The efficiency of biomass energy is highly conditional. Unlike the clear-cut efficiency ratings of a solar panel or wind turbine, the effectiveness of biomass depends entirely on the type of feedstock used, the conversion technology applied, and the specific goal you are trying to achieve. It can be a highly effective renewable resource in the right context, but its raw energy conversion efficiency is often lower than fossil fuels.
The true value of biomass isn't measured by a single efficiency number. Instead, its strength lies in being a renewable, dispatchable, and often carbon-neutral component of a larger, diversified energy system.

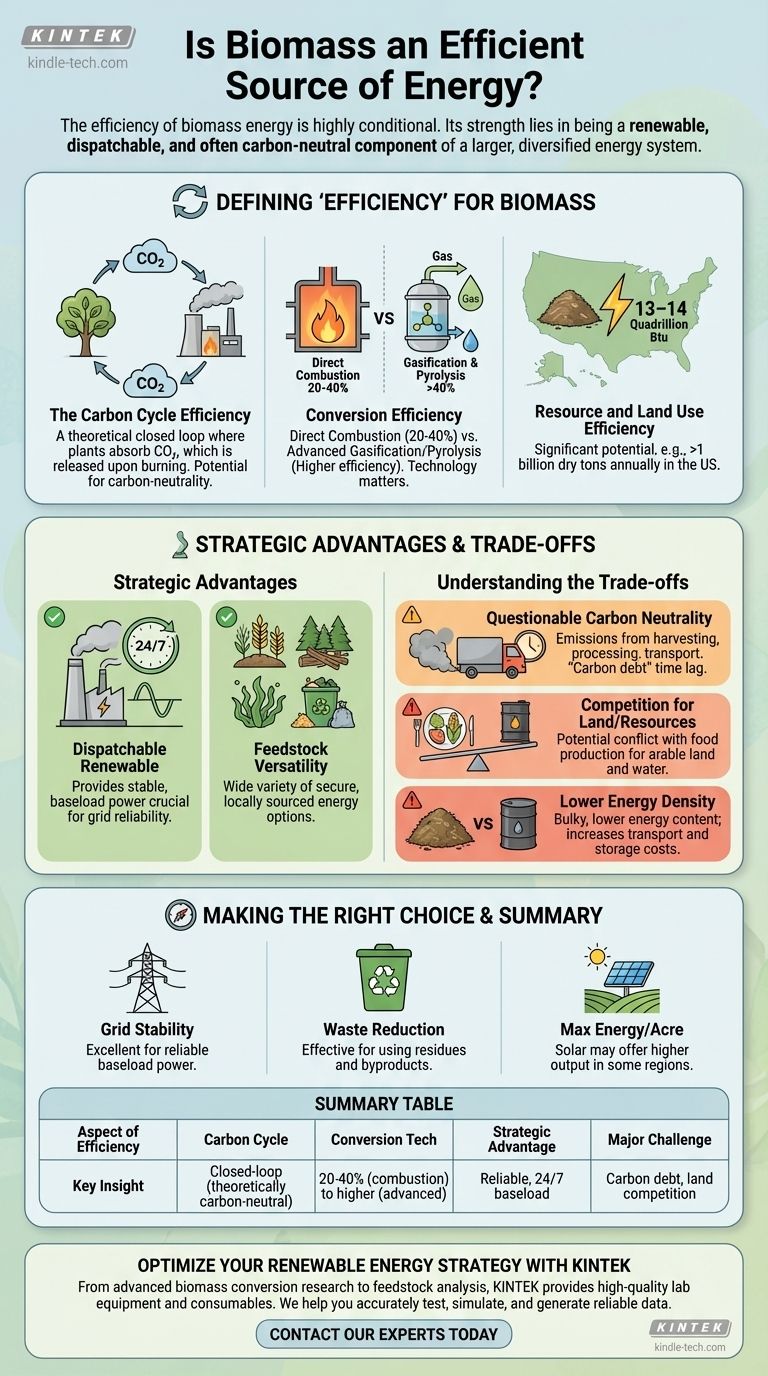
Defining "Efficiency" for Biomass
The term "efficiency" can be misleading when discussing biomass. We must evaluate it across three distinct dimensions to understand its true potential.
The Carbon Cycle Efficiency
The most compelling argument for biomass is its role in the carbon cycle. Plants absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere as they grow.
When this biomass is used for energy, that same amount of CO2 is released back into the atmosphere. In theory, this creates a closed loop, making it a carbon-neutral process.
Conversion Efficiency
This is the traditional measure of how much raw material is converted into usable energy. This varies significantly based on the technology.
- Direct Combustion: Burning biomass to create steam that turns a turbine is the most common method. Its thermal efficiency is often in the 20-40% range, similar to older coal plants but less efficient than modern natural gas plants.
- Gasification and Pyrolysis: These advanced thermal processes convert biomass into a gas (syngas) or liquid (bio-oil) fuel first. These fuels can then be used in more efficient engines or turbines, pushing overall efficiencies higher.
Resource and Land Use Efficiency
This metric looks at the energy output relative to the resources required, such as land and water. The potential here is significant.
The United States alone could potentially produce over 1 billion dry tons of biomass annually. This equates to around 13–14 quadrillion Btu of energy, which could meet a substantial portion of the nation's energy needs.
The Strategic Advantages of Biomass
Beyond simple efficiency numbers, biomass offers unique strategic benefits that other renewables lack.
A Dispatchable Renewable
Unlike solar and wind, which are intermittent, biomass power plants can run 24/7. This provides stable, baseload power that is crucial for grid reliability.
Feedstock Versatility
Biomass isn't a single fuel; it's a category. It includes everything from agricultural crops and forestry residues to algae and municipal solid waste. This wide availability and variety make it a secure and locally sourced energy option.
Understanding the Trade-offs
An objective evaluation requires acknowledging the significant challenges and limitations associated with biomass.
The Question of True Carbon Neutrality
The "carbon-neutral" label is an oversimplification. It doesn't account for the emissions generated from harvesting, processing, and transporting the biomass.
Furthermore, there is a time lag. A tree that takes 50 years to grow releases its stored carbon in minutes when burned. This "carbon debt" must be repaid by new growth over decades.
Competition for Land and Resources
Growing dedicated energy crops can compete directly with food production for arable land and water. This can create complex economic and ethical dilemmas, potentially impacting food security and prices.
Lower Energy Density
Compared to fossil fuels, biomass is bulky and has a lower energy content per unit of weight. This makes transportation and storage more costly and energy-intensive, reducing its net energy benefit, especially if it has to be moved long distances.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Biomass is not a universal solution, but it is a powerful tool when applied correctly. Your decision should be guided by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is grid stability: Biomass is an excellent renewable choice for providing reliable, dispatchable baseload power that intermittent sources cannot.
- If your primary focus is waste reduction: Using agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, or municipal waste for energy is a highly effective way to create value from low-value materials.
- If your primary focus is maximum energy per acre: Depending on the region, large-scale solar farms may offer a higher raw energy output for the same amount of land compared to some energy crops.
By understanding its specific strengths and weaknesses, you can effectively integrate biomass into a balanced and sustainable energy strategy.
Summary Table:
| Aspect of Efficiency | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Carbon Cycle | Creates a closed-loop, theoretically carbon-neutral process by recycling atmospheric CO2. |
| Conversion Technology | Efficiency ranges from 20-40% for direct combustion to higher rates for advanced gasification/pyrolysis. |
| Strategic Advantage | Provides reliable, 24/7 baseload power, unlike intermittent solar or wind. |
| Major Challenge | Faces issues like carbon debt from slow regrowth and competition for land with food production. |
Optimize your renewable energy strategy with the right lab equipment.
Whether you're researching advanced biomass conversion technologies like gasification and pyrolysis or analyzing feedstock efficiency, having the right tools is critical. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to energy researchers and sustainability labs.
We help you:
- Accurately test and analyze biomass feedstock properties.
- Simulate and optimize thermal conversion processes.
- Generate reliable data to support your energy projects.
Ready to enhance your biomass research? Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Customizable CO2 Reduction Flow Cell for NRR ORR and CO2RR Research
- FS Electrochemical Hydrogen Fuel Cells for Diverse Applications
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Achieve Precise Temperature Control for Your Experiments
- What are the typical volumes and aperture configurations for a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Optimize Your Electrochemical Setup
- What optical features does the H-type electrolytic cell have? Precision Quartz Windows for Photoelectrochemistry
- What is the purpose of the double-layer structure in the H-type electrolytic cell? Achieve Precise Thermal Control
- What is the overall structure of the H-type double-layer optical water bath electrolytic cell? Precision Design for Controlled Experiments



