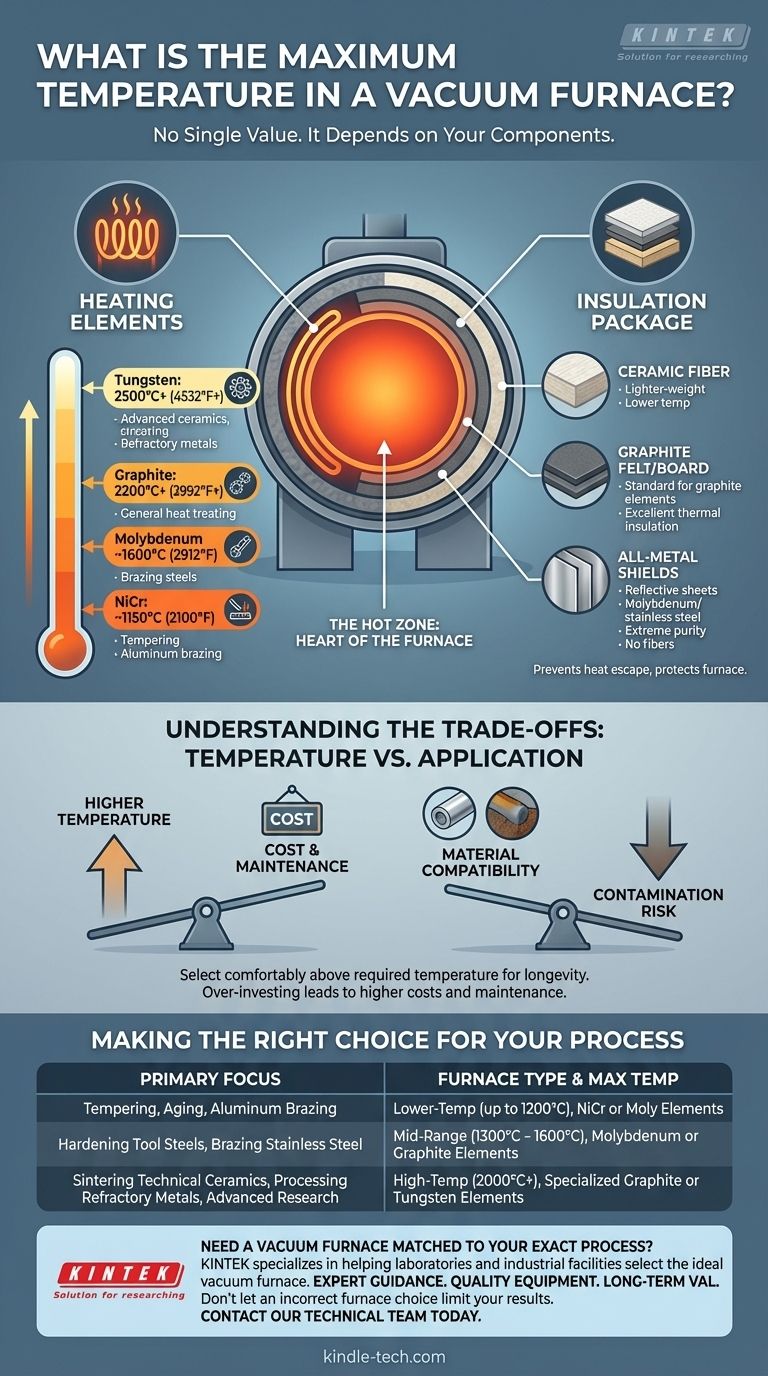
The maximum temperature of a vacuum furnace is not a single value but depends entirely on its construction, particularly the materials used for its heating elements and insulation. While some common furnaces operate up to 1600°C (2912°F), specialized models can safely reach temperatures well over 2200°C (3992°F).
The ultimate temperature limit of a vacuum furnace is defined by the physical melting point and operational stability of its internal components. Understanding these materials is the key to matching a furnace's capability to a specific industrial or research process.

What Determines a Vacuum Furnace's Maximum Temperature?
The "hot zone" is the heart of the furnace. The materials chosen for its two primary components—heating elements and insulation—dictate the system's performance ceiling.
The Role of Heating Elements
Heating elements are the components that generate the heat. The material they are made from is the single most important factor in determining the furnace's maximum temperature.
- Nickel-Chromium (NiCr): Used in lower-temperature applications, typically maxing out around 1150°C (2100°F).
- Molybdenum (Moly): A common choice for mid-range furnaces. Molybdenum elements can operate consistently up to about 1600°C and are often used for brazing and heat-treating steels.
- Graphite: A very popular and cost-effective material that can reach temperatures of 2200°C (3992°F) or even higher. It offers excellent thermal uniformity.
- Tungsten: Used for the most demanding high-temperature applications. Tungsten elements can operate in excess of 2500°C (4532°F), making them suitable for sintering advanced ceramics and processing refractory metals.
The Importance of Insulation
The insulation package prevents heat from escaping the hot zone and damaging the rest of the furnace. It must be able to withstand the temperatures generated by the elements.
- Ceramic Fiber: Lighter-weight insulation used in lower-temperature furnaces.
- Graphite Felt/Board: The standard insulation used in furnaces with graphite heating elements. It is lightweight and provides excellent thermal insulation at very high temperatures.
- All-Metal Shields: These are layers of reflective metal sheets (typically molybdenum and stainless steel) that contain the heat. They are used in applications requiring extreme purity and a very clean vacuum, as they do not shed fibers like other insulation types.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Temperature vs. Application
Selecting a furnace isn't just about choosing the highest possible temperature. Higher performance comes with significant trade-offs in cost, maintenance, and process compatibility.
Higher Temperature vs. Cost
There is a direct and steep correlation between a furnace's maximum temperature and its price. A furnace with tungsten elements and advanced insulation capable of 2500°C can be many times more expensive than a 1300°C moly-element furnace.
Material Compatibility and Contamination
The choice of hot zone material can impact your parts. Graphite elements, for instance, can cause carburization (the absorption of carbon) in certain metals at high temperatures, which is undesirable for some alloys.
In such cases, an all-metal hot zone using molybdenum or tungsten is necessary, even if it is more expensive. This provides a cleaner environment.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Operating any furnace consistently at its absolute maximum rated temperature will drastically shorten the life of its heating elements and insulation.
Prudent operational practice involves selecting a furnace with a maximum temperature that is comfortably above your required process temperature. This ensures component longevity and reduces long-term maintenance costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific application dictates the furnace you need. The key is to match the furnace's capability to your process requirements without over-investing in unnecessary temperature range.
- If your primary focus is tempering, aging, or brazing aluminum: A lower-temperature furnace (up to 1200°C) with NiCr or moly elements is sufficient and highly economical.
- If your primary focus is hardening tool steels, brazing stainless steel, or general heat treating: A mid-range furnace (1300°C - 1600°C) with molybdenum or graphite elements is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is sintering technical ceramics, processing refractory metals, or advanced research: You require a high-temperature furnace (2000°C+) with specialized graphite or tungsten components.
By understanding what defines a furnace's limits, you can make an informed decision that aligns technology with your true operational need.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element Material | Typical Max Temperature | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel-Chromium (NiCr) | ~1150°C (2100°F) | Tempering, aging, aluminum brazing |
| Molybdenum (Moly) | ~1600°C (2912°F) | Hardening tool steels, brazing stainless steel |
| Graphite | 2200°C+ (3992°F+) | General heat treating, sintering ceramics |
| Tungsten | 2500°C+ (4532°F+) | Processing refractory metals, advanced research |
Need a Vacuum Furnace Matched to Your Exact Process?
Choosing the right furnace is critical for performance, cost-efficiency, and material compatibility. The experts at KINTEK specialize in helping laboratories and industrial facilities select the ideal vacuum furnace.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: We'll analyze your specific application—whether it's brazing, sintering, or heat treating—to recommend a furnace with the correct temperature range and hot zone materials.
- Quality Equipment: KINTEK supplies reliable lab equipment, including vacuum furnaces with various heating elements (Graphite, Molybdenum, Tungsten) to prevent issues like carburization and ensure process purity.
- Long-Term Value: We help you avoid over-investing in unnecessary capabilities, ensuring you get a furnace that delivers longevity and reduces maintenance costs.
Don't let an incorrect furnace choice limit your results. Contact our technical team today for a personalized consultation and discover the right solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance
- What are vacuum furnace parts? A Guide to the Core Systems for Precision Heat Treatment
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Hot Zone Materials and Processed Metals
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries



















