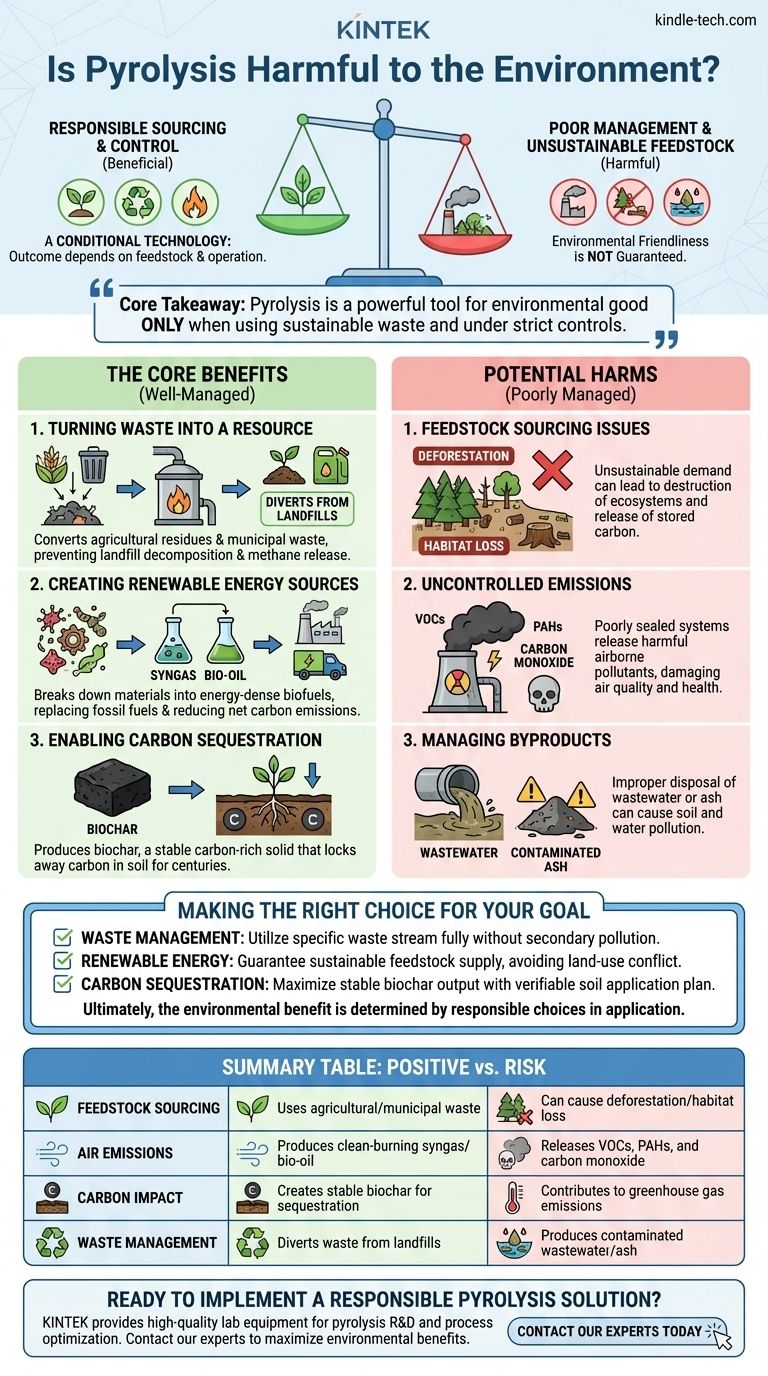
Ultimately, the environmental impact of pyrolysis is not inherent to the technology itself. Its effect on the environment can range from highly beneficial to actively harmful, depending entirely on two factors: the source of the material being processed (the feedstock) and the level of control over the operation. When using sustainable waste materials and operating under strict controls, pyrolysis is a powerful tool for environmental good.
The core takeaway is that pyrolysis is a conditional technology. Its environmental friendliness is not guaranteed but is instead a direct result of responsible feedstock sourcing and rigorous operational management to prevent pollution.

The Core Benefits of a Well-Managed Pyrolysis System
When implemented correctly, pyrolysis offers significant environmental advantages by transforming low-value materials into high-value products.
Turning Waste into a Resource
The most significant benefit comes from its ability to process materials that would otherwise be considered waste.
This includes agricultural residues, wood processing waste, and even certain types of municipal solid waste. By converting these materials, pyrolysis diverts them from landfills, where they would decompose and release methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
Creating Renewable Energy Sources
Pyrolysis breaks down complex organic materials into simpler, energy-dense products.
Syngas and bio-oil are two primary outputs that can be used as clean-burning fuels. These biofuels can replace fossil fuels in various applications, reducing the net carbon emissions associated with energy generation.
Enabling Carbon Sequestration
Perhaps the most unique benefit is the production of biochar, a stable, carbon-rich solid.
Unlike biomass that decomposes and releases its carbon back into the atmosphere, biochar is highly resistant to decay. When added to soil, it locks away carbon for centuries, effectively removing it from the atmosphere and acting as a form of carbon sequestration.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Potential Harms
The promise of pyrolysis is balanced by significant risks that must be managed to avoid negative environmental consequences.
The Critical Issue of Feedstock Sourcing
The single most important factor is where the biomass comes from.
Using genuine waste streams is environmentally positive. However, if demand for feedstock leads to deforestation or the conversion of natural habitats to grow dedicated energy crops, the process becomes overwhelmingly harmful, destroying ecosystems and releasing massive amounts of stored carbon.
The Risk of Uncontrolled Emissions
A poorly managed pyrolysis process can be a direct source of pollution.
If the system is not properly sealed and monitored, it can release harmful airborne pollutants. These include volatile organic compounds (VOCs), carbon monoxide, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which can harm air quality and human health.
Managing Byproducts
Not every output of the process is a valuable product.
Depending on the feedstock, the process can produce wastewater or ash containing contaminants. Proper management and disposal of these byproducts are essential to prevent soil and water pollution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if pyrolysis is an environmentally sound choice, you must evaluate it against your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is waste management: The key is to ensure the process fully utilizes your specific waste stream without creating a secondary pollution problem from emissions or residues.
- If your primary focus is renewable energy: The critical factor is guaranteeing a sustainable feedstock supply chain that does not cause negative land-use changes or compete with food production.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration: The goal is to maximize the output of stable biochar and ensure a clear, verifiable plan for its long-term application in soil.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is a powerful tool whose environmental benefit is determined not by the process itself, but by the responsible choices made in its application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Positive Outcome | Risk if Poorly Managed |
|---|---|---|
| Feedstock Sourcing | Uses agricultural/municipal waste | Can cause deforestation/habitat loss |
| Air Emissions | Produces clean-burning syngas/bio-oil | Releases VOCs, PAHs, and carbon monoxide |
| Carbon Impact | Creates stable biochar for sequestration | Contributes to greenhouse gas emissions |
| Waste Management | Diverts waste from landfills | Produces contaminated wastewater/ash |
Ready to implement a responsible pyrolysis solution?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis R&D and process optimization. Whether you are focused on waste management, renewable energy production, or carbon sequestration, our reliable equipment helps you achieve precise control and monitor emissions effectively.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs and help you maximize the environmental benefits of your pyrolysis projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What happens to the flux when brazing temperature is reached? It Activates to Ensure a Perfect Bond
- What is the annealing process in heat treatment? Make Metals Softer and More Workable
- Why are vacuum furnaces or high-purity inert atmosphere furnaces required for joining refractory metals?
- What is the difference between gasification pyrolysis and combustion? Choose the Right Thermal Process
- What role does the crystallizer perform in magnesium recovery? Master Pure Sublimation and Yield
- What is the primary function of high-temperature furnaces in mechanical characterization? Simulating Extreme Reality
- What is the function of a vacuum drying oven in the preparation of PEO/LSTZ composite polymer electrolyte membranes?
- Which material cannot be hardened? Understanding Non-Hardenable Metals for Your Projects



















