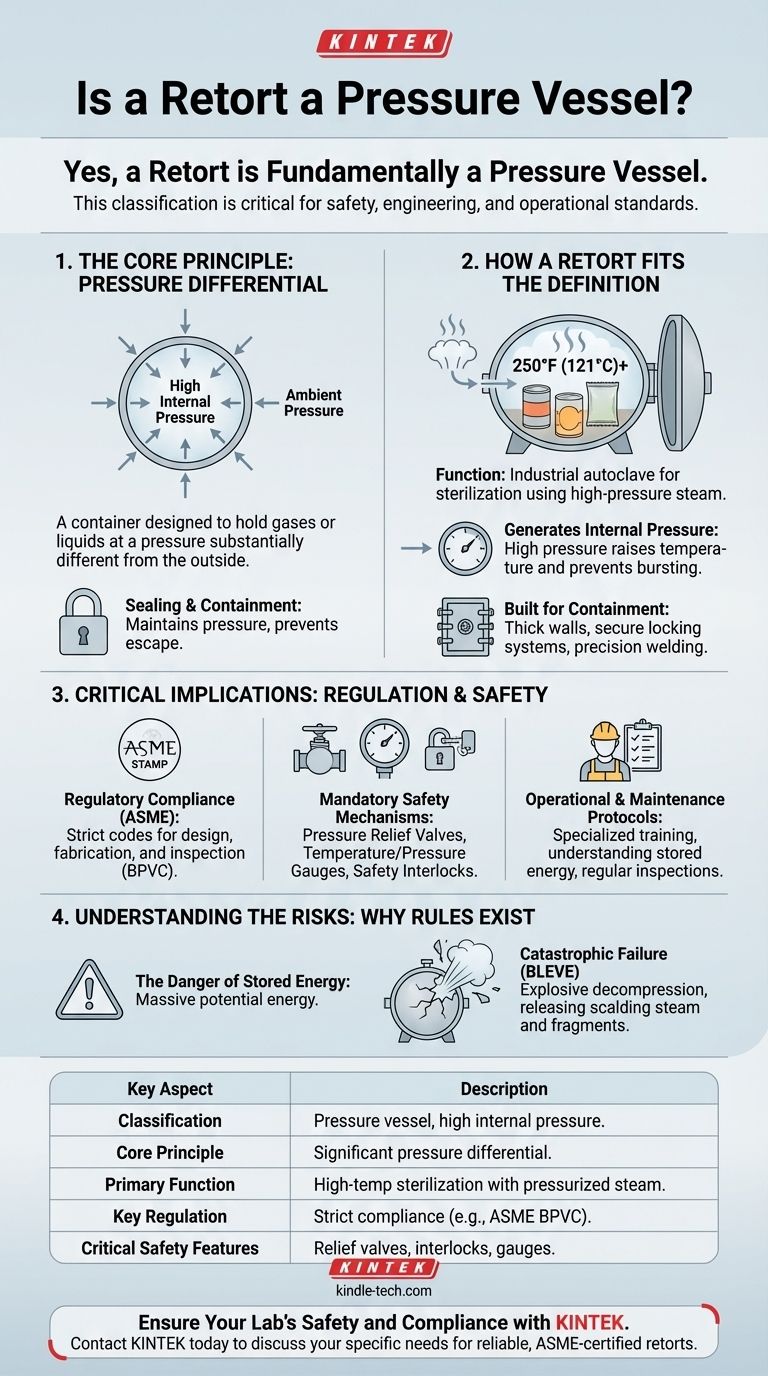
Yes, a retort is fundamentally a type of pressure vessel. This classification is not a minor technicality; it's a critical designation based on its core function. A retort is specifically designed to hold contents at a pressure substantially higher than the surrounding atmospheric pressure, typically by using steam to achieve high temperatures for sterilization.
The crucial takeaway is that classifying a retort as a pressure vessel subjects it to stringent engineering, manufacturing, and operational safety standards. This is because the immense stored energy within a pressurized system poses a significant risk of catastrophic failure if not properly managed.

What Defines a Pressure Vessel?
To understand why a retort fits this category, we must first define the term. The classification is based on a simple but critical engineering principle.
The Core Principle: Pressure Differential
A pressure vessel is any container designed to hold gases or liquids at a pressure substantially different from the ambient pressure. This pressure differential is the key defining characteristic.
The vessel's structure must be strong enough to safely contain this pressure without rupturing.
The Role of Sealing and Containment
By design, a pressure vessel is a sealed system. Its purpose is to maintain a specific internal pressure, preventing its contents from escaping and the outside atmosphere from entering.
This requires robust gaskets, seals, and locking mechanisms that can withstand the operational forces.
How a Retort Fits the Definition
A retort's function in thermal processing, especially in the food industry for canning, directly aligns with the principles of a pressure vessel.
The Function of a Retort
Retorts are essentially industrial autoclaves used for commercial sterilization. They work by heating products in sealed containers (like cans or pouches) to temperatures well above the boiling point of water.
To achieve temperatures of 250°F (121°C) or higher, the retort must use a heating medium, typically steam, under significant pressure.
Generating Internal Pressure
As steam is forced into the sealed retort chamber, the internal pressure increases dramatically. This pressure is essential for raising the temperature to the level required for sterilization and preventing the product containers from bursting.
This process creates the exact pressure differential that defines a pressure vessel.
Built for Containment
The construction of a retort reflects its purpose. It features thick steel walls, heavy-duty doors with secure locking systems, and precision-welded seams—all hallmarks of pressure vessel engineering designed to safely manage high internal stress.
The Critical Implications of This Classification
Treating a retort as a pressure vessel has profound consequences for safety, regulation, and operation. Ignoring this classification can lead to disastrous outcomes.
Regulatory Compliance (ASME)
In most jurisdictions, pressure vessels must be designed, fabricated, and inspected according to strict codes. The most common standard in North America is the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC).
This code mandates specific requirements for materials, design calculations, welding procedures, and quality control. A certified retort will bear an ASME stamp, verifying its compliance.
Mandatory Safety Mechanisms
Because of the inherent risks, retorts are legally required to have multiple safety features. These include:
- Pressure Relief Valves: Automatically vent steam if the pressure exceeds a safe limit.
- Temperature and Pressure Gauges: Provide operators with critical real-time data.
- Safety Interlocks: Prevent the door from being opened while the vessel is still pressurized.
Operational and Maintenance Protocols
Operating a pressure vessel requires specialized training. Personnel must understand the dangers of stored energy and follow strict procedures for startup, operation, and shutdown.
Furthermore, a regular inspection and maintenance schedule is crucial for checking the integrity of welds, seals, and safety valves.
Understanding the Risks: Why the Rules Exist
The stringent regulations exist for one reason: the immense amount of energy stored within a pressurized system.
The Danger of Stored Energy
A pressurized retort contains a massive amount of potential energy. If the vessel's integrity is compromised, this energy is released suddenly and violently.
A failure is not a simple leak. It is a rapid, explosive decompression that can propel metal fragments and release scalding steam over a wide area.
Potential for Catastrophic Failure
This type of event, sometimes called a BLEVE (Boiling Liquid Expanding Vapor Explosion), is extraordinarily dangerous. The primary risk is not just the pressure but the instantaneous conversion of high-temperature water into a massive volume of steam.
This is why uncertified or poorly maintained pressure vessels are considered one of the most significant safety hazards in any industrial facility.
Key Considerations for Your Operation
Understanding this classification should directly inform your actions regarding equipment procurement, training, and maintenance.
- If you are purchasing equipment: Always verify that any retort has proper ASME (or an equivalent regional standard) certification stamped directly on its nameplate.
- If you are operating a retort: Ensure all operators are thoroughly trained on the specific safety procedures and inherent risks of pressurized systems.
- If you are responsible for maintenance: You must implement and adhere to a strict inspection schedule for seals, valves, and overall vessel integrity as mandated by regulations and manufacturer guidelines.
Viewing your retort first and foremost as a pressure vessel is the foundational step to ensuring a safe, compliant, and reliable operation.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Classification | A retort is a pressure vessel designed to hold contents at high internal pressure. |
| Core Principle | Operates based on a significant pressure differential from the ambient atmosphere. |
| Primary Function | Achieves high-temperature sterilization (e.g., 121°C/250°F) using pressurized steam. |
| Key Regulation | Must comply with strict codes like the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC). |
| Critical Safety Features | Includes pressure relief valves, safety interlocks, and temperature/pressure gauges. |
Ensure Your Lab's Safety and Compliance with KINTEK
Understanding that your retort is a pressure vessel is the first step to a safe and compliant operation. The risks of improper use are significant, but the right equipment and expertise make all the difference.
KINTEK specializes in providing reliable, fully certified lab equipment, including retorts that meet stringent ASME standards. We help laboratories like yours mitigate risk and achieve precise, safe sterilization processes.
Ready to enhance your lab's safety and efficiency? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs. Our experts are here to provide you with the right equipment and support for your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Electric Split Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
People Also Ask
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- What is the size of the autoclave? Choose the Right Capacity for Your Lab
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- What role does an autoclave play in remediation experiments? Ensure Precision by Eliminating Biological Noise
- What is the pressure bar for autoclave sterilization? Master the Critical Link Between Pressure and Temperature



















