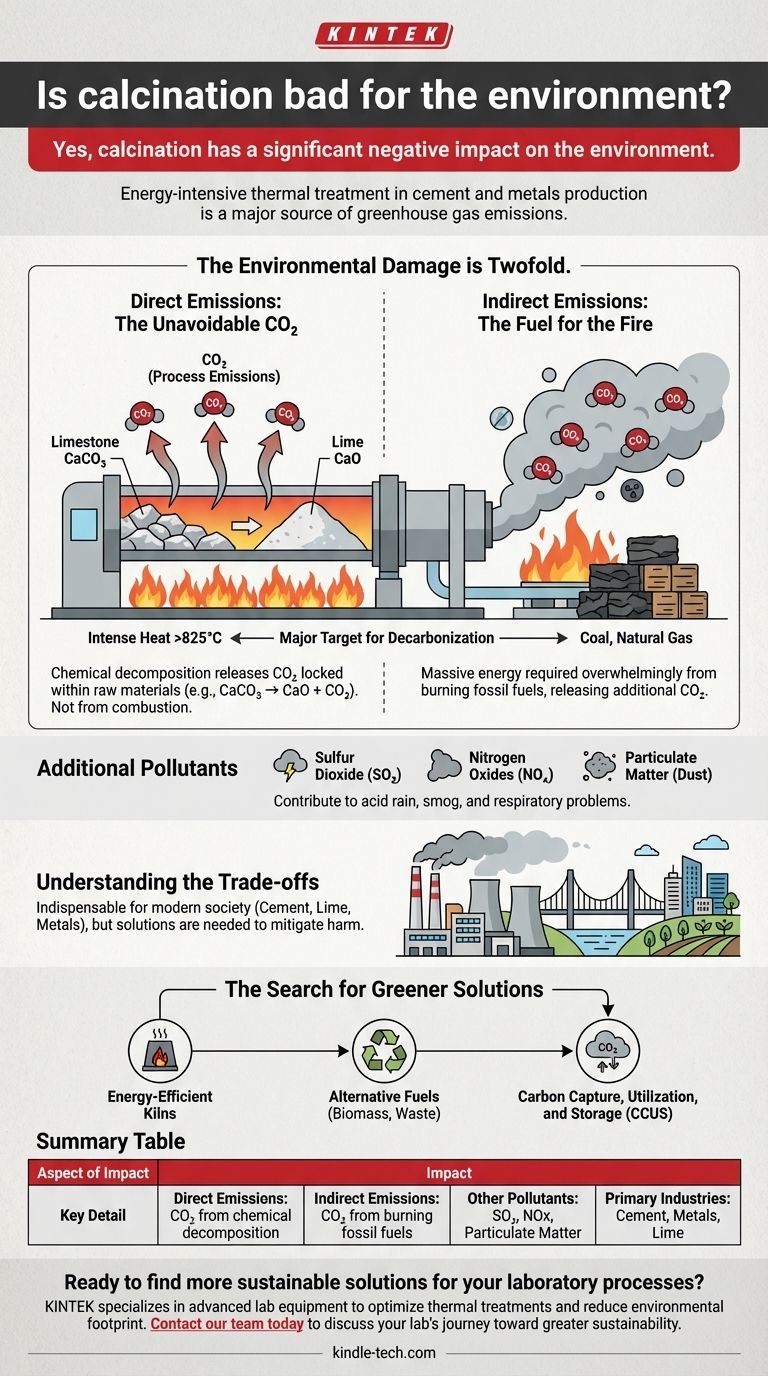
Yes, calcination has a significant negative impact on the environment. This thermal treatment process is fundamental to major industries like cement and metals production, but it is inherently energy-intensive and a major source of greenhouse gas emissions. The core environmental harm stems from both the chemical reactions it triggers and the massive amount of fuel required to generate the necessary heat.
The environmental damage from calcination is twofold: it directly releases CO₂ locked within raw materials and indirectly releases more CO₂ from burning fossil fuels to power the process. This makes it a primary target for decarbonization efforts in heavy industry.

What is Calcination? A Fundamental Look
The Core Process: Heat and Transformation
Calcination is a process of heating a solid material to a high temperature, typically in the absence or with a limited supply of air. The goal isn't to melt the material but to cause a chemical decomposition or a physical transformation.
This process is used to remove volatile substances, such as water or carbon dioxide, from raw materials. It's a foundational step in creating products like cement, lime, and refined metal ores.
A Critical Industrial Example: Cement
The most prominent example of calcination is in cement production. Limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) is heated in a kiln to over 825°C (1517°F).
This intense heat breaks the limestone down into lime (calcium oxide, CaO), which is the primary ingredient in cement, and carbon dioxide (CO₂). The chemical reaction itself—CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂—liberates vast quantities of CO₂ that was stored in the rock.
The Two Sources of Environmental Impact
Direct Emissions: The Unavoidable CO₂
The chemical decomposition of materials during calcination is a major source of direct, or "process," emissions. In the case of cement, this accounts for over half of the industry's total CO₂ output.
This CO₂ is released directly from the raw material as a result of the chemical change. It is not a byproduct of combustion and would be released even if the heat were generated from a completely clean energy source.
Indirect Emissions: The Fuel for the Fire
Calcination requires incredibly high temperatures. Achieving and maintaining these temperatures in industrial kilns consumes an enormous amount of energy, which is overwhelmingly supplied by burning fossil fuels like coal and natural gas.
The combustion of these fuels releases additional CO₂, alongside other pollutants, into the atmosphere. This represents the second major environmental impact of the process.
Additional Pollutants: Beyond Carbon Dioxide
Depending on the specific material being processed and the fuel used, calcination can also release other harmful air pollutants.
These often include sulfur dioxide (SO₂), which contributes to acid rain, and nitrogen oxides (NOx), which contribute to smog and respiratory problems. Particulate matter (dust) is also a significant concern, requiring control systems to mitigate its release.
Understanding the Trade-offs
An Essential Industrial Process
Despite its environmental drawbacks, calcination is indispensable for modern society. Without it, we could not produce the cement needed for our infrastructure, the lime used in agriculture and chemical manufacturing, or refine many of the metals that form the backbone of our economy.
The challenge is not simply to stop calcination, but to find ways to mitigate its harm while it remains a necessary process.
The Search for Greener Solutions
The significant environmental footprint of calcination has made it a key focus for innovation. Researchers and engineers are actively exploring solutions to reduce its impact.
These efforts include developing more energy-efficient kilns, using alternative fuels like biomass or waste, and pioneering carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies to trap CO₂ emissions before they reach the atmosphere.
How to Contextualize Calcination's Impact
- If your primary focus is on industrial emissions: Recognize that calcination is a dominant source of CO₂ in non-energy sectors, with the cement industry being the most significant contributor.
- If your primary focus is on climate solutions: Understand that meaningful industrial decarbonization is impossible without addressing the emissions from calcination through new technologies like carbon capture or entirely new chemical pathways.
- If your primary focus is on material science: The environmental cost of calcination is a major driver for developing novel building materials and refining processes that require less heat or different chemical inputs.
Ultimately, understanding the environmental impact of calcination is key to appreciating the immense challenge of decarbonizing our most fundamental industries.
Summary Table:
| Aspect of Impact | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Direct Emissions | CO₂ released from chemical decomposition of raw materials (e.g., limestone). |
| Indirect Emissions | CO₂ from burning fossil fuels to generate the intense heat required. |
| Other Pollutants | Can release sulfur dioxide (SO₂), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter. |
| Primary Industries | Cement production, metals refining, lime manufacturing. |
Ready to find more sustainable solutions for your laboratory processes? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables that can help you optimize your thermal treatments and reduce your environmental footprint. Our experts can help you select energy-efficient technologies tailored to your research and production goals. Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your lab's journey toward greater sustainability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing



















