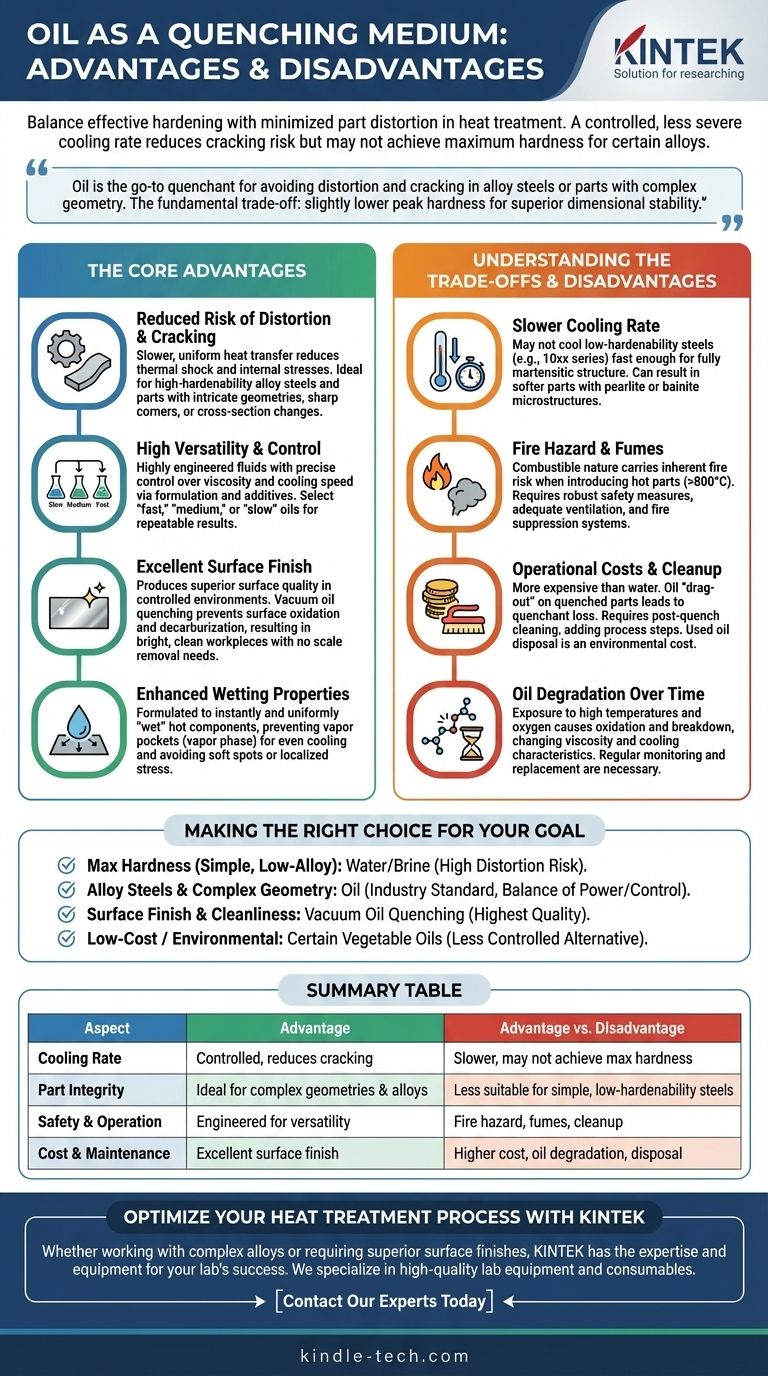
In the world of heat treatment, oil quenching offers a critical balance between effective hardening and minimizing part distortion. Its primary advantage is a controlled, less severe cooling rate compared to water, which dramatically reduces the risk of cracking. However, this same characteristic means it may not achieve the absolute maximum hardness possible for certain steel alloys that require a more drastic quench.
Oil is the go-to quenchant when your priority is avoiding distortion and cracking in alloy steels or parts with complex geometry. The fundamental trade-off is accepting a slightly lower peak hardness in exchange for superior dimensional stability and part integrity.

The Core Advantages of Oil Quenching
The popularity of oil as a quenchant stems from its ability to solve the most common and costly problems associated with heat treatment: part failure and dimensional inaccuracy.
Reduced Risk of Distortion and Cracking
Oil transfers heat from a hot part more slowly and uniformly than water. This less severe cooling rate reduces the immense thermal shock and internal stresses that cause parts to warp, distort, or crack.
This makes oil the ideal choice for high-hardenability alloy steels or parts with intricate geometries, sharp corners, or significant changes in cross-section.
High Versatility and Control
Unlike water, quenching oils are highly engineered fluids. Their properties, such as viscosity and cooling speed, can be precisely controlled through formulation and the use of specialized additives.
This allows you to select a "fast," "medium," or "slow" oil to perfectly match the requirements of a specific steel alloy and part configuration, ensuring repeatable and reliable results.
Excellent Surface Finish
When performed in a controlled environment, oil quenching produces superior surface quality. Vacuum oil quenching, in particular, is a premium process that prevents surface oxidation and decarburization.
The result is a bright, clean workpiece that requires no subsequent scale removal or cleaning, saving time and downstream processing costs.
Enhanced Wetting Properties
Modern quenching oils are formulated to "wet" the entire surface of a hot component instantly and uniformly. This prevents the formation of stable vapor pockets (the "vapor phase") that can cause uneven cooling and lead to soft spots or localized stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Disadvantages
While highly effective, oil quenching is not without its limitations. These trade-offs are primarily related to safety, cost, and its inherent cooling speed.
Slower Cooling Rate
The very feature that prevents cracking—a slower cooling rate—is also a limitation. For some low-hardenability steels (like 10xx series carbon steels), oil may not cool the part fast enough to achieve a fully martensitic structure.
This can result in a part that is softer than desired, as the steel transforms into other microstructures like pearlite or bainite instead of hard martensite.
Fire Hazard and Fumes
Oil is combustible. Plunging a component heated to over 800°C (1500°F) into oil carries an inherent fire risk if the process is not properly controlled.
This necessitates robust safety measures, including adequate ventilation to manage fumes and smoke, and appropriate fire suppression systems.
Operational Costs and Cleanup
Specialized quenching oils are more expensive than water. Furthermore, oil tends to cling to quenched parts, a phenomenon known as "drag-out," which leads to quenchant loss.
These oily parts require a post-quench cleaning or washing step, adding another process and associated costs. Finally, used oil is considered industrial waste and must be disposed of according to environmental regulations.
Oil Degradation Over Time
Over its service life, quenching oil is exposed to high temperatures and oxygen, causing it to oxidize and degrade. This breakdown changes the oil's viscosity and alters its cooling characteristics, leading to inconsistent results.
Regular monitoring of the oil's condition and eventual replacement are necessary maintenance tasks to ensure process stability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between oil and other quenchants depends entirely on your material, part geometry, and desired final properties.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum hardness in simple, low-alloy steels: Water or brine is often a better choice, provided you can accept the significantly higher risk of distortion or cracking.
- If your primary focus is hardening alloy steels or parts with complex geometry: Oil is the industry standard, offering an excellent and reliable balance of hardening power and dimensional control.
- If your primary focus is surface finish and process cleanliness for critical components: Vacuum oil quenching provides the highest quality results, eliminating post-quench surface defects and cleaning operations.
- If your primary focus is low-cost or environmentally conscious hardening for less critical tasks: Certain vegetable oils can be a viable, though less controlled, alternative to petroleum-based products.
Understanding these trade-offs empowers you to select a quenching process that delivers the required material properties without compromising the integrity of your part.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Rate | Controlled, reduces cracking & distortion | Slower, may not achieve max hardness for some steels |
| Part Integrity | Ideal for complex geometries & alloy steels | Less suitable for simple, low-hardenability steels |
| Safety & Operation | Engineered for versatility & control | Fire hazard, fumes, and requires cleanup |
| Cost & Maintenance | Excellent surface finish (e.g., vacuum quenching) | Higher cost, oil degradation, and disposal needs |
Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right quenching medium is critical for achieving the perfect balance of hardness, dimensional stability, and part integrity. Whether you're working with complex alloy steel components or require the superior surface finish of vacuum oil quenching, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your lab's success.
We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific heat treatment needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your quenching process, improve repeatability, and ensure the highest quality results for your materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Square Bidirectional Pressure Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum heat treatment work? Achieve Superior Material Properties in a Pristine Environment
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- Can I vacuum the inside of my furnace? A Guide to Safe DIY Cleaning vs. Professional Service
- What is vacuum furnace high temperature? Unlock the Range for Your Material Processing
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance





