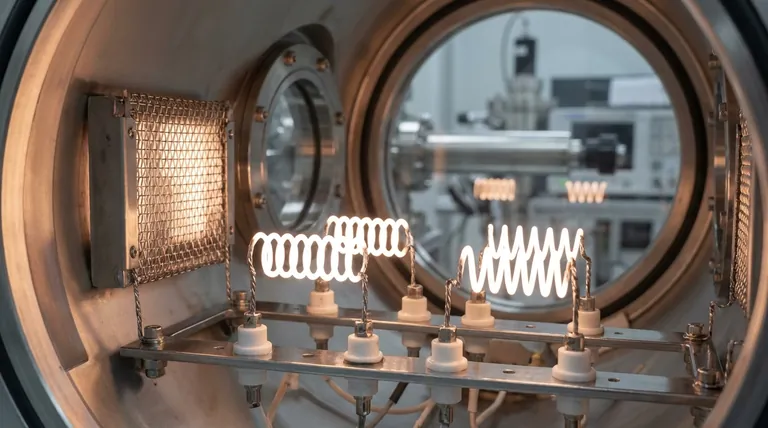
At their core, tungsten heating elements are specialized components made from tungsten wire or mesh, designed for applications requiring extremely high temperatures. They leverage tungsten's exceptionally high melting point to generate heat far beyond the capacity of common alloys, but this capability comes with strict operational requirements, primarily the need to operate in a vacuum or a protective atmosphere.
The central takeaway is that tungsten heaters offer unparalleled high-temperature performance, but they are not a universal solution. Their extreme vulnerability to oxidation in air and physical brittleness demand a carefully controlled environment, making them ideal for specialized industrial processes, not general-purpose heating.
The Core Principles of Tungsten Heaters
Tungsten is chosen for one primary reason: its ability to withstand immense heat. Understanding how this property is harnessed and the forms it takes is key to evaluating its suitability for your application.
Exceptionally High Temperature Capability
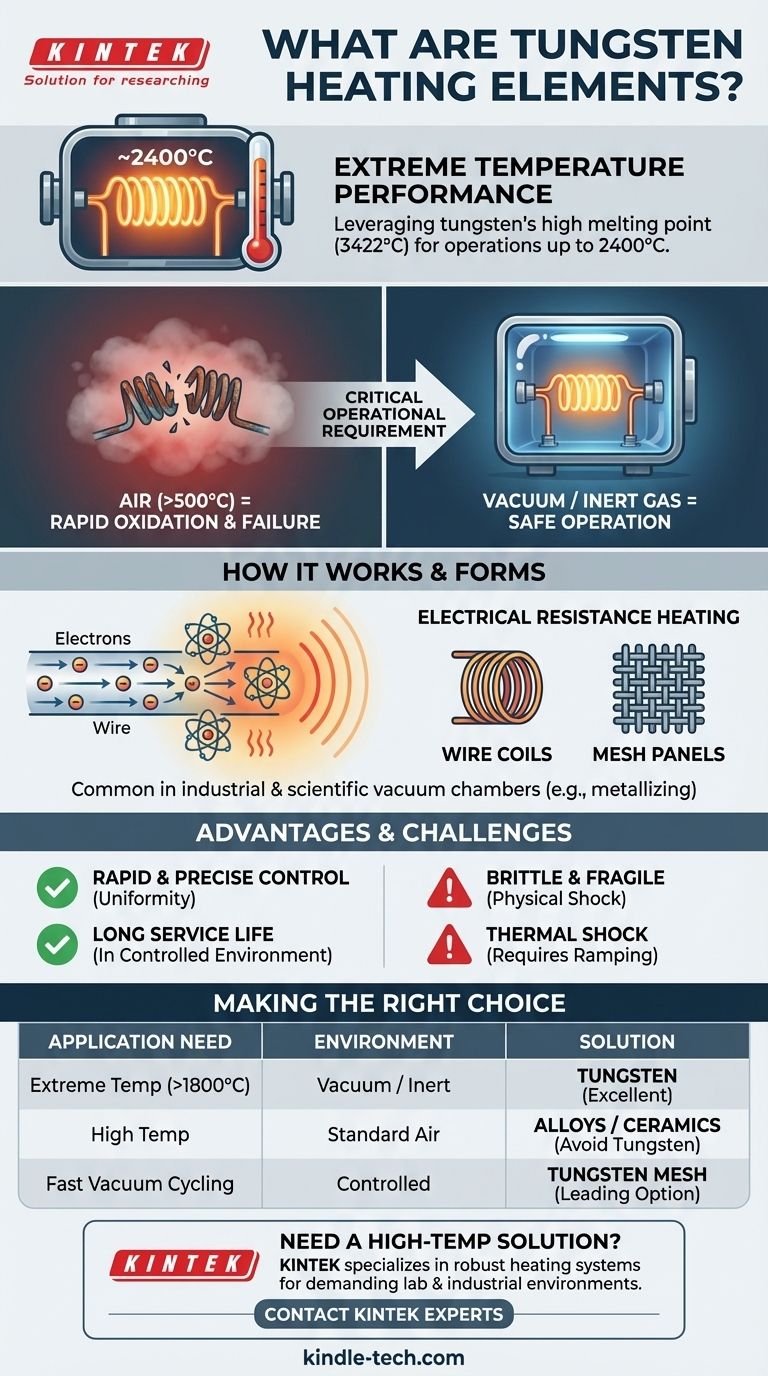
Tungsten possesses the highest melting point of any metal, at 3422°C (6192°F). This allows tungsten heating elements to achieve maximum operating temperatures around 2400°C (4352°F).
This thermal resilience makes tungsten the material of choice for processes that are simply too hot for other common heating elements like nichrome or Kanthal.
How They Generate Heat
The heating mechanism is based on electrical resistance. When an electric current is passed through the tungsten wire or mesh, the electrons collide with the tungsten atoms.
This transfer of kinetic energy from the electrons to the atoms causes them to vibrate rapidly, generating intense heat which is then radiated into the surrounding chamber.
Common Forms and Applications
Tungsten heaters are typically produced as wire coils or mesh panels. Their applications are almost exclusively industrial and scientific, occurring within vacuum chambers.
Common uses include vacuum metallizing processes like aluminizing for mirrors, chrome plating on plastics, and creating decorative coatings on various articles.
Critical Operating Constraints and Trade-offs
The primary challenge of using tungsten is not its heating ability, but managing its significant environmental and physical vulnerabilities. Ignoring these constraints will lead to rapid and catastrophic failure.
The Problem of Oxidation
This is tungsten's most significant weakness. When exposed to oxygen at high temperatures, it oxidizes very quickly, becomes brittle, and fails.
Tungsten heating elements must not be exposed to air above 500°C (932°F). This is why they are almost always used in a high-vacuum environment or under an inert gas like argon or nitrogen.
The Risk of Embrittlement
Tungsten is an inherently brittle material, especially at or near room temperature. It is highly susceptible to thermal shock.
To prevent fracture, a ramping temperature control system is required. This system slowly increases the temperature during cold start-ups, allowing the element to heat up uniformly and avoid the stresses that cause it to crack.
Susceptibility to Physical Shock
In addition to thermal shock, these elements are also vulnerable to mechanical shock and vibration. They are fragile components that must be handled with care during installation and maintenance to prevent damage.
Advantages of Modern Tungsten Heaters
When operated within their required parameters, tungsten elements offer distinct advantages that are critical for high-tech manufacturing and research.
Rapid and Precise Temperature Control
Modern designs, particularly tungsten mesh heaters, allow for very fast heating rates and highly uniform temperature distribution across the heating zone.
This precise control is essential for sensitive deposition processes where temperature consistency directly impacts the quality of the final product.
Long Service Life (Under Proper Conditions)
If protected from oxygen and thermal shock, tungsten elements can have a very long and reliable service life.
The key is strict adherence to operating procedures. A well-maintained vacuum system and a proper temperature controller are not optional accessories; they are essential for the element's survival.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a heating element requires matching its capabilities and limitations to your specific process goals.
- If your primary focus is achieving extreme temperatures (above 1800°C) in a controlled environment: Tungsten is an excellent, and often necessary, choice, but you must invest in the required vacuum or inert gas infrastructure.
- If your primary focus is heating in a standard air environment: Tungsten is completely unsuitable for high temperatures; you should consider robust alloys like Kanthal (FeCrAl) or ceramic materials like Silicon Carbide.
- If your primary focus is fast, precise thermal cycling for vacuum processes: Tungsten mesh heaters are a leading option, provided you can accommodate their need for careful handling and slow temperature ramping from a cold start.
By understanding this fundamental trade-off, you can determine if tungsten's high-temperature performance justifies its stringent operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Max Operating Temperature | ~2400°C (4352°F) |
| Key Advantage | Unparalleled high-temperature performance |
| Critical Constraint | Must operate in a vacuum or inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation |
| Common Forms | Wire coils, mesh panels |
| Ideal For | Vacuum metallizing, high-temperature R&D, and specialized industrial heating |
Need a reliable high-temperature heating solution for your lab or industrial process?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including robust heating systems designed for demanding environments. Our expertise ensures you get the right solution that balances extreme temperature capabilities with operational safety and longevity.
Let's discuss how we can support your specific application requirements. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why tungsten is not used as heating element? Discover the critical role of oxidation resistance.
- What are the disadvantages of tungsten filament? Key Limitations in Lighting Technology
- Why tungsten is not used in heating devices? The Critical Role of Oxidation Resistance
- Can tungsten be used as a heating element? Unlocking Extreme Heat for High-Temperature Applications
- What happens when tungsten is heated? Harnessing Extreme Heat for Demanding Applications
















