A prime example of PECVD is Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (RF-PECVD), a high-efficiency technique used to precisely control the growth of materials like vertical graphene for advanced electronics. This method is one of several specialized PECVD processes, including High-Density Plasma CVD (HDP-CVD) and Microwave ECR-PECVD, each designed to deposit specific thin films for different applications.
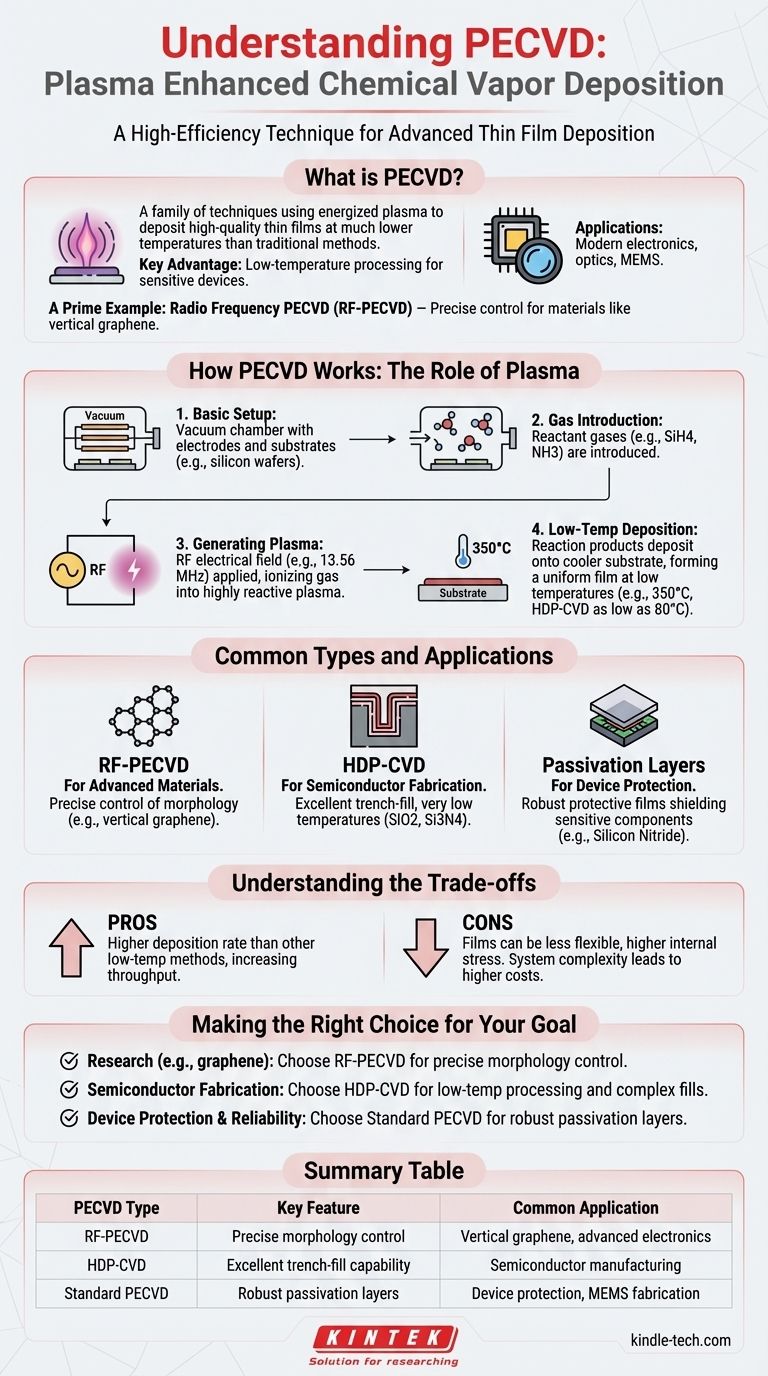
PECVD is not a single process but a family of techniques that use an energized plasma to deposit high-quality thin films at much lower temperatures than traditional methods. This key advantage makes it indispensable for manufacturing modern electronics, optics, and micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS).
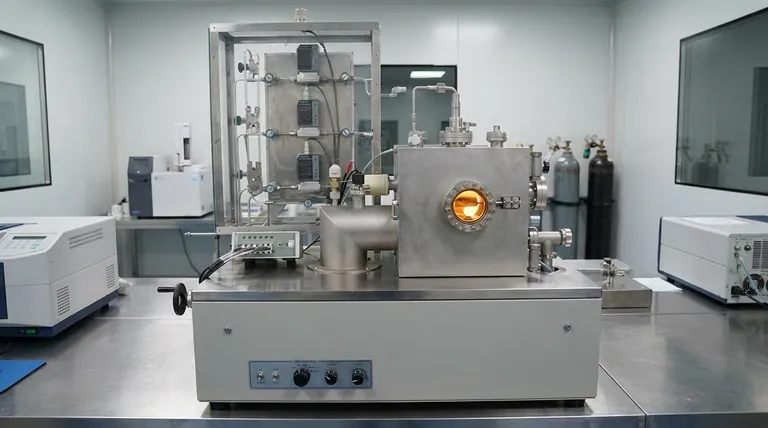

How PECVD Works: The Role of Plasma
To understand any example of PECVD, you must first grasp its core principle: using plasma to drive chemical reactions without extreme heat.
The Basic Setup
A PECVD system consists of a vacuum chamber containing two parallel electrodes. Substrates, such as silicon wafers, are placed on one of these electrodes.
Reactant gases are then introduced into the chamber. For example, to deposit silicon nitride (Si3N4), silane (SiH4) and ammonia (NH3) gases might be used.
Generating the Plasma
An electrical field, typically a radio frequency (RF) of 13.56 MHz, is applied across the electrodes. This energy ionizes the gas, stripping electrons from the atoms and creating a highly reactive state of matter known as plasma.
This plasma provides the energy needed to break down the reactant gases and induce a chemical reaction, a job that would otherwise require very high temperatures.
The Low-Temperature Advantage
The reaction products then deposit onto the cooler substrate, forming a thin, uniform film. This occurs at relatively low temperatures, often around 350°C, and in some specialized versions like HDP-CVD, as low as 80°C.
This is the critical benefit of PECVD. It allows for film deposition on materials and devices that cannot withstand the high temperatures of other CVD methods.
Common Types and Their Applications
The term "PECVD" describes a category of processes. The specific example you use depends entirely on the goal.
RF-PECVD for Advanced Materials
As mentioned, RF-PECVD is a widely used variant. It has gained significant attention for its ability to precisely control the morphology of new materials, such as growing perfectly aligned vertical graphene for next-generation displays or sensors.
HDP-CVD for Semiconductor Fabrication
High-Density Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition (HDP-CVD) is a version of PECVD that uses a much denser plasma. This allows for even lower processing temperatures and is essential in modern microchip manufacturing.
Its key strength is creating films with excellent trench-fill capabilities, meaning it can uniformly coat the microscopic trenches and complex 3D structures on a silicon wafer. Common films deposited this way include silicon dioxide (SiO2) and silicon nitride (Si3N4).
Passivation and Protective Layers
One of the most common industrial applications for PECVD is creating passivation layers. These are protective films, often of silicon nitride, that shield the sensitive electronic components on a chip from moisture, contamination, and physical damage. It's also used for hard masking and creating sacrificial layers in MEMS fabrication.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PECVD is not a universal solution. The choice to use it involves specific compromises.
Deposition Rate vs. Film Quality
PECVD generally offers a higher deposition rate than other low-temperature methods like Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD). This increases manufacturing throughput.
However, the films produced by PECVD can be less flexible and have higher internal stress compared to films grown at higher temperatures, which must be managed during device design.
System Complexity
The equipment for PECVD is inherently complex. It requires RF power supplies, vacuum pumps, and sophisticated gas handling systems. This complexity translates to higher capital and maintenance costs compared to simpler thermal deposition systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct deposition method depends entirely on the requirements of your final device.
- If your primary focus is advanced material research (like graphene): RF-PECVD offers the precise control needed for controlling material morphology.
- If your primary focus is modern semiconductor manufacturing: HDP-CVD is essential for its low-temperature processing and ability to fill complex topographical features.
- If your primary focus is device protection and reliability: Standard PECVD is the industry workhorse for depositing robust passivation layers like silicon nitride (Si3N4).
Ultimately, understanding the specific type of PECVD allows you to select the right tool to build more efficient and reliable next-generation devices.
Summary Table:
| PECVD Type | Key Feature | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| RF-PECVD | Precise morphology control | Vertical graphene, advanced electronics |
| HDP-CVD | Excellent trench-fill capability | Semiconductor manufacturing |
| Standard PECVD | Robust passivation layers | Device protection, MEMS fabrication |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precision PECVD solutions? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for thin film deposition. Whether you're working on semiconductor fabrication, MEMS development, or advanced material research, our expertise can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application



















