For most engineering applications, a standard plating thickness typically ranges from 0.0005 inches to 0.0015 inches (0.012 mm to 0.038 mm). This thickness provides a durable and functional surface with a hardness of approximately 48 to 52 Rockwell C, suitable for a wide variety of industrial uses.
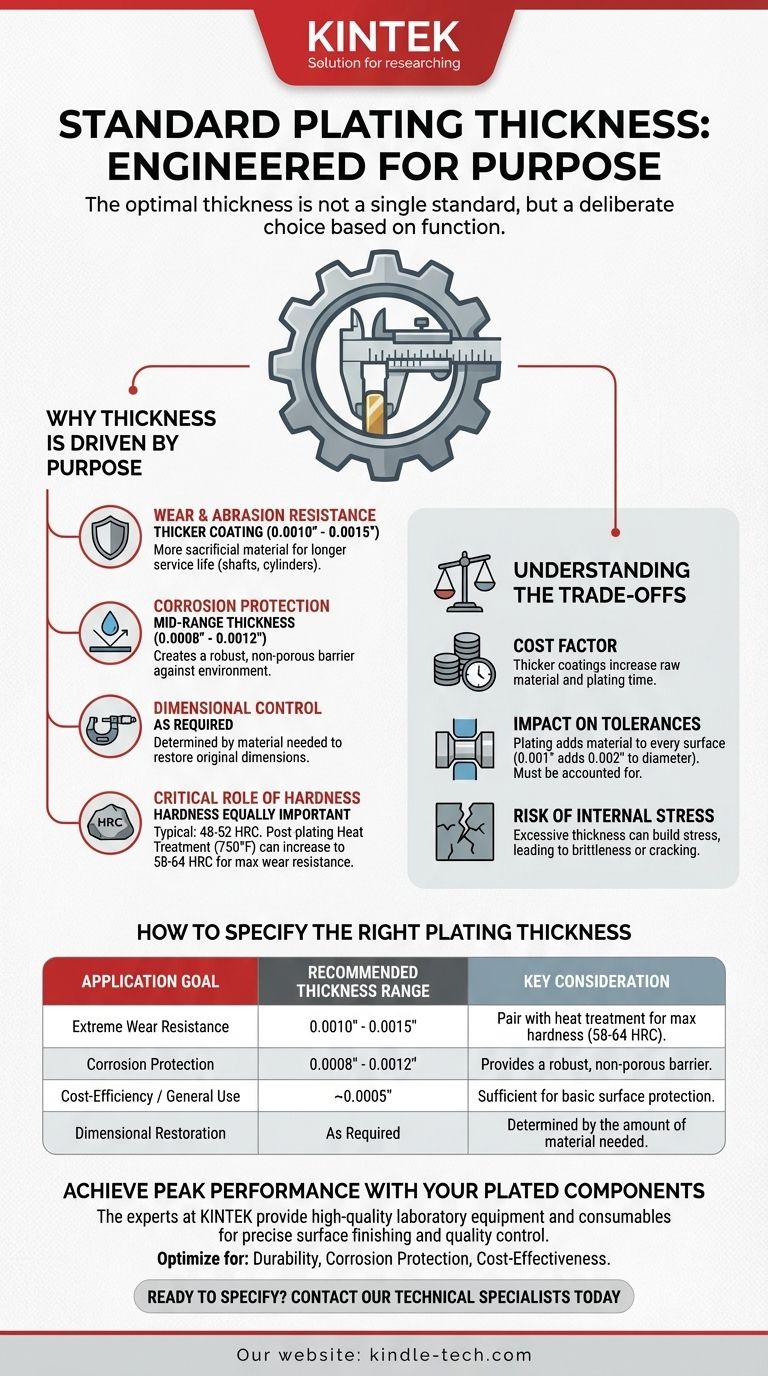
The concept of a single "standard" plating thickness is misleading. The optimal thickness is not a fixed number but a deliberate engineering choice dictated entirely by the part's intended function, environment, and performance requirements.

Why Thickness is Driven by Purpose
While a general range exists, the specific thickness you choose within that range—or even outside of it—depends on what you need the plating to accomplish. The function of the coating is the most critical factor in its specification.
Plating for Wear and Abrasion Resistance
For components subjected to friction or abrasive wear, a thicker coating is generally better.
A greater thickness provides more sacrificial material, extending the service life of the part before the base metal is exposed. This is common for shafts, hydraulic cylinders, and sliding components.
Plating for Corrosion Protection
The primary goal for corrosion resistance is to create a complete, non-porous barrier between the substrate and its environment.
Even a relatively thin coating can provide excellent protection, but a greater thickness adds robustness and helps ensure there are no microscopic pores that could become sites for corrosion.
Plating for Dimensional Control
Plating is often used to restore worn or mismachined parts to their original dimensions.
In these cases, the "standard" goes out the window. The thickness is determined by the amount of material that must be added to meet the final dimensional tolerance.
The Critical Role of Hardness
Thickness is only half of the performance equation. The hardness of the plating is equally important for durability.
As noted, typical engineering plating has a hardness of 48-52 Rockwell C. However, post-plating processes like heat treating for one hour at approximately 750°F (400°C) can significantly increase this to 58-64 Rockwell C, dramatically improving wear resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a plating thickness is an exercise in balancing performance with practical limitations. Simply defaulting to the thickest possible coating is often a mistake.
The Cost Factor
Plating is an additive process. A thicker coating requires more raw material and significantly more time in the plating tank, both of which directly increase the cost of the operation.
Impact on Tight Tolerances
Plating adds material to every surface. This must be accounted for in the initial design, especially for parts with tight tolerances, threads, or mating surfaces. A 0.001-inch plating adds 0.002 inches to the diameter of a shaft.
Risk of Internal Stress
As plating thickness increases, internal stresses within the coating can build up. If not properly managed, excessively thick coatings can become brittle, leading to cracking or poor adhesion to the base material.
How to Specify the Right Plating Thickness
Your final specification should be a conscious choice based on the part's specific application and budget.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear resistance: Specify a thickness in the upper end of the range (0.0010" to 0.0015") and consider specifying post-plating heat treatment for maximum hardness.
- If your primary focus is corrosion protection: A mid-range thickness (0.0008" to 0.0012") provides a robust and reliable barrier for most industrial environments.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for general use: A thickness at the lower end of the range (0.0005") is often sufficient for providing basic surface protection and a durable finish.
- If your primary focus is restoring part dimensions: The required thickness is simply the amount of material needed to bring the part back into its specified tolerance.
Ultimately, the right plating thickness is the one that meets your performance goals without over-engineering the solution.
Summary Table:
| Application Goal | Recommended Thickness Range | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Wear Resistance | 0.0010" - 0.0015" | Pair with heat treatment for max hardness (58-64 HRC). |
| Corrosion Protection | 0.0008" - 0.0012" | Provides a robust, non-porous barrier. |
| Cost-Efficiency / General Use | ~0.0005" | Sufficient for basic surface protection. |
| Dimensional Restoration | As Required | Determined by the amount of material needed. |
Achieve Peak Performance with Your Plated Components
Choosing the correct plating thickness is critical for the longevity and reliability of your parts. The experts at KINTEK are here to help you navigate these specifications. We provide high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables essential for precise surface finishing and quality control.
Let us help you optimize your process for:
- Durability: Select the ideal thickness and hardness for maximum wear resistance.
- Corrosion Protection: Ensure a flawless, protective barrier for harsh environments.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Avoid over-engineering and control your project budget.
Ready to specify the perfect plating for your application? Contact our technical specialists today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum sintering? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Performance for Advanced Materials
- What are the factors influencing shrinkage during sintering? Control Dimensional Changes for Precision Parts
- Does sintering use diffusion? The Atomic Mechanism for Building Stronger Materials
- Why is a high vacuum required for sintering Ti-43Al-4Nb-1Mo-0.1B? Ensure Purity & Fracture Toughness
- Why must green bodies produced via binder jetting undergo treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace?



















