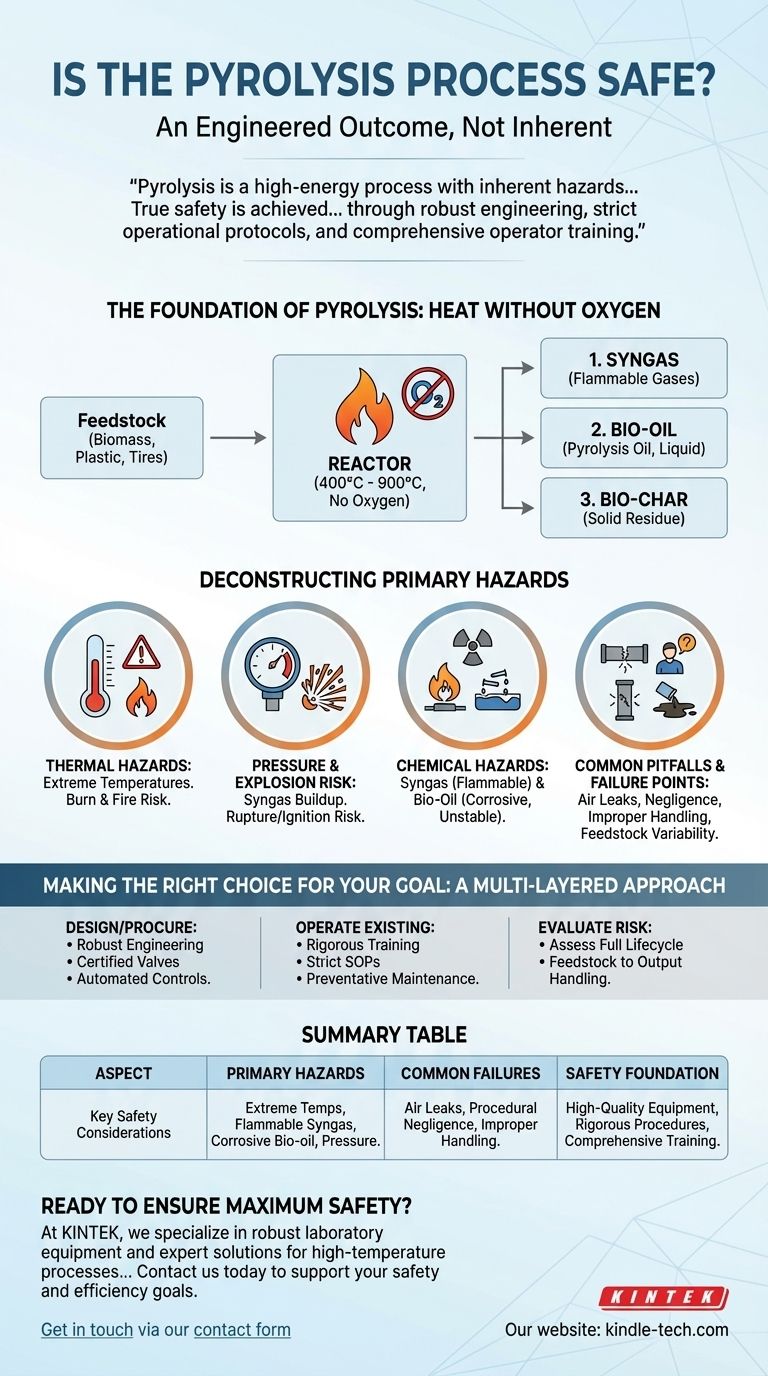
The safety of the pyrolysis process is not inherent; it is an engineered outcome. This industrial process involves heating materials to extremely high temperatures, often producing flammable gases and corrosive liquids. Therefore, its safety profile is entirely dependent on the quality of the equipment, the rigor of the operational procedures, and a comprehensive understanding of the chemical risks involved.
Pyrolysis is a high-energy process with inherent hazards, including extreme heat, flammable gas production, and corrosive byproducts. True safety is achieved not by eliminating these risks, but by systematically managing them through robust engineering, strict operational protocols, and comprehensive operator training.

The Foundation of Pyrolysis
To understand the risks, one must first understand the process. Pyrolysis is a form of thermochemical decomposition.
The Core Principle: Heat Without Oxygen
The feedstock, such as biomass, plastic, or tires, is heated to very high temperatures, typically between 400°C and 900°C.
Critically, this occurs in a reactor with an absence of oxygen. This prevents combustion and instead forces the material to break down into smaller molecules.
The Three Key Outputs
The process separates the feedstock into three primary products, each with its own characteristics and handling requirements.
- Syngas: A mixture of flammable gases.
- Bio-oil: A liquid product, also known as pyrolysis oil.
- Bio-char: A solid, carbon-rich residue.
The proportion of these outputs depends on factors like temperature, feedstock type, and process duration (slow vs. fast pyrolysis).
Deconstructing the Primary Hazards
Safety management in pyrolysis requires addressing multiple, distinct risk vectors that arise directly from the process and its products.
Thermal Hazards: Extreme Temperatures
The most obvious hazard is the operational temperature itself. Any failure in the reactor's containment or insulation presents a severe burn risk to personnel and a fire risk to the facility.
Pressure and Explosion Risk
Heating materials generates syngas, which increases the pressure inside the reactor. If this gas is not properly vented or utilized, the vessel can over-pressurize and rupture catastrophically.
Furthermore, if oxygen is allowed to leak into the high-temperature reactor, the flammable syngas can ignite, causing an explosion.
Chemical Hazards of Syngas
Syngas is itself a fuel. Any leaks in the system can release this flammable gas into the surrounding environment, creating a significant fire or explosion hazard if it encounters an ignition source.
Chemical Hazards of Bio-Oil
Pyrolysis oil is fundamentally different from conventional petroleum. It has a high oxygen content, which makes it corrosive to common materials like carbon steel.
It is also thermally unstable and can polymerize, or thicken, when exposed to air. This requires specialized storage and handling procedures to prevent equipment damage and safety incidents.
Common Pitfalls and Failure Points
Most incidents are not caused by the fundamental process but by breakdowns in the systems designed to control it.
Air Leaks: The Critical Failure Point
The single most critical requirement for controlled pyrolysis is the absence of oxygen. A failure in a seal, a crack in the reactor, or an improper procedure that introduces air can instantly turn controlled decomposition into uncontrolled combustion.
Negligence and Procedural Failures
As with any complex industrial process, human error is a major risk factor. Negligence or failure to follow Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for startup, shutdown, or maintenance can bypass critical safety systems.
Improper Handling of Outputs
The hazards do not end when the reaction is complete. Storing corrosive bio-oil in the wrong type of container or allowing flammable syngas to accumulate are common post-process failure modes.
Feedstock Variability
The composition of the output products is directly influenced by the input feedstock. Inconsistent or contaminated feedstock can produce unexpected gas volumes or chemical compositions, potentially overwhelming the system's safety design parameters.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ensuring safety is about implementing a multi-layered approach that addresses equipment, processes, and people.
- If your primary focus is designing or procuring a system: Prioritize robust engineering with high-quality materials, certified pressure relief valves, and automated control systems with safety interlocks.
- If your primary focus is operating an existing facility: The core of your safety program must be rigorous operator training, strict adherence to SOPs, and a diligent preventative maintenance schedule.
- If your primary focus is evaluating the overall risk: Assess the entire lifecycle, from feedstock reception and storage to the final handling, storage, and transport of the syngas, bio-oil, and bio-char.
Ultimately, a safe pyrolysis process is a direct reflection of disciplined engineering and operational excellence.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Safety Considerations |
|---|---|
| Primary Hazards | Extreme temperatures, flammable syngas, corrosive bio-oil, pressure buildup. |
| Common Failure Points | Air leaks into the reactor, procedural negligence, improper output handling. |
| Safety Foundation | High-quality equipment, rigorous operational procedures, comprehensive operator training. |
Ready to ensure your pyrolysis process is engineered for maximum safety?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust laboratory equipment and expert solutions for managing high-temperature processes. Whether you are designing a new system or optimizing an existing one, our team can help you select the right equipment and establish the rigorous protocols needed to mitigate risks and ensure operational excellence.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your lab's safety and efficiency goals. Get in touch via our contact form.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?



















