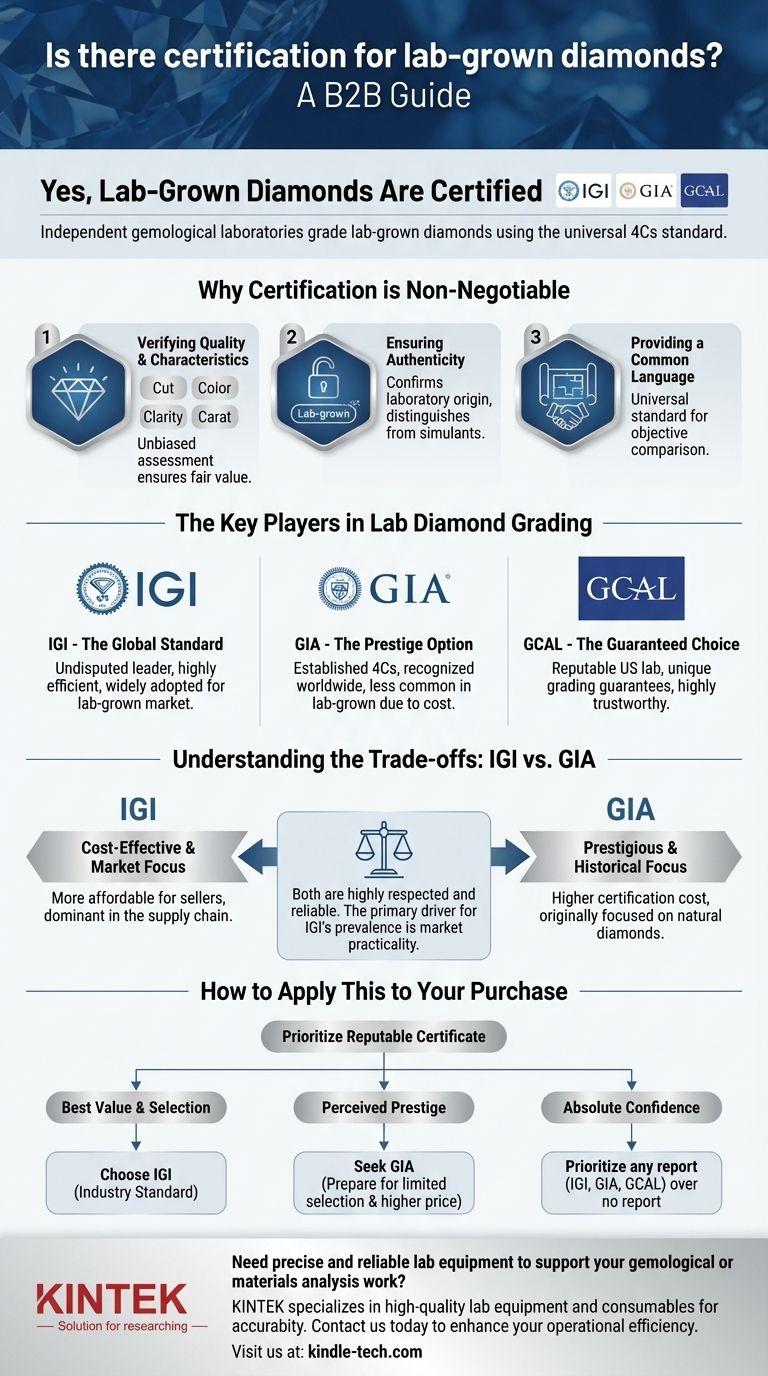
Yes, lab-grown diamonds are certified by the same independent gemological laboratories that grade natural diamonds. Reputable organizations like the International Gemological Institute (IGI), the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), and the Gem Certification & Assurance Lab (GCAL) all issue detailed grading reports for lab-grown stones. These reports provide an objective analysis of a diamond's quality based on the universal 4Cs: cut, color, clarity, and carat weight.
The critical takeaway is not just that lab-grown diamonds are certified, but understanding why you will most often see an IGI certificate. This choice is driven by the practical economics of the lab diamond market, not a difference in the diamond's fundamental quality.

Why Certification is Non-Negotiable
A grading report, often called a "certificate," is the single most important document accompanying your diamond purchase. It provides independent verification that the stone you are buying matches the quality and characteristics advertised by the seller.
Verifying Quality and Characteristics
The primary function of a grading report is to provide an unbiased assessment of the diamond's 4Cs. A trained gemologist evaluates the stone's proportions (Cut), absence of color (Color), presence of inclusions (Clarity), and weight (Carat). This ensures you are paying a fair price for the specific quality you receive.
Ensuring Authenticity
The report explicitly states that the diamond is laboratory-grown. This confirms its origin and distinguishes it from natural diamonds or diamond simulants like cubic zirconia or moissanite. Since 2019, major labs like GIA have stopped using the term "synthetic" on reports, aligning with FTC guidance that lab diamonds are real diamonds.
Providing a Common Language
A grading report acts as a universal blueprint for the diamond. It allows you to objectively compare two different diamonds from two different retailers, even if you cannot see them side-by-side.
The Key Players in Lab Diamond Grading
While several labs exist, the market for lab-grown diamonds is dominated by two main players, with a third reputable option also available.
IGI (International Gemological Institute)
IGI is the undisputed leader and global standard for lab-grown diamond certification. Having embraced the lab-grown market early on, they have developed a highly efficient and respected grading process. The vast majority of lab-grown diamonds available today are certified by IGI.
GIA (Gemological Institute of America)
GIA is arguably the most recognized name in diamond grading worldwide, having established the 4Cs grading standard itself. While historically focused on natural diamonds, GIA now provides comprehensive reports for lab-grown stones. A GIA report carries immense prestige but is seen less frequently in the lab-grown market.
GCAL (Gem Certification & Assurance Lab)
GCAL is another highly reputable US-based lab. It is unique in that it often backs its grading with a guarantee, offering a level of assurance that sets it apart. While less common than IGI, a GCAL report is considered a reliable and trustworthy assessment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: IGI vs. GIA
The most common question buyers face is why a diamond has an IGI report instead of a GIA report. The answer is not about one lab being "better," but about market practicalities.
The Decisive Factor of Cost
The primary value proposition of a lab-grown diamond is its affordability compared to a natural diamond. GIA's certification services are significantly more expensive than IGI's. For a seller to maintain a competitive price point, using the more cost-effective IGI report is the logical business choice.
Market Adoption and Focus
IGI became the expert in grading lab-grown diamonds well before GIA fully entered this segment. As a result, the entire supply chain—from growers to cutters to retailers—is built around the IGI process. This has solidified IGI's position as the industry standard for lab-grown stones.
Is One "Stricter" Than the Other?
There is ongoing debate about whether GIA grades more strictly than IGI. However, for practical purposes, both institutions are highly respected and reliable. Choosing a diamond certified by either IGI or GIA provides the assurance you need. The key is that the grading was performed by a credible, independent third party.
How to Apply This to Your Purchase
Your choice should be guided by your priorities. The presence of a reputable certificate is what matters most.
- If your primary focus is the best value and widest selection: Confidently choose a diamond with an IGI report, as this is the industry standard for lab-grown stones.
- If your primary focus is perceived prestige: You can seek out a GIA-certified lab diamond, but be prepared for a much smaller selection and a potentially higher price for a stone of similar quality.
- If your primary focus is absolute confidence: Prioritize a diamond with any report from IGI, GIA, or GCAL over a diamond with no report at all.
Ultimately, a reputable grading report empowers you to buy with confidence, ensuring the diamond you choose is exactly what it claims to be.
Summary Table:
| Certifying Body | Key Characteristics | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| IGI (International Gemological Institute) | Global standard for lab-grown diamonds; cost-effective and widely adopted. | Industry standard for most lab-grown diamonds. |
| GIA (Gemological Institute of America) | Highly prestigious; established the 4Cs grading system. | Less common in lab-grown market; often carries a higher price. |
| GCAL (Gem Certification & Assurance Lab) | Known for guarantees; reputable and trustworthy. | Less common than IGI but offers a high level of assurance. |
Need precise and reliable lab equipment to support your gemological or materials analysis work? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving the exact needs of laboratories that require accuracy and durability. Whether you're grading diamonds or conducting advanced material testing, our products are designed to meet rigorous standards. Contact us today to find the right equipment for your lab and enhance your operational efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Cylindrical Press Mold with Scale for Lab
- CVD Diamond Wire Drawing Die Blanks for Precision Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the primary advantages of the CVD method for growing diamonds? Engineering High-Purity Gems and Components
- What are the limitations of diamonds? Beyond the Myth of Perfection
- How plasma is used in diamond coating films? Unlock the Power of MPCVD for Superior Coatings
- What is the microwave plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition process? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Coatings
- How does Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapour Deposition (MPCVD) work? Your Guide to High-Purity Diamond Film Growth





