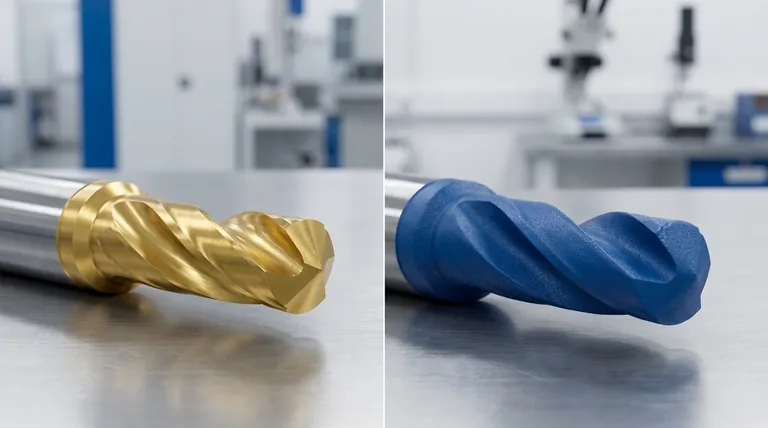
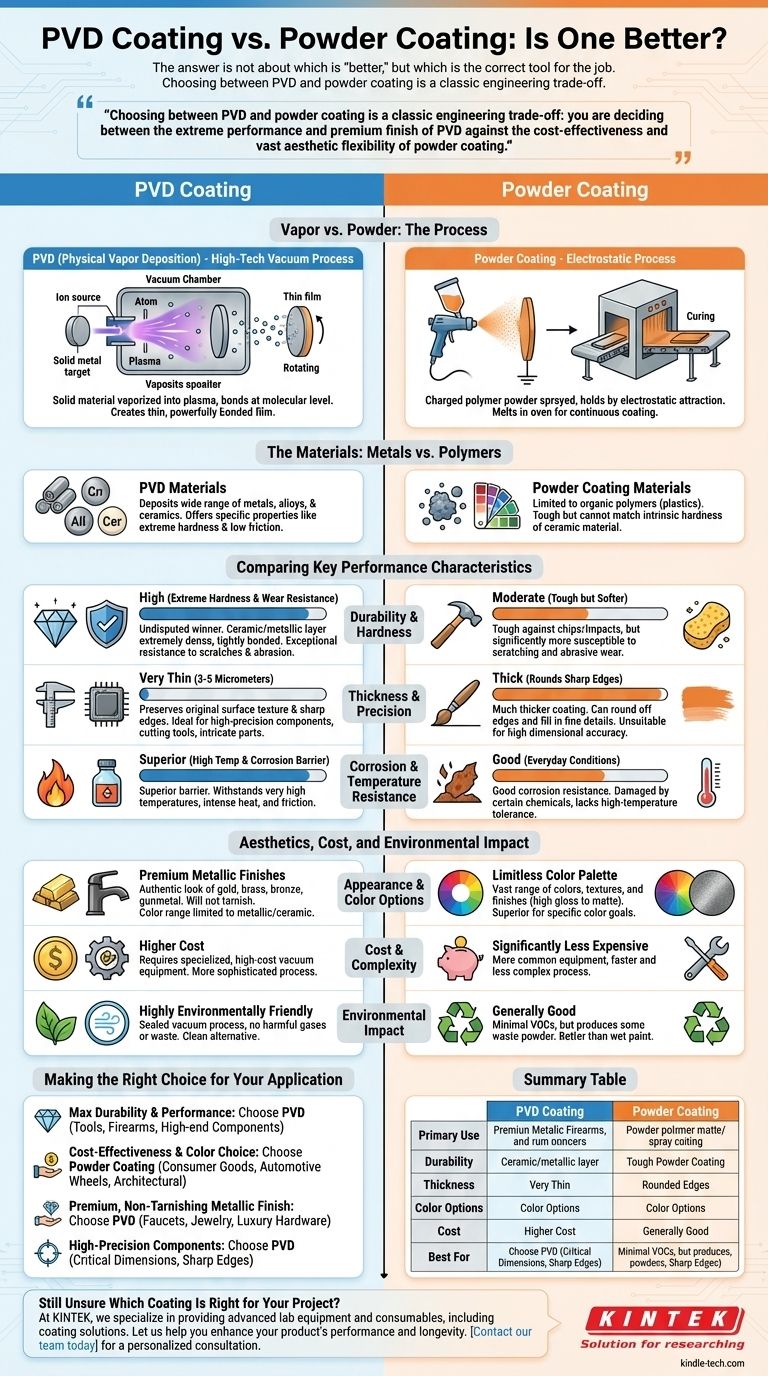
The answer is not about which is "better," but which is the correct tool for the job. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a high-performance process that bonds a thin, incredibly hard ceramic or metal film to a surface in a vacuum, offering superior durability. Powder coating, in contrast, applies a thicker, less expensive polymer layer using an electrostatic charge, providing excellent color variety and solid protection for general use.
Choosing between PVD and powder coating is a classic engineering trade-off: you are deciding between the extreme performance and premium finish of PVD against the cost-effectiveness and vast aesthetic flexibility of powder coating.

What's the Fundamental Difference?
To understand their applications, you must first understand that PVD and powder coating are entirely different technologies at a molecular level.
The Process: Vapor vs. Powder
PVD, or Physical Vapor Deposition, is a high-tech process conducted inside a vacuum chamber. A solid material (like titanium or chromium) is vaporized into a plasma, and its atoms or molecules are then deposited onto the target object, creating a thin, powerfully bonded film.
Powder coating is an electrostatic process. A polymer powder is given an electric charge and sprayed onto a grounded part. The electrostatic attraction holds the powder in place until the part is cured in an oven, which melts the powder into a smooth, continuous coating.
The Materials: Metals vs. Polymers
PVD can deposit a wide range of metals, alloys, and ceramics. This versatility allows it to create surfaces with specific properties like extreme hardness or low friction.
Powder coating is limited to organic polymers, which are essentially plastics. While modern polymers are highly advanced, they cannot match the intrinsic hardness of a ceramic material.
Comparing Key Performance Characteristics
The differences in process and material lead to dramatic differences in performance.
Durability and Hardness
PVD is the undisputed winner in hardness and wear resistance. The resulting ceramic or metallic layer is extremely dense and tightly bonded to the substrate, providing exceptional resistance to scratches, abrasion, and wear.
Powder coating is tough and protects against chips and impacts, but as a softer polymer coating, it is significantly more susceptible to scratching and abrasive wear than PVD.
Thickness and Precision
PVD coatings are extremely thin, typically only 3 to 5 micrometers. This preserves the original surface texture and sharp edges of the part, making it ideal for high-precision components like cutting tools, blades, and intricate watch parts.
Powder coatings are much thicker, which can round off sharp edges and fill in fine details. While this can create a desirable smooth finish, it is unsuitable for parts requiring high dimensional accuracy.
Corrosion and Temperature Resistance
PVD provides a superior barrier against corrosion and can withstand very high temperatures. This is why it's used on industrial tools that see intense heat and friction.
Powder coating offers good corrosion resistance for everyday conditions but can be damaged by certain chemicals and does not have the high-temperature tolerance of PVD.
Aesthetics, Cost, and Environmental Impact
Performance isn't the only factor; practical considerations often dictate the best choice.
Appearance and Color Options
Powder coating offers a nearly limitless palette of colors, textures, and finishes (from high gloss to matte). If your primary goal is a specific color, powder coating is the superior choice.
PVD excels at creating authentic premium metallic finishes. It can make stainless steel look identical to gold, brass, bronze, or gunmetal grey, and this finish will not tarnish or patina. Its color range, however, is limited to what can be achieved with metals and ceramics.
Cost and Complexity
Powder coating is significantly less expensive than PVD. The equipment is more common, and the process is faster and less complex.
PVD requires specialized, high-cost vacuum equipment and is a more sophisticated process, which is reflected in its higher price point.
Environmental Impact
PVD is a highly environmentally friendly process. It occurs in a sealed vacuum and produces no harmful gases or waste byproducts, making it a clean alternative to traditional electroplating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Select the coating that aligns with the primary requirements of your product.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and performance: Choose PVD for its unmatched hardness, wear resistance, and thin, precise application, ideal for tools, firearms, and high-end components.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and color choice: Choose powder coating for its lower cost and vast range of available colors, perfect for consumer goods, automotive wheels, and architectural elements.
- If your primary focus is a premium, non-tarnishing metallic finish: Choose PVD to authentically replicate the look of precious metals on faucets, jewelry, and luxury hardware.
- If your primary focus is high-precision components: Choose PVD because its ultra-thin film will not alter the part's critical dimensions or dull sharp edges.
Ultimately, your choice is guided by balancing the budget and aesthetic versatility of powder coating against the absolute performance and longevity of PVD.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD Coating | Powder Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | High-performance tools, precision parts, luxury finishes | Consumer goods, architectural elements, cost-effective protection |
| Durability | Extremely hard, scratch and wear-resistant | Good impact resistance, softer and more prone to scratches |
| Thickness | 3–5 micrometers (preserves part dimensions) | Thicker layer (can round edges and fill details) |
| Color Options | Limited to metallic/ceramic finishes (e.g., gold, gunmetal) | Wide range of colors, textures, and gloss levels |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized vacuum equipment | Lower and more accessible |
| Best For | Extreme durability, precision, and premium aesthetics | Budget-friendly projects and vibrant color requirements |
Still Unsure Which Coating Is Right for Your Project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables, including coating solutions tailored to your specific needs. Whether you require the extreme durability of PVD for precision tools or the cost-effective versatility of powder coating for consumer products, our experts can help you make the best choice.
Let us help you enhance your product's performance and longevity.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK’s solutions can meet your laboratory and manufacturing challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















