The primary advantages of a vacuum furnace stem from its ability to create a highly controlled, contamination-free environment. By removing the atmosphere and its reactive gases, these furnaces prevent oxidation and ensure exceptional purity, leading to superior material properties. This precise environmental control, combined with uniform temperature management and automated processes, delivers consistent, high-quality results for a wide range of heat treatment applications.
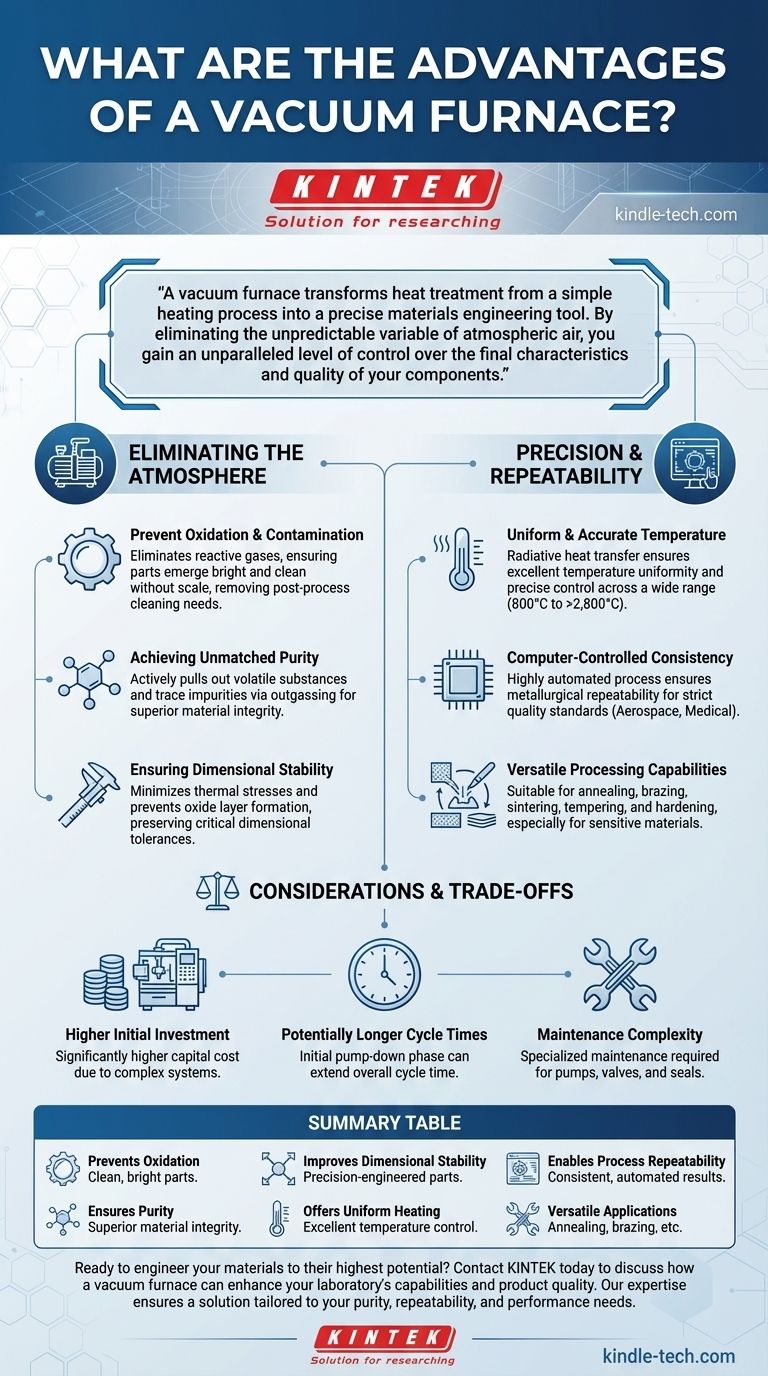
A vacuum furnace transforms heat treatment from a simple heating process into a precise materials engineering tool. By eliminating the unpredictable variable of atmospheric air, you gain an unparalleled level of control over the final characteristics and quality of your components.

The Foundation of Control: Eliminating the Atmosphere
The defining feature of a vacuum furnace is the removal of air before and during the heating cycle. This fundamental step is the source of its most significant advantages.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
In a conventional furnace, the oxygen and other gases in the air react with the hot surface of a part, creating scale and discoloration. A vacuum furnace eliminates these reactive gases, ensuring parts emerge from the heat treatment cycle bright and clean. This removes the need for post-process cleaning and preserves the integrity of the component's surface.
Achieving Unmatched Purity
The vacuum environment is not just about preventing new contaminants; it is also about removing existing ones. The vacuum pumping system actively pulls volatile substances and trace impurities out of the material itself, a process known as outgassing. This results in a final product with higher purity and improved structural integrity.
Ensuring Dimensional Stability
Uniform heating in a controlled, gas-free environment minimizes the thermal stresses that cause parts to warp or distort. By preventing the formation of an oxide layer, the component's surface remains unchanged, preserving critical dimensional tolerances which is essential for precision-engineered parts.
Precision and Repeatability in Heat Treatment
With the environment under control, the focus shifts to the thermal process itself. Vacuum furnaces offer exceptional accuracy and consistency.
Uniform and Accurate Temperature
Heat transfer in a vacuum occurs primarily through radiation, which promotes excellent temperature uniformity across the entire workload. Advanced control systems allow for precise management of temperature, often within a few degrees, over a very wide operating range (from 800°C to over 2,800°C).
Computer-Controlled Consistency
Modern vacuum furnaces are highly automated. The entire heat treatment cycle—from pumping down the vacuum to heating, soaking, and quenching—can be programmed and executed by a computer. This ensures metallurgical repeatability from one batch to the next, a critical requirement for industries with strict quality standards like aerospace and medical.
Versatile Processing Capabilities
The controlled environment of a vacuum furnace makes it suitable for a wide array of thermal processes. It is a highly versatile tool capable of performing annealing, brazing, sintering, tempering, and hardening, often for materials that would be compromised in a traditional atmosphere furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not the universal solution for all heat treatment needs. Their advantages come with specific considerations.
Higher Initial Investment
Vacuum furnaces, with their complex chambers, seals, and high-performance pumping systems, represent a significantly higher capital cost compared to conventional atmosphere furnaces.
Potentially Longer Cycle Times
The process of achieving a deep vacuum (pumping down) takes time. While the rapid cooling (quenching) phase can be very fast, the initial pump-down phase can make the overall cycle time longer than some simpler atmosphere-based processes.
Maintenance Complexity
The systems required to create and maintain a vacuum—including pumps, valves, and seals—demand specialized and diligent maintenance to ensure leak-free performance and operational reliability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a vacuum furnace depends entirely on the required quality, material, and complexity of your final product.
- If your primary focus is high-purity components (medical, aerospace): The contamination-free environment is non-negotiable for achieving the required material integrity and performance.
- If your primary focus is brazing complex assemblies: The clean, flux-free process of vacuum brazing ensures strong, void-free joints without post-braze cleaning.
- If your primary focus is hardening high-performance tool steels: The precise control over heating and rapid gas quenching delivers superior mechanical properties and minimal distortion.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-complexity parts: The cost, cycle time, and maintenance overhead may make a conventional atmosphere furnace a more practical and economical choice.
Ultimately, a vacuum furnace provides an exceptional level of process control, enabling you to engineer materials to their highest potential.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Prevents Oxidation | Eliminates scale and discoloration for clean, bright parts. |
| Ensures Purity | Removes contaminants via outgassing for superior material integrity. |
| Improves Dimensional Stability | Minimizes warping and distortion for precision-engineered parts. |
| Offers Uniform Heating | Provides excellent temperature control across the entire workload. |
| Enables Process Repeatability | Delivers consistent, automated results batch after batch. |
| Versatile Applications | Suitable for annealing, brazing, sintering, tempering, and hardening. |
Ready to engineer your materials to their highest potential?
A vacuum furnace from KINTEK transforms your heat treatment process, delivering the contamination-free environment and precise control required for superior results in aerospace, medical, and tool steel applications. Our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get a solution tailored to your specific needs for purity, repeatability, and performance.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how a vacuum furnace can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of vacuum hardening? Achieve Superior Precision and Cleanliness for Critical Components
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- Why do you vacuum for heat treatment? Achieve Flawless, High-Performance Metal Components
- What is vacuum furnace high temperature? Unlock the Range for Your Material Processing
- What does a vacuum furnace do? Achieve High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Components



















