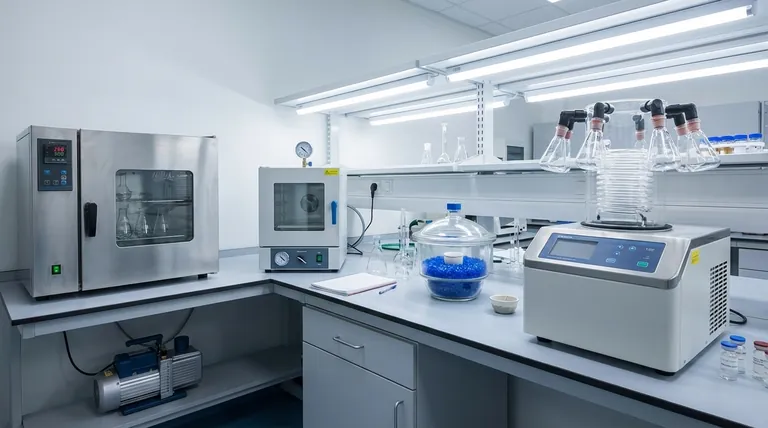
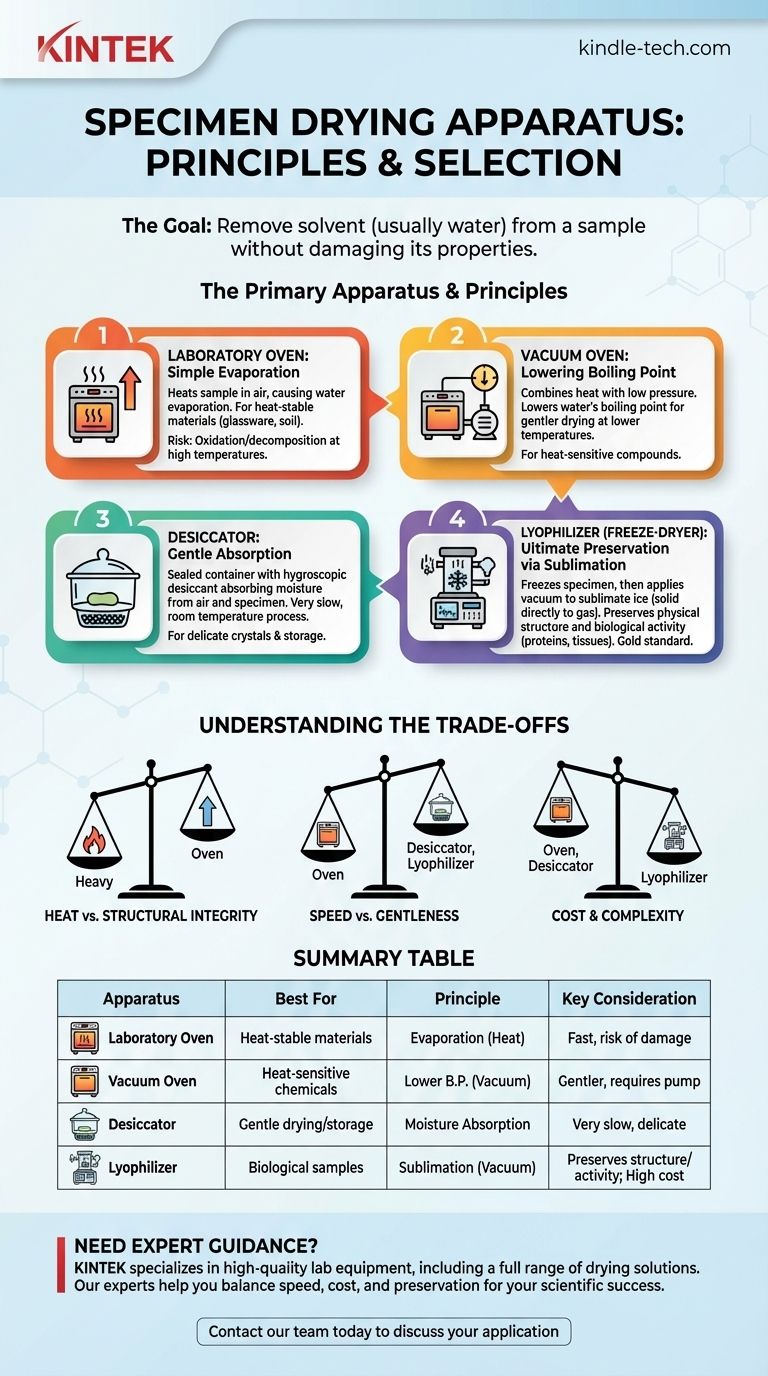
The primary apparatus for drying specimens includes laboratory ovens, desiccators, and lyophilizers (freeze-dryers). Each operates on a different principle and is chosen based on the specimen's sensitivity to heat and the required level of preservation. Simple heat-stable materials are dried in an oven, while delicate biological samples require a more advanced method like lyophilization.
The critical decision is not simply what apparatus to use, but how the drying process will affect your specimen. The choice is a direct trade-off between speed, cost, and the preservation of the sample's physical and chemical integrity.

The Principles of Specimen Drying
The goal of drying is to remove a solvent, most often water, from a sample. The method you choose depends entirely on the sample's properties. Applying the wrong technique can irreversibly damage or destroy your specimen.
The Laboratory Oven: Simple Evaporation with Heat
A standard laboratory oven is the most common and straightforward drying tool. It works by heating the sample in the presence of air, causing water to evaporate.
These ovens are best for materials that are not sensitive to heat. This includes things like cleaning glassware, drying soil or inorganic chemical samples, and sterilizing heat-stable equipment.
Most lab ovens use convection (circulating hot air) to ensure even and efficient drying. Temperature can be precisely controlled, but high temperatures can cause oxidation or decomposition in sensitive materials.
The Vacuum Oven: Lowering the Boiling Point
A vacuum oven combines heat with a low-pressure environment. By removing air with a vacuum pump, the pressure inside the chamber is drastically reduced.
This pressure reduction lowers the boiling point of water. This allows you to dry samples at a much lower temperature than you could in a standard oven, minimizing the risk of heat damage.
Vacuum ovens are ideal for moderately heat-sensitive compounds, materials prone to oxidation, or for achieving a more thorough level of dryness than a standard oven can provide.
Protecting Delicate and Biological Samples
When a specimen's structure or biological activity must be preserved, aggressive heating is not an option. Gentle, non-destructive methods are required.
The Desiccator: Gentle Drying via Absorption
A desiccator is a sealed container that uses a hygroscopic substance (a desiccant) like silica gel or anhydrous calcium sulfate to absorb moisture from the air, and therefore from the specimen.
This is a very slow and gentle process that occurs at room temperature. It is primarily used for two purposes: slowly drying very delicate crystals or storing previously dried samples to prevent them from reabsorbing atmospheric moisture.
A vacuum desiccator is a variation that can be placed under a vacuum. This accelerates the process but is still fundamentally about passive moisture absorption by the desiccant.
The Lyophilizer (Freeze-Dryer): Ultimate Preservation via Sublimation
Lyophilization, or freeze-drying, is the gold standard for preserving delicate biological materials, pharmaceuticals, and food. It works on the principle of sublimation, where water passes directly from a solid (ice) to a gas (vapor) without entering a liquid phase.
The process involves first freezing the specimen solid. Then, a deep vacuum is applied, and a small amount of heat is introduced. This gives the ice molecules just enough energy to sublimate, leaving the sample's structure intact.
This method avoids the damaging effects of liquid water and high heat, perfectly preserving the physical structure and biological activity of samples like proteins, microbes, tissues, and pharmaceuticals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a drying method involves balancing three critical factors: sample sensitivity, time, and cost.
Heat vs. Structural Integrity
An oven provides rapid drying but can easily destroy the structure of a biological sample. A lyophilizer, on the other hand, is exceptionally gentle and preserves cellular and molecular structures but is a much more complex process.
Speed vs. Gentleness
Ovens are the fastest method for robust samples. Desiccators are the slowest but are very gentle and require minimal energy. Lyophilization is also a slow, multi-hour (or multi-day) process.
Cost and Complexity
Laboratory ovens and desiccators are inexpensive, common, and simple to operate. Vacuum ovens are moderately expensive and require a separate vacuum pump. Lyophilizers are highly expensive, complex to run, and require significant maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of apparatus must be dictated by your experimental outcome. A mismatched method will compromise your results.
- If your primary focus is simple water removal from robust materials (like glassware or soil): A standard laboratory oven is the most efficient and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is drying heat-sensitive chemicals or preventing oxidation: A vacuum oven provides a necessary balance of speed and gentleness.
- If your primary focus is preserving the biological or structural integrity of a sensitive sample (like proteins or tissues): You must use a lyophilizer (freeze-dryer) to avoid irreversible damage.
- If your primary focus is slowly removing residual moisture or storing a dried sample: A desiccator is the correct and simplest tool for the job.
Understanding these core principles empowers you to select the method that precisely matches your scientific objective.
Summary Table:
| Apparatus | Best For | Principle | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Oven | Heat-stable materials (glassware, soil) | Evaporation via heat | Fast, but can damage sensitive samples |
| Vacuum Oven | Heat-sensitive chemicals, preventing oxidation | Lowers boiling point with vacuum | Gentler than standard oven, requires pump |
| Desiccator | Gentle drying/storage at room temperature | Moisture absorption by desiccant | Very slow process, ideal for delicate crystals |
| Lyophilizer (Freeze-Dryer) | Biological samples (proteins, tissues), pharmaceuticals | Sublimation (ice to vapor) under vacuum | Preserves structure/activity; high cost & complexity |
Need expert guidance on selecting the perfect drying apparatus for your specific laboratory needs?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of drying solutions from robust ovens to advanced lyophilizers. Our experts understand the critical balance between speed, cost, and sample preservation. We can help you choose the right equipment to ensure your specimens' integrity and your experiment's success.
Contact our team today to discuss your application and find the ideal drying solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of an electrolytic polishing device for EK-181 steel TEM samples? Ensure Peak Sample Integrity
- What is the process of mounting in metallurgy? A Guide to Perfect Specimen Preparation
- How should a sample be installed onto the sample holder? Ensure Mechanical Stability & Electrical Integrity
- How should an RVC sheet be handled and set up during an experiment? Ensure Precision and Data Integrity
- What is a hot mounting press machine? Precision Control for Metallurgy & Electronics Assembly



















