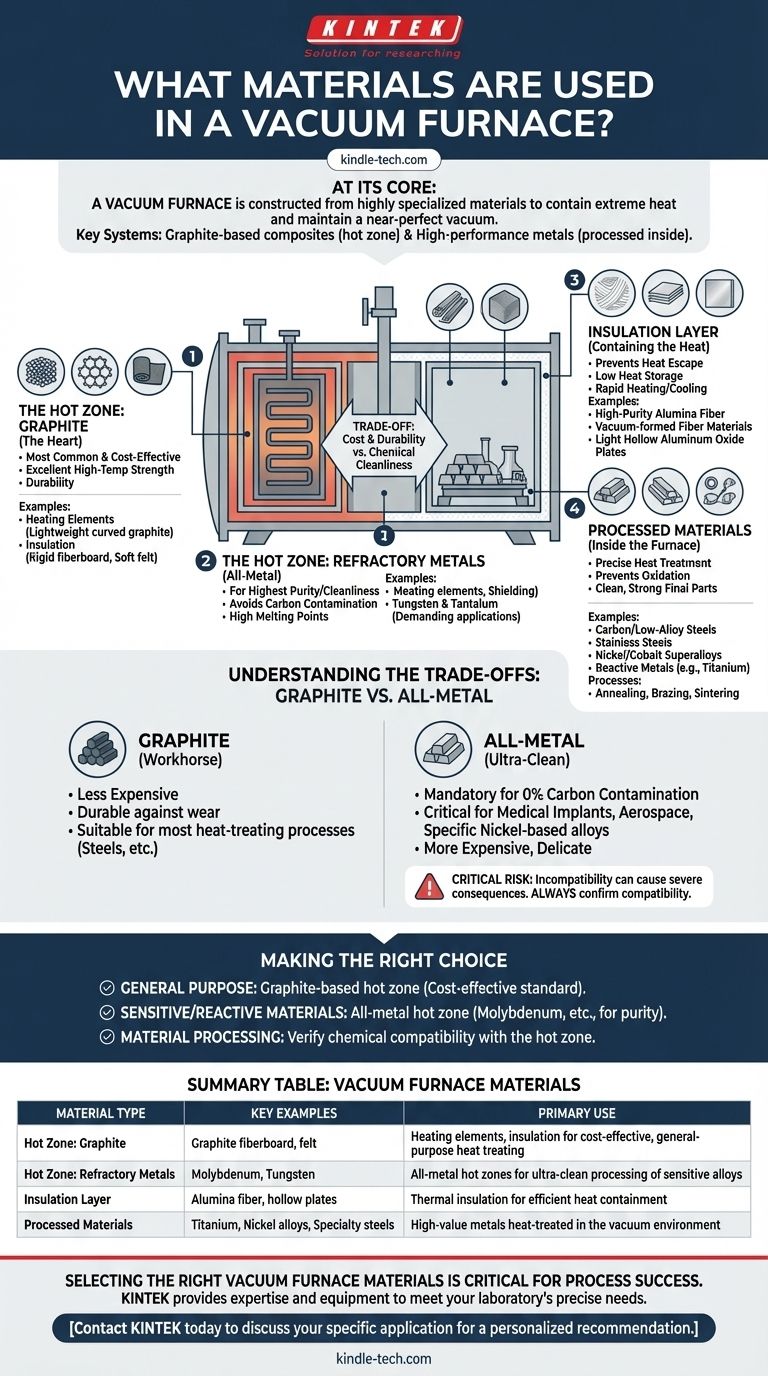
At its core, a vacuum furnace is constructed from highly specialized materials designed to contain extreme heat while maintaining a near-perfect vacuum. The two most critical material systems are graphite-based composites for the furnace's internal "hot zone" and a range of high-performance metals like titanium, nickel alloys, and specialty steels that are processed within the furnace itself.
The choice of materials for a vacuum furnace's construction is a direct trade-off between cost, durability, and the required level of chemical cleanliness for the process. This decision dictates which materials can be safely and effectively heat-treated inside.

The Anatomy of a Vacuum Furnace: Key Material Zones
To understand the materials used, we must first look at the distinct functional zones of the furnace, each with its own unique material requirements.
The Hot Zone: The Heart of the Furnace
The hot zone is the insulated internal chamber that contains the heating elements and the workload. Its materials must withstand incredibly high temperatures without degrading or contaminating the parts being treated.
There are two primary material systems for hot zones: graphite and refractory metals.
Hot Zone Material 1: Graphite
Graphite is the most common material for hot zones due to its excellent high-temperature strength, durability, and relatively low cost.
Heating elements are often made from lightweight curved graphite, while the insulation consists of rigid graphite fiberboard or soft felt. This makes for a robust, all-graphite internal system.
Hot Zone Material 2: Refractory Metals
For applications demanding the highest purity and cleanliness, an "all-metal" hot zone is used. These are constructed from refractory metals, which have extremely high melting points.
Molybdenum is a common choice for both the heating elements (as strips) and the radiation shielding. Tungsten and tantalum are also used for even more demanding applications. This approach avoids the potential for carbon contamination that can occur in graphite furnaces.
The Insulation Layer: Containing the Heat
Outside the immediate hot zone, a furnace lining provides thermal insulation. This layer must prevent heat from escaping to the outer vacuum chamber.
These linings are often made of high-purity alumina fiber, vacuum-formed fiber materials, or light hollow aluminum oxide plates. These materials offer low heat storage, allowing for rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking or degrading.
Materials Processed Within the Furnace
Vacuum furnaces are not defined just by what they are made of, but by what they can process. The vacuum environment is critical because it prevents oxidation and other chemical reactions at elevated temperatures.
High-Performance Metals and Alloys
The controlled atmosphere allows for the precise heat treatment of a wide range of sensitive and high-value materials.
Commonly processed materials include carbon and low-alloy steels, stainless steels, nickel and cobalt superalloys, and reactive metals like titanium and its alloys.
Why the Process Dictates the Material
Processes like annealing, brazing, and sintering rely on the vacuum to ensure clean, strong, and uncontaminated final parts. The absence of oxygen is what makes these high-quality results possible.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Graphite vs. All-Metal
Choosing between a graphite or an all-metal hot zone is the most significant material decision in vacuum furnace design and operation.
The Case for Graphite
Graphite is the workhorse of the industry. It is less expensive, highly durable against mechanical wear, and suitable for the vast majority of heat-treating processes for steels and many other alloys.
The Case for Refractory Metals (All-Metal)
An all-metal hot zone is mandatory when even trace amounts of carbon are unacceptable. This is crucial for processing certain medical implants, aerospace components, and specific nickel-based alloys that can react with carbon.
While more expensive and delicate, the ultra-clean environment an all-metal furnace provides is essential for these niche but critical applications.
The Critical Risk of Incompatibility
Placing the wrong material inside a furnace can have severe consequences. Certain materials can react with graphite at high temperatures, while others may alloy with and destroy molybdenum heating elements. Always confirming material compatibility with the furnace manufacturer is a non-negotiable safety and operational step.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the specific goal of your heat-treating process.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, general-purpose heat treating: A furnace with a graphite-based hot zone is the standard and most economical choice.
- If your primary focus is processing highly sensitive or reactive materials (like titanium or medical-grade alloys): An all-metal hot zone using refractory metals like molybdenum is necessary to prevent carbon contamination and ensure process purity.
- If you are selecting a material to be processed: You must verify its chemical compatibility with the furnace's specific hot zone materials to prevent damage and ensure a successful outcome.
Understanding the interplay between these materials is the key to mastering the vacuum heat-treatment process.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Examples | Primary Use in Vacuum Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Hot Zone: Graphite | Graphite fiberboard, felt | Heating elements, insulation for cost-effective, general-purpose heat treating |
| Hot Zone: Refractory Metals | Molybdenum, Tungsten | All-metal hot zones for ultra-clean processing of sensitive alloys |
| Insulation Layer | Alumina fiber, hollow aluminum oxide plates | Thermal insulation for efficient heat containment |
| Processed Materials | Titanium, Nickel alloys, Specialty steels | High-value metals heat-treated in the vacuum environment |
Selecting the right vacuum furnace materials is critical to your process success. Whether you need a cost-effective graphite hot zone for general heat treating or an ultra-clean all-metal system for sensitive aerospace or medical alloys, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory's precise needs. Our specialists can help you navigate the trade-offs to ensure optimal performance and material compatibility.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and receive a personalized recommendation for your vacuum furnace requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum furnace high temperature? Unlock the Range for Your Material Processing
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- Why is environmental control within a vacuum furnace important for diffusion bonding? Master Titanium Alloy Laminates
- What are the advantages of vacuum hardening? Achieve Superior Precision and Cleanliness for Critical Components
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries



















