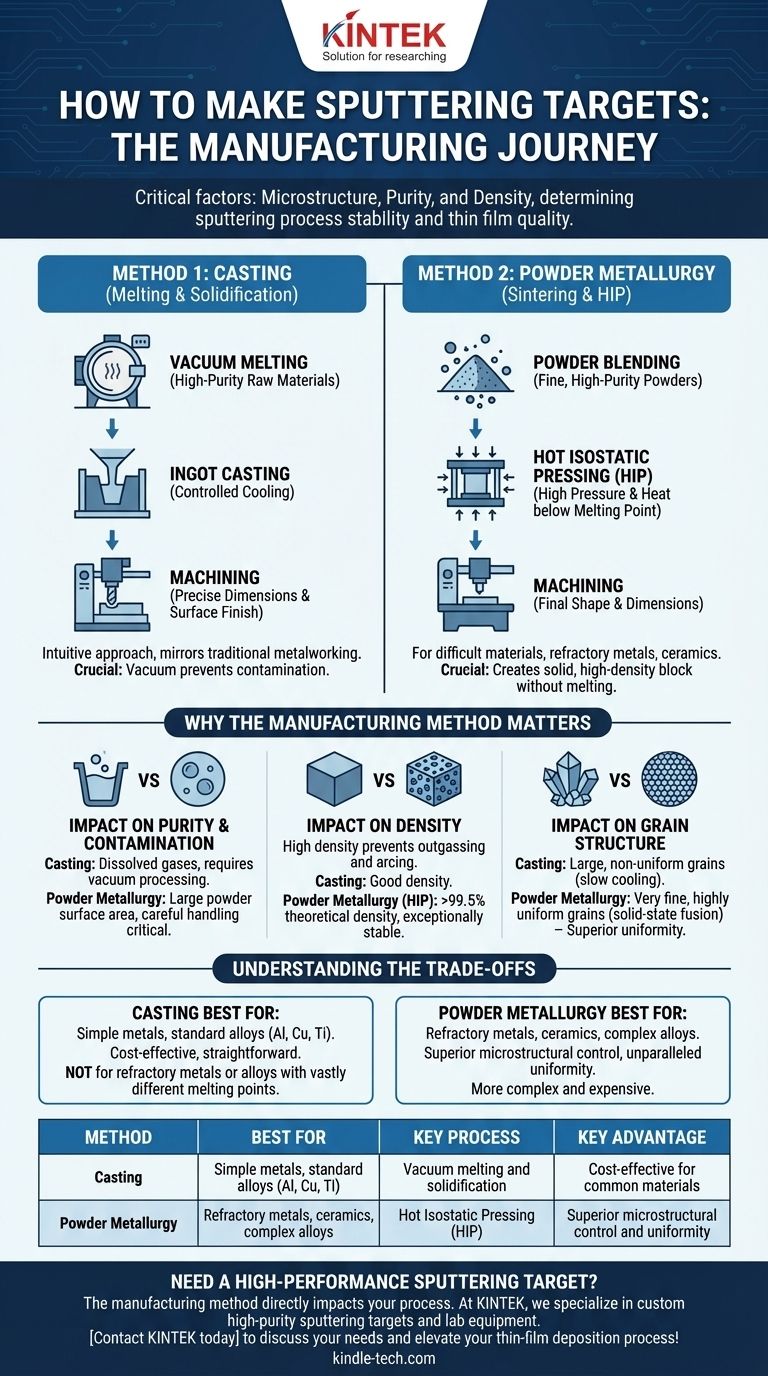
Sputtering targets are primarily manufactured using two distinct methods: casting and powder metallurgy. The choice between them is determined by the material's properties, such as its melting point and composition. For many standard alloys, the process involves melting high-purity raw materials in a vacuum, casting them into an ingot, and then machining the ingot to the final required dimensions.
The manufacturing method is not just a fabrication step; it is the most critical factor determining the target's microstructure, purity, and density. These properties, in turn, directly control the stability of your sputtering process and the quality of your deposited thin film.

The Foundational Methods: Casting vs. Powder Metallurgy
Understanding how a target is made is essential for troubleshooting film inconsistencies and selecting the right material for a new process. Each method produces a target with a fundamentally different internal structure.
Method 1: Casting (Melting and Solidification)
Casting is an intuitive approach that mirrors traditional metalworking. The process begins by melting high-purity raw materials in a tightly controlled environment.
This molten metal is then poured into a mold to cool and solidify into a rough shape called an ingot.
Crucially, this entire process is typically performed in a vacuum furnace. The vacuum prevents the molten metal from reacting with oxygen or nitrogen in the air, which would introduce contaminants into the final target.
Once cooled, the ingot undergoes extensive machining. This final step cuts the target to the precise dimensions required by the sputtering cathode and creates the necessary surface finish.
Method 2: Powder Metallurgy (Sintering)
Powder metallurgy (PM) is a more advanced technique used for materials that are difficult or impossible to cast. This includes materials with extremely high melting points or alloys made of elements that don't mix well when molten.
The process starts with extremely fine, high-purity powders of the constituent materials. These powders are precisely measured and blended to ensure a perfectly homogeneous mixture.
This powder mixture is then consolidated under immense pressure and high temperature. A common technique is Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), where the material is heated well below its melting point while being subjected to high pressure from all directions.
This combination of heat and pressure causes the powder particles to bond and fuse, creating a solid, high-density block without ever melting. This solid block is then machined to its final shape, just like a cast ingot.
Why the Manufacturing Method Matters
The choice between casting and PM directly impacts the physical characteristics of the target, which has a significant effect on sputtering performance.
Impact on Purity and Contamination
Both methods aim for high purity, but the source of contamination differs. In casting, the primary risk is dissolved gases like oxygen from any residual air. Vacuum processing is essential to minimize this.
In PM, the risk comes from the large surface area of the initial powders, which can adsorb moisture or other contaminants. Careful powder handling is critical.
Impact on Density
A high-density target is crucial for a stable process. Porosity (empty space) within a target can trap gas, which may violently "outgas" during sputtering, causing arcing and spitting particles onto your substrate.
While casting produces dense targets, techniques like HIP in powder metallurgy are renowned for achieving densities greater than 99.5% of the theoretical maximum, creating an exceptionally stable material.
Impact on Grain Structure
This is the most significant difference. Casting involves slow cooling from a liquid, which often results in large and non-uniform crystal grains.
Powder metallurgy, by contrast, fuses small particles together in a solid state, producing a target with a very fine and highly uniform grain structure. A uniform grain structure leads to a more consistent sputtering rate across the entire target face, improving the uniformity of the deposited film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is universally superior; the ideal choice depends entirely on the material being processed and the desired outcome.
The Case for Casting
Casting is often more cost-effective and straightforward for common metals and alloys like aluminum, copper, or titanium. It is well-suited for materials with a single, reasonable melting point.
However, casting struggles with refractory metals (e.g., tungsten) due to their extreme melting points. It is also unsuitable for alloys whose components have vastly different melting points, as they can separate during cooling (segregation).
The Case for Powder Metallurgy
Powder metallurgy excels where casting fails. It is the preferred, and often only, method for producing refractory metal targets, ceramic targets (like Indium Tin Oxide, or ITO), and complex alloys.
The primary benefit is the superior microstructural control, which delivers unparalleled sputtering uniformity. The main drawback is that it is generally a more complex and expensive process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
The fabrication method is a key specification you should consider when sourcing a target.
- If your material is a simple metal or standard alloy: Casting is often the most economical and effective method that provides excellent results.
- If your material is a complex alloy, refractory metal, or ceramic: Powder metallurgy is almost always the superior or only viable choice to ensure material integrity and performance.
- If your primary goal is maximum film uniformity and process stability: Prioritize a target made via powder metallurgy (specifically HIP) for its fine, homogeneous grain structure.
Understanding the manufacturing journey of your target is the first step to controlling the quality and consistency of your final thin film.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Process | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Casting | Simple metals, standard alloys (Al, Cu, Ti) | Vacuum melting and solidification | Cost-effective for common materials |
| Powder Metallurgy | Refractory metals, ceramics, complex alloys | Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) | Superior microstructural control and uniformity |
Need a High-Performance Sputtering Target for Your Lab?
The manufacturing method directly impacts your sputtering process stability and thin-film quality. At KINTEK, we specialize in producing high-purity sputtering targets and lab equipment tailored to your specific material and application requirements. Whether you need cast targets for standard alloys or powder metallurgy targets for refractory metals and ceramics, our expertise ensures optimal performance and film uniformity.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your target needs and elevate your thin-film deposition process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating










