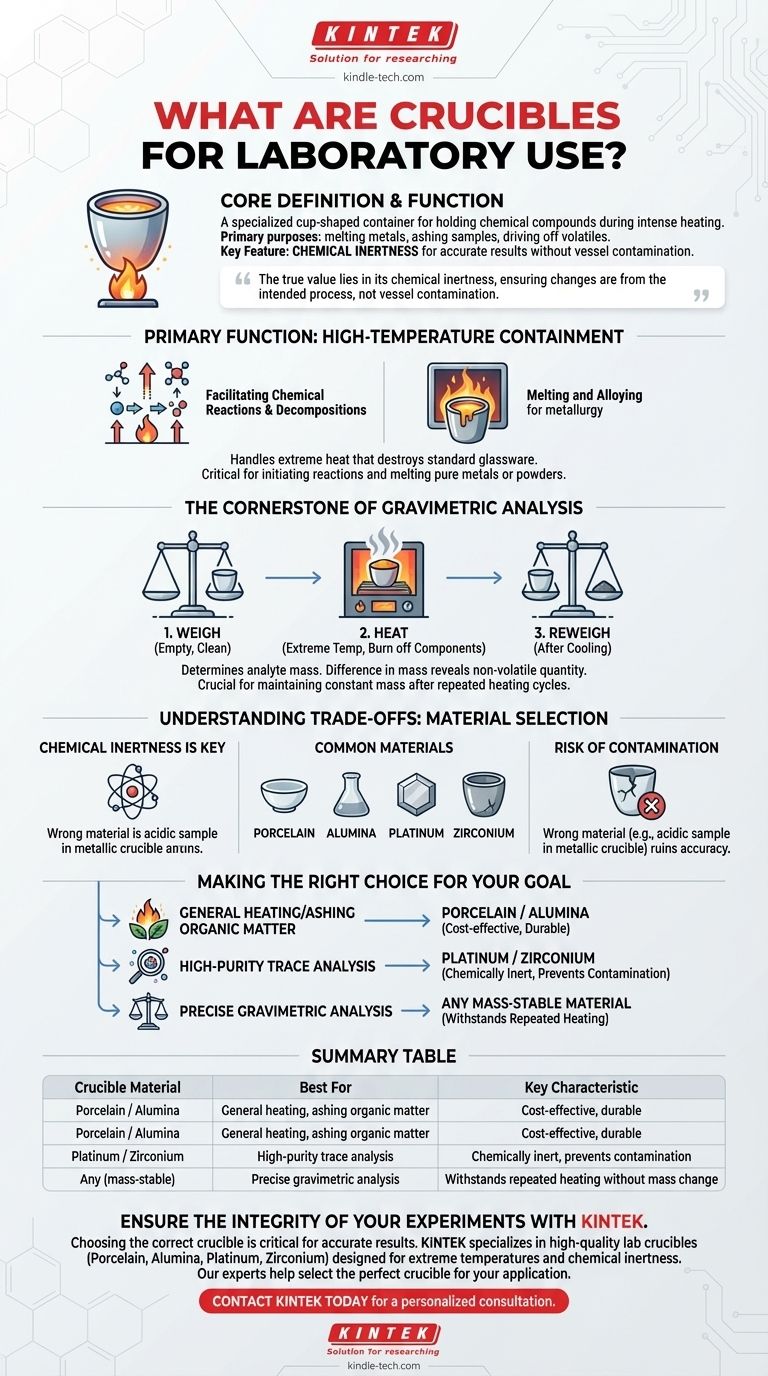
At its core, a laboratory crucible is a specialized, cup-shaped container engineered to hold chemical compounds during intense heating. Made from materials that can withstand extreme temperatures without breaking down or reacting, its primary purpose is to serve as a stable vessel for processes like melting metals, ashing samples, or driving off volatile substances.
The true value of a crucible lies not just in its heat resistance, but in its chemical inertness. Its purpose is to be an invisible container, ensuring that any changes measured in a sample are a result of the intended process, not contamination from the vessel itself.
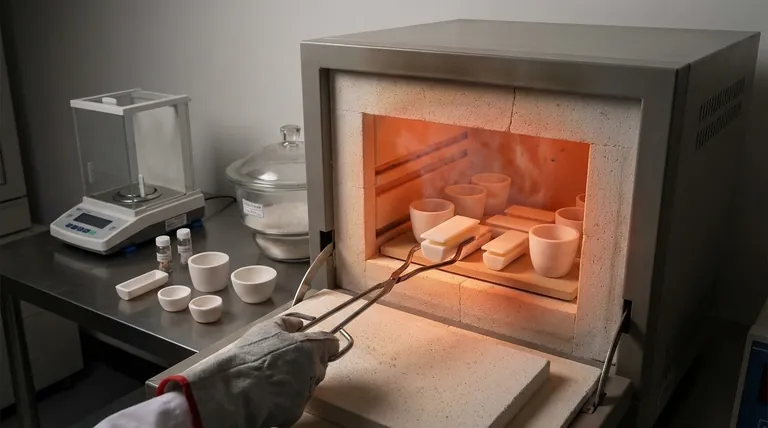

The Primary Function: High-Temperature Containment
Crucibles are fundamental tools in any process that requires heating a substance to a temperature that would destroy standard glassware. Their design is simple, but their role is critical.
Facilitating Chemical Reactions
Many chemical reactions and decompositions only occur at very high temperatures. A crucible provides the stable environment needed to initiate these processes safely and without introducing unwanted variables.
Melting and Alloying
In metallurgy and materials science, crucibles are essential for melting pure metals or mixing metallic powders to create alloys. Their ability to handle the extreme heat of molten metals is indispensable.
The Cornerstone of Gravimetric Analysis
One of the most precise and common uses for a crucible in analytical chemistry is for gravimetric analysis, a technique used to determine the mass of an analyte.
The Weigh-Heat-Reweigh Process
This method involves carefully weighing an empty, clean crucible. A sample is then added, and the crucible is heated to an extreme temperature to burn off or volatilize specific components.
After cooling, the crucible and its remaining residue are weighed again. The difference in mass reveals the quantity of the non-volatile substance.
Ensuring Analytical Accuracy
The success of gravimetric analysis hinges on the crucible's ability to maintain a constant mass, even after repeated cycles of intense heating and cooling. Any loss or gain of mass from the crucible itself would render the results invalid.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Material Selection is Critical
Not all crucibles are created equal. The material it is made from dictates its application and is the most important factor in preventing experimental failure.
The Need for Chemical Inertness
For high-purity analysis of trace elements, the crucible must be completely inert. This means it cannot react with, leach into, or absorb any part of the sample it holds.
Common Crucible Materials
Crucibles are typically made of porcelain, alumina, or an inert metal like platinum or zirconium. Porcelain is a cost-effective choice for general-purpose heating, while platinum is reserved for ultra-sensitive analyses where any risk of contamination must be eliminated.
The Risk of Contamination
Using the wrong crucible is a common pitfall. If the crucible material reacts with the chemical sample—for example, an acidic compound attacking a metallic crucible—it will contaminate the analyte and ruin the experiment's accuracy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate crucible is a foundational decision that directly impacts the integrity of your results.
- If your primary focus is general heating or ashing organic matter: A standard porcelain or alumina crucible provides a durable, cost-effective, and reliable solution.
- If your primary focus is high-purity trace analysis: An inert metal crucible, such as one made from platinum, is essential to prevent sample contamination and ensure accurate results.
- If your primary focus is precise gravimetric analysis: You need a crucible material that can withstand repeated, intense heating cycles without any degradation or change in its own mass.
Ultimately, choosing the correct crucible is a critical step in ensuring the integrity and accuracy of your high-temperature experimental work.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Best For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Porcelain / Alumina | General heating, ashing organic matter | Cost-effective, durable |
| Platinum / Zirconium | High-purity trace analysis | Chemically inert, prevents contamination |
| Any (mass-stable) | Precise gravimetric analysis | Withstands repeated heating without mass change |
Ensure the integrity of your high-temperature experiments with the right crucible from KINTEK.
Choosing the correct crucible is critical for accurate results in processes like gravimetric analysis, melting metals, or trace element testing. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab crucibles made from materials like porcelain, alumina, platinum, and zirconium, designed to withstand extreme temperatures without contaminating your samples.
Our experts can help you select the perfect crucible for your specific application, ensuring chemical inertness, durability, and precise performance. Protect your research integrity and achieve reliable outcomes every time.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation on our full range of laboratory crucibles and consumables.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
People Also Ask
- How does the use of corrosion-resistant ceramic crucibles ensure the chemical purity of materials? | KINTEK
- What are the advantages of selecting an alumina crucible for TGA? Ensure High-Precision Thermal Analysis Data
- What role do high-purity alumina crucibles play in high-temperature steam oxidation? Ensure Data Integrity up to 1350°C
- Why is a high-purity alumina crucible preferred for high-temperature oxidation? Ensure Unmatched Data Integrity
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for LATP? Preserve Purity and Conductivity in Sintering



















