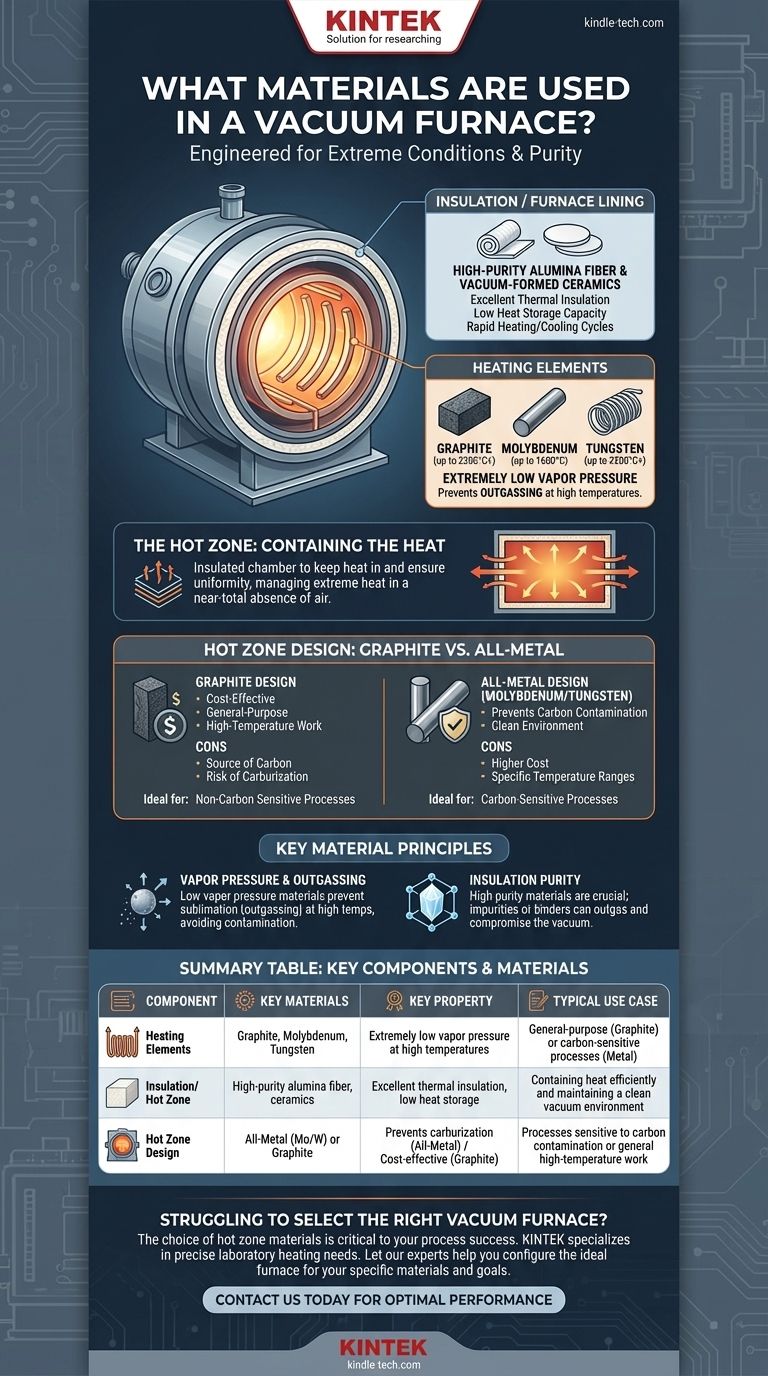
The primary materials used in a vacuum furnace are specifically chosen for their ability to withstand extreme conditions. The core components, known as the "hot zone," typically feature heating elements made of graphite, molybdenum, or tungsten. The furnace lining and insulation are constructed from materials like high-purity alumina fiber and other vacuum-formed ceramics to contain the intense heat efficiently.
The central challenge in vacuum furnace design is managing extreme heat in a near-total absence of air. Therefore, every material selected must not only survive high temperatures but also possess extremely low vapor pressure to prevent it from "outgassing" and contaminating the materials being processed.

The Anatomy of a Vacuum Furnace: Key Components and Materials
A vacuum furnace is a system of specialized parts, each requiring materials suited to its unique function. The most critical area is the hot zone, where the heating and processing occur.
The Hot Zone: Containing the Heat
The hot zone is the insulated chamber that contains the heating elements and the workload. Its primary job is to keep heat in and ensure temperature uniformity.
The insulation, or furnace lining, is made from advanced ceramics. Materials like high-purity alumina fiber, vacuum-formed fiber materials, and light hollow aluminum oxide plates are common.
These materials are chosen for their excellent thermal insulation performance and low heat storage capacity. This allows for rapid heating and cooling cycles without the risk of cracking or degrading.
Heating Elements: The Engine of the Furnace
The heating elements are responsible for generating the furnace's high temperatures. In a vacuum, combustion is not possible, so heating is done electrically.
The three most common materials for heating elements are graphite, molybdenum, and tungsten. Each has a distinct operating temperature range and specific characteristics.
The single most important property for these materials is their low vapor pressure. Even at extreme temperatures (up to 2200°C), they release very few particles, which is essential for maintaining a clean vacuum environment.
From Past to Present: All-Metal vs. Graphite Designs
Many early vacuum furnaces utilized an all-metal hot zone design, often featuring molybdenum or tungsten for both the heating elements and the radiation shields that serve as insulation.
Today, many furnaces use graphite-based components, including lightweight curved graphite heating elements and graphite fiber insulation. This design is often more cost-effective and suitable for a wide range of applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Material Selection
The choice between different materials is not arbitrary; it is a calculated decision based on the specific process requirements, including temperature, the material being processed, and budget.
Preventing Contamination: The Role of Vapor Pressure
In the near-perfect vacuum of a furnace, materials behave differently. Any substance with a high vapor pressure will begin to sublimate, or turn from a solid directly into a gas, a process known as outgassing.
This gas can contaminate the surface of the parts being heat-treated, potentially ruining the final product. Graphite, molybdenum, and tungsten are prized because they resist this effect even at thousands of degrees.
Graphite vs. Molybdenum: A Critical Choice
The choice between a graphite or an all-metal (molybdenum/tungsten) hot zone is a fundamental one.
A graphite hot zone is excellent for general-purpose, high-temperature work. However, it can be a source of carbon. If the material being processed is sensitive to carbon contamination (a phenomenon called carburization), then graphite is unsuitable.
An all-metal hot zone using molybdenum or tungsten elements is the solution for processes where carbon contamination must be avoided. Molybdenum is typically used up to 1600°C, while tungsten is reserved for even higher temperatures.
The Importance of Insulation Purity
The term "high-purity" for insulation materials like alumina fiber is critical. Any impurities or binding agents within the insulation could also outgas at high temperatures.
This would compromise the vacuum level and contaminate the workload. Therefore, only specialized, high-purity materials are used to line the furnace.
Matching Materials to Your Application
Choosing the correct furnace configuration depends entirely on your process goals.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures (above 2000°C): Tungsten or high-grade graphite heating elements are the only viable options.
- If your primary focus is preventing carbon contamination: An all-metal hot zone with molybdenum or tungsten heating elements is the standard and necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, cost-effective processing: A furnace with graphite heating elements and insulation provides excellent performance for a wide array of applications.
Understanding these core material principles allows you to select or operate a vacuum furnace that precisely meets the demands of your specific process.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Materials | Key Property | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heating Elements | Graphite, Molybdenum, Tungsten | Extremely low vapor pressure at high temperatures | General-purpose (Graphite) or carbon-sensitive processes (Metal) |
| Insulation / Hot Zone | High-purity alumina fiber, ceramics | Excellent thermal insulation, low heat storage | Containing heat efficiently and maintaining a clean vacuum environment |
| Hot Zone Design | All-Metal (Molybdenum/Tungsten) or Graphite | Prevents carburization (All-Metal) / Cost-effective (Graphite) | Processes sensitive to carbon contamination or general high-temperature work |
Struggling to select the right vacuum furnace for your application? The choice of hot zone materials—graphite vs. all-metal—is critical to your process success, whether you need to prevent carbon contamination or achieve extreme temperatures. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving precise laboratory heating needs. Our experts can help you configure the ideal furnace for your specific materials and goals. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and ensure optimal performance for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the annealing temperature of molybdenum? Optimize Your Thermal Processing for Pure Mo & Alloys
- What are the 3 phases of quenching process? Master the Cooling Stages for Perfect Hardness
- How do vacuum furnaces and flexible diaphragm systems ensure the quality of diffusion bonding? Expert Guide
- What is thin film deposition thermal evaporation? A Simple Guide to High-Vacuum Coating
- How does the use of a vacuum drying oven affect the performance of LiMn2O4 (LMO) cathodes? Unlock Battery Stability
- What is the purpose of the calcination process? A Guide to Purifying and Transforming Materials
- How does a programmable high-temperature furnace ensure accuracy for TBC experiments? Precision Thermal Cycling
- What is the function of a vacuum drying oven in catalyst recovery? Maximize Cycle Life and Maintain Active Sites



















