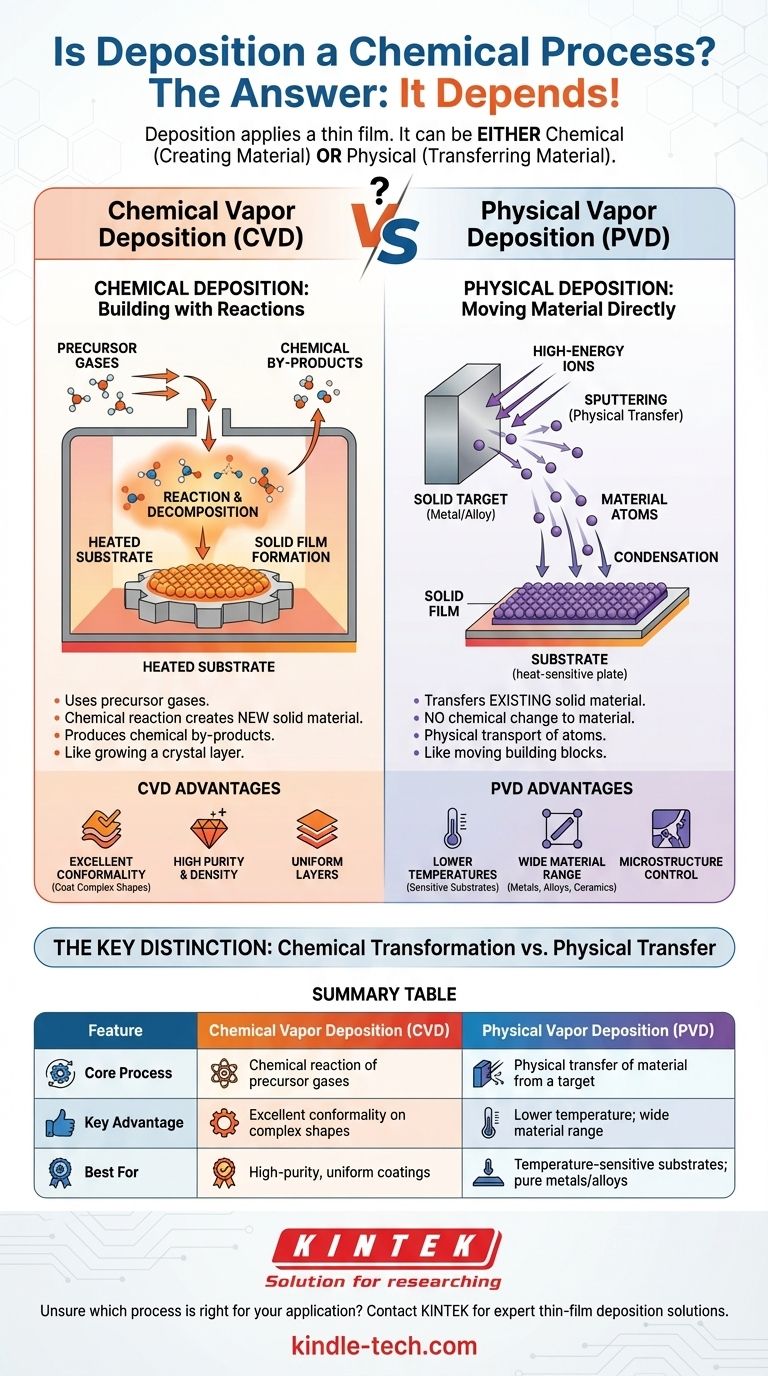
The answer is not a simple yes or no. Deposition is a broad term for applying a thin film onto a surface, and it can be either a chemical process or a physical one. The specific method used determines its classification, with Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) being a prime example of a chemical process.
The core distinction lies in how the film material arrives and forms on the substrate. A chemical process uses precursor gases that react to create a new, solid material on the surface, while a physical process essentially transfers an existing solid material from a source to the substrate without a chemical change.
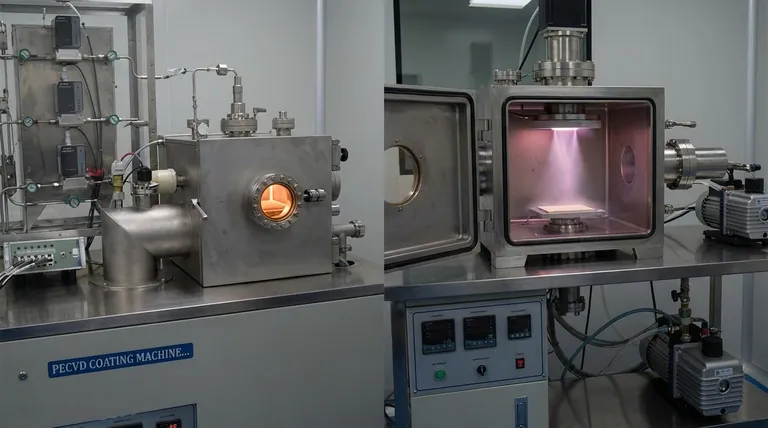

The Two Faces of Deposition: Chemical vs. Physical
At its heart, deposition is about building a layer of material atom by atom. The fundamental difference between the two major classes of deposition—chemical and physical—is whether you are creating the material on the surface or simply moving it there.
Chemical Deposition: Building with Reactions
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process that relies entirely on chemical reactions to form the film.
In CVD, volatile precursor gases are introduced into a reaction chamber, often a vacuum. These gases do not contain the final film material itself, but rather the atomic ingredients.
When these gases reach the heated substrate, they react and decompose, forming a new, solid material that deposits onto the surface. This process also creates chemical by-products that are then removed from the chamber.
Physical Deposition: Moving Material Directly
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), in contrast, does not involve chemical reactions to create the film. It is a physical transfer process.
Methods like sputter deposition fall under the PVD category. In sputtering, a target made of the desired film material is bombarded with high-energy ions.
This bombardment physically knocks atoms off the target, which then travel through the vacuum and condense onto the substrate, forming the thin film. The material on the substrate is chemically identical to the material on the target.
How to Tell the Difference
The key indicator of a chemical process is the transformation of matter. If you start with precursor gases and end with a solid film and separate by-product gases, a chemical reaction has occurred.
If you start with a solid target and simply move those same atoms to a substrate, the process is physical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a chemical or physical process is not arbitrary; it depends entirely on the desired properties of the final film and the constraints of the manufacturing process.
Advantages of Chemical Deposition (CVD)
Because CVD involves a chemical reaction that "grows" a film on a surface, it is exceptionally good at creating uniform, dense, and highly pure layers.
This method can coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with remarkable consistency, a property known as conformality. The versatility and control offered by managing the chemical reactions are its primary strengths.
Advantages of Physical Deposition (PVD)
PVD processes like sputtering can often be performed at lower temperatures than many CVD processes. This makes PVD suitable for depositing films on substrates that are sensitive to heat, such as plastics.
Furthermore, PVD can deposit a vast range of materials, including pure metals, alloys, and certain ceramics, that can be difficult or impossible to create with CVD precursors. It offers a large degree of control over the film's microstructure.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Goal
The decision to use a chemical or physical deposition technique is a critical engineering choice driven by the end goal.
- If your primary focus is high purity and uniform coating on complex shapes: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is designed to excel at this by chemically growing a new layer.
- If your primary focus is depositing a wide range of materials or working with temperature-sensitive substrates: A Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) method like sputtering is often the superior choice.
Ultimately, understanding whether you need to chemically create or physically transfer a material is the key to mastering thin-film deposition.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Process | Chemical reaction of precursor gases | Physical transfer of material from a target |
| Key Advantage | Excellent conformality on complex shapes | Lower temperature; wide material range |
| Best For | High-purity, uniform coatings | Temperature-sensitive substrates; pure metals/alloys |
Unsure which deposition process is right for your application? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert solutions for all your thin-film deposition needs. Whether you require the high-purity coatings of CVD or the versatility of PVD, our team can help you select the perfect system. Contact our experts today to discuss your project and optimize your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application



















