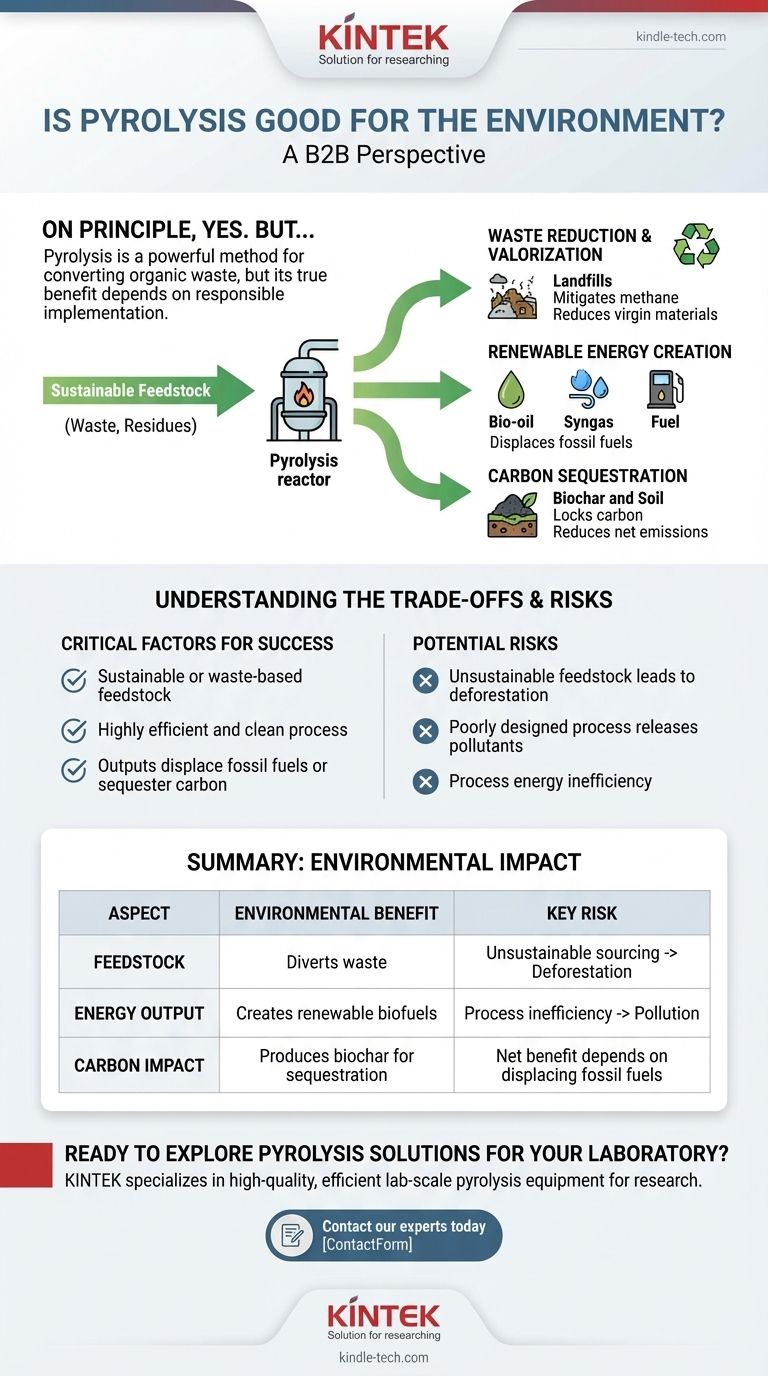
On principle, yes. Pyrolysis presents a powerful method for converting organic waste into valuable, environmentally friendly products like biofuels and biochar. It reduces landfill burdens and creates alternatives to fossil fuels. However, its true environmental benefit is not guaranteed; it depends entirely on responsible implementation, particularly the sourcing of materials and the efficiency of the process.
The environmental value of pyrolysis is not inherent in the technology itself. Its success is determined by three critical factors: using sustainable or waste-based feedstock, ensuring the process is highly efficient and clean, and utilizing the outputs to displace fossil fuels or sequester carbon.
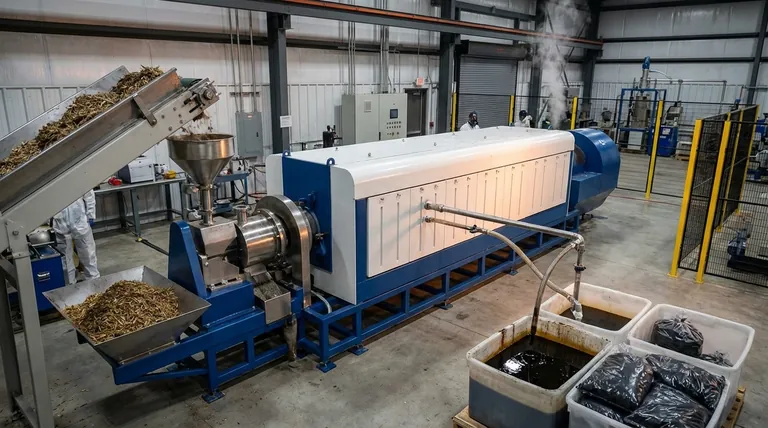

The Primary Environmental Benefits of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that decomposes organic material at high temperatures in the absence of oxygen. This unique approach unlocks several key environmental advantages when managed correctly.
Reducing and Valorizing Waste
Pyrolysis offers an effective solution for diverting a wide range of waste streams from landfills. This includes agricultural residues, wood waste, municipal solid waste, and even plastics and tires.
By converting this waste into useful products, pyrolysis mitigates the release of landfill methane (a potent greenhouse gas) and reduces the need for virgin raw materials.
Creating Renewable Energy
The process generates bio-oil and syngas, both of which can be used as fuel. This creates a renewable energy source from materials that would otherwise be discarded.
By substituting for traditional fossil fuels, these pyrolysis-derived biofuels help decrease the pollution and greenhouse gas emissions associated with burning coal, oil, and natural gas.
Enabling Carbon Sequestration
A key output of pyrolysis is biochar, a stable, carbon-rich solid resembling charcoal. When added to soil, biochar resists decomposition for centuries.
This effectively locks carbon away, removing it from the atmospheric cycle. Biochar sequestration is a powerful and recognized strategy for reducing net carbon emissions and can play a significant role in global carbon markets.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While the potential benefits are significant, the environmental outcome of pyrolysis is not automatic. Several critical factors can turn a promising solution into a problematic one.
The Critical Role of Feedstock
The single most important factor is the source of the organic material, or feedstock. Using genuine waste products like crop residues or municipal waste is a clear environmental win.
However, if pyrolysis operations lead to the harvesting of virgin forests or the use of unsustainable biomass, it can cause deforestation, habitat destruction, and a net increase in carbon emissions.
The Potential for Process Pollution
A poorly designed or inefficiently operated pyrolysis plant can release harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. The process must be well-controlled to ensure that all outputs are captured and that emissions are minimized.
The energy needed to run the pyrolysis reactor is also a consideration. To be truly beneficial, the process should be highly energy-efficient, ideally using its own syngas output to become self-sustaining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Pyrolysis is not a monolithic solution but a versatile tool whose environmental impact depends on its application.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Pyrolysis is an exceptional technology for diverting organic and plastic waste from landfills, turning a disposal liability into valuable assets.
- If your primary focus is renewable energy: The process provides a viable pathway to produce biofuels from waste, but its carbon neutrality is entirely dependent on using sustainable feedstock.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration: Pyrolysis is uniquely powerful due to its ability to create biochar, offering a robust and scalable method for long-term carbon removal.
Ultimately, when implemented with a commitment to sustainable sourcing and operational excellence, pyrolysis is a profoundly beneficial technology for the environment.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Environmental Benefit | Key Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Feedstock | Diverts organic/plastic waste from landfills | Unsustainable sourcing can cause deforestation |
| Energy Output | Creates renewable biofuels (bio-oil, syngas) | Process inefficiency can lead to pollution |
| Carbon Impact | Produces biochar for long-term carbon sequestration | Net benefit depends on displacing fossil fuels |
Ready to explore pyrolysis solutions for your laboratory or pilot project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in supplying high-quality, efficient lab-scale pyrolysis equipment and consumables. Whether your goal is waste valorization, renewable energy research, or carbon sequestration studies, our reactors are designed for precision, control, and clean operation.
We help you ensure your pyrolysis process is environmentally sound by providing:
- Reliable Equipment: For consistent, efficient, and clean thermal conversion.
- Expert Support: To optimize your process parameters for maximum yield and minimal emissions.
Let's work together to turn waste into valuable resources. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and how KINTEK can support your environmental research and development goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are zeolites advantages and disadvantages? Maximize Molecular Selectivity and Efficiency
- What are the main components of an industrial furnace? Explore Essential Elements for Precision Heating
- What is a vacuum boiler? A Safer, More Efficient Heating System Explained
- What is the function of an open-type reactor in SHS brass surface treatment? Achieve Precise Diffusion Saturation
- Are wood pellets biomass? Understanding the Renewable Fuel Powering Modern Heating
- What factors should be considered when choosing a ULT freezer for a lab? Ensure Maximum Sample Security and Efficiency
- What is bio-oil used for pyrolysis? Unlocking Renewable Fuel & Chemical Potential
- How does an Ultrafast High-temperature Sintering (UHS) system work? Achieve 3000°C in Seconds


















