The environmental impact of biomass is a story of contradictions. While often presented as a renewable alternative to fossil fuels, its use can lead to significant environmental harm, including severe air pollution, widespread deforestation, and long-term land degradation. These negative outcomes are not inherent to biomass itself but are a direct consequence of how the fuel is sourced and how it is burned.
The core issue is not the use of organic matter for energy, but the method. The most severe environmental damage from biomass stems from unsustainable harvesting practices combined with inefficient, uncontrolled combustion, particularly in traditional open-fire settings.

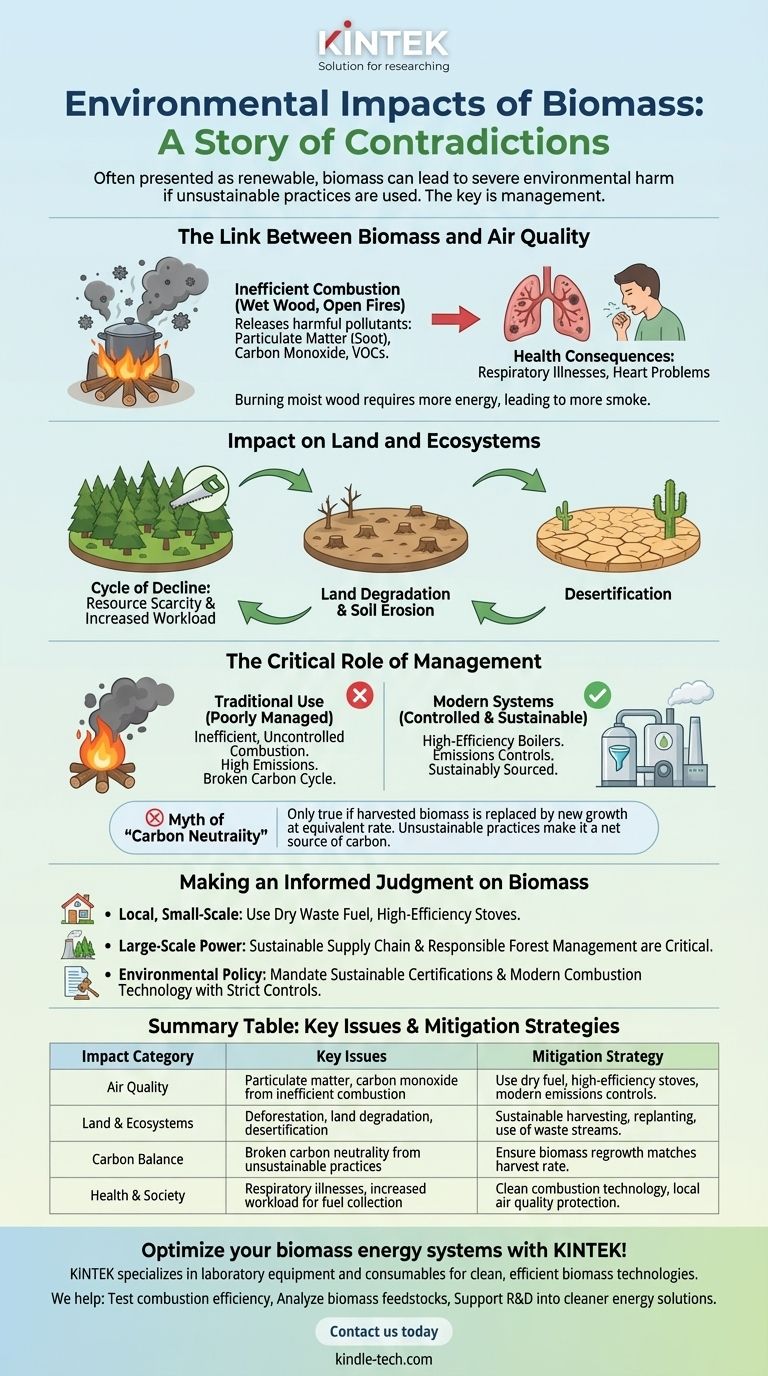
The Link Between Biomass and Air Quality
The most immediate and localized impact of biomass energy is on the air we breathe. The technology used for combustion is the single most important factor determining the severity of this impact.
Emissions from Inefficient Combustion
When organic matter like wood is burned in open fires or rudimentary stoves, the combustion is incomplete. This process releases a cocktail of harmful pollutants directly into the atmosphere, including particulate matter (soot), carbon monoxide, and other volatile organic compounds.
The Problem with Moisture
The reference to "moist wood" is critical. Burning damp fuel wood requires energy to first boil off the water, lowering the fire's temperature. This leads to even more incomplete combustion, producing significantly more smoke and harmful emissions for the amount of heat generated.
Health Consequences
This "unclean air" has direct and severe consequences for human health. The smoke emitted from inefficient biomass burning is a leading cause of respiratory illnesses, heart problems, and other health issues, especially for populations that rely on it for daily cooking and heating.
Impact on Land and Ecosystems
Beyond air quality, the way biomass is sourced can cause irreversible damage to landscapes and ecosystems, creating a cycle of environmental decline.
The Threat of Deforestation
When the demand for fuelwood outpaces the natural regrowth of forests, deforestation is the inevitable result. This happens when entire areas are cleared for fuel without a plan for replanting, disrupting the entire ecosystem.
Leading to Land Degradation
Deforestation is the first step toward broader land degradation. Without tree cover to hold soil in place, erosion by wind and water accelerates. Over time, this loss of topsoil can lead to desertification, turning once-fertile land into unproductive terrain.
The Cycle of Unsustainable Harvesting
These impacts create a vicious cycle. As nearby forests are depleted, people—often women and children—must travel farther and spend more time collecting fuel. This increased workload and resource scarcity further degrades the environment and diminishes quality of life.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Critical Role of Management
It is a mistake to view all biomass energy as equally harmful. The negative impacts described above are characteristic of poorly managed, traditional uses, not modern, controlled systems.
Traditional Use vs. Modern Systems
There is a vast difference between a family burning scavenged, damp wood in an open-air fire and an industrial facility burning sustainably sourced wood pellets in a high-efficiency boiler with emissions controls. Modern systems are designed to maximize heat output while minimizing harmful pollutants.
The Myth of "Carbon Neutrality"
Biomass is often called "carbon neutral" because the carbon released when it's burned was previously absorbed from the atmosphere by the plant. However, this is only true if the harvested biomass is replaced by new growth at an equivalent rate. Unsustainable harvesting breaks this cycle, turning a potentially neutral process into a net source of carbon emissions.
The Danger of Oversimplification
Labeling biomass as simply "good" or "bad" is misleading. Its environmental credential depends entirely on the sustainability of its entire lifecycle—from how the feedstock is grown and harvested to how efficiently and cleanly it is combusted.
Making an Informed Judgment on Biomass
To evaluate the impact of a biomass project, you must look beyond the fuel type and analyze the entire system.
- If your primary focus is local, small-scale energy: The key is to use dry fuel from waste streams (like sawdust or agricultural residue) and invest in high-efficiency, low-emission stoves to protect air quality and health.
- If your primary focus is large-scale power generation: The sustainability of the supply chain, including proof of responsible forest management and replanting efforts, is the single most critical factor.
- If your primary focus is environmental policy: Regulations must mandate both sustainable sourcing certifications and the use of modern combustion technology with strict emissions controls to prevent negative outcomes.
Ultimately, the sustainability of biomass energy is not a given; it is a direct result of deliberate and responsible choices.
Summary Table:
| Impact Category | Key Issues | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Air Quality | Particulate matter, carbon monoxide from inefficient combustion | Use dry fuel, high-efficiency stoves, modern emissions controls |
| Land & Ecosystems | Deforestation, land degradation, desertification | Sustainable harvesting, replanting, use of waste streams |
| Carbon Balance | Broken carbon neutrality from unsustainable practices | Ensure biomass regrowth matches harvest rate |
| Health & Society | Respiratory illnesses, increased workload for fuel collection | Clean combustion technology, local air quality protection |
Optimize your biomass energy systems with KINTEK!
Unsure how to balance your energy needs with environmental responsibility? KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables that support the research and development of clean, efficient biomass technologies. Whether you're developing high-efficiency combustion systems or analyzing sustainable feedstocks, our tools help you make data-driven decisions.
We help our laboratory customers:
- Test and improve combustion efficiency to reduce harmful emissions.
- Analyze biomass feedstocks for moisture content and sustainability.
- Support R&D into cleaner energy solutions.
Contact us today to discuss how our equipment can support your project's sustainability goals. Get in touch via our contact form and let's build a cleaner energy future together.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory High Throughput Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs






