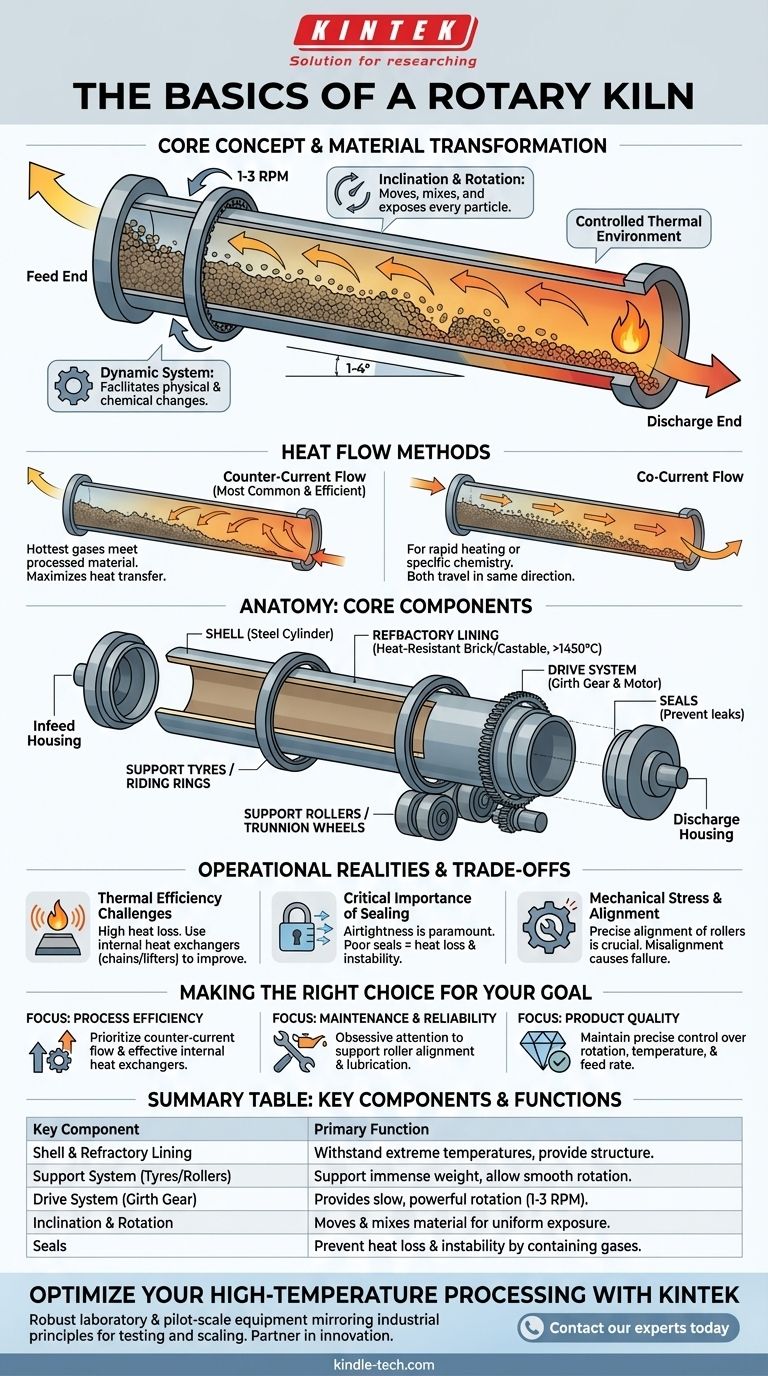
At its core, a rotary kiln is a massive, slowly rotating industrial furnace designed for the continuous high-temperature processing of solids. It consists of a long, cylindrical steel shell lined with heat-resistant material, which is mounted at a slight angle to the horizontal. This simple-sounding design is the workhorse behind countless industrial processes, from cement manufacturing to mineral processing.
The genius of the rotary kiln is not just its ability to generate high heat, but how its slight inclination and constant rotation work in concert. This combination continuously moves, mixes, and exposes every particle of material to a controlled thermal environment on a massive scale.

How a Rotary Kiln Achieves Material Transformation
A rotary kiln is more than a container; it's a dynamic system. Its design directly facilitates the physical and chemical changes required for the end product.
The Principle of Inclination and Rotation
The entire kiln is tilted at a slight angle, typically between 1 and 4 degrees. As the kiln rotates slowly (usually 1-3 revolutions per minute), gravity gently pulls the material downhill from the upper feed end toward the lower discharge end.
This constant, gentle tumbling action is the key to its effectiveness. It ensures thorough mixing and guarantees that all the material is uniformly exposed to the hot gases passing through the kiln.
The Flow of Heat: Counter-Current vs. Co-Current
To heat the material, hot gases are passed through the length of the cylinder. This can be done in one of two ways.
Counter-current flow is the most common and thermally efficient method. Hot gases are introduced at the lower discharge end and travel uphill, exiting at the upper feed end. This means the hottest gases meet the most processed material, maximizing heat transfer.
Co-current flow involves introducing the hot gas at the same end as the material feed. Both travel in the same direction. This method is used when rapid heating or specific process chemistry is required.
Anatomy of a Rotary Kiln: Core Components
While designs vary, all rotary kilns are built from a set of fundamental components engineered to withstand extreme heat and immense mechanical stress.
The Shell and Refractory Lining
The shell is the external steel cylinder that forms the body of the kiln. It provides the structural integrity.
Inside the shell is the refractory lining, a brick or castable layer of extremely heat-resistant material. This lining protects the steel shell from the process temperatures, which can exceed 1450°C (2640°F), and prevents chemical corrosion.
The Support System: Tyres, Rollers, and Thrust Rollers
A kiln's immense weight is supported by two or more massive steel rings, called support tyres or riding rings, which are fitted around the shell.
These tyres ride on heavy-duty steel wheels called support rollers or trunnion wheels, which are mounted on a concrete foundation. This assembly allows the kiln to rotate smoothly.
Thrust rollers are positioned against the side of a tyre to prevent the kiln from sliding downhill due to its inclination.
The Drive System
The drive gear is a large ring gear, often called a girth gear, attached to the kiln shell. It is turned by a smaller pinion gear connected to a high-torque industrial motor. This system provides the slow, powerful rotation necessary for operation.
Infeed, Discharge, and Seals
At the stationary upper end, a feed housing directs raw material into the rotating kiln. At the lower end, the processed material exits through a discharge housing.
Crucially, seals are installed at both ends to prevent cold air from leaking into the kiln and hot gases or dust from escaping. Proper sealing is vital for thermal efficiency and environmental control.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Operational Realities
Operating a rotary kiln involves managing a constant balance between production goals and physical limitations.
Thermal Efficiency Challenges
Rotary kilns are enormous and radiate a significant amount of heat, making them energy-intensive. To improve efficiency, many kilns incorporate internal heat exchangers, such as chains or lifters, which help transfer heat from the gas stream into the material bed more effectively.
The Critical Importance of Sealing
Airtightness is paramount. Poor seals lead directly to heat loss, requiring more fuel to maintain the target temperature. They also cause process instability by allowing uncontrolled air to enter, which can disrupt the sensitive chemistry of the firing process.
Mechanical Stress and Alignment
The combination of extreme weight, constant rotation, and thermal expansion puts incredible stress on the kiln's components. Precise alignment of the support rollers is the single most important factor for reliable operation. Misalignment causes uneven wear on the tyres and rollers, leading to costly mechanical failures and downtime.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the core principles of a rotary kiln allows you to focus on the factors that matter most for your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Prioritize a counter-current gas flow design and the use of effective internal heat exchangers to maximize heat transfer.
- If your primary focus is maintenance and reliability: Pay obsessive attention to the alignment, lubrication, and condition of the support rollers and tyres.
- If your primary focus is product quality: Maintain precise control over the kiln's rotation speed, temperature profile, and feed rate to ensure every particle undergoes uniform processing.
By understanding these fundamental principles, you can appreciate the rotary kiln not as a simple tube, but as a finely tuned system for industrial-scale material transformation.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Shell & Refractory Lining | Steel cylinder with heat-resistant lining to withstand extreme temperatures. |
| Support System (Tyres/Rollers) | Supports the kiln's immense weight and allows for smooth rotation. |
| Drive System (Girth Gear) | Provides the slow, powerful rotation (1-3 RPM) necessary for operation. |
| Inclination & Rotation | Gently moves and mixes material for uniform heat exposure. |
| Seals | Prevents heat loss and process instability by containing hot gases. |
Optimize Your High-Temperature Processing with KINTEK
Understanding the fundamentals of a rotary kiln is the first step toward achieving efficient and reliable industrial-scale production. Whether you're processing minerals, manufacturing cement, or developing new materials, the right equipment is critical for product quality and operational uptime.
KINTEK specializes in supplying robust laboratory and pilot-scale equipment that mirrors these industrial principles. Our expertise helps you test, scale, and perfect your processes before committing to large-scale investment.
Let KINTEK be your partner in innovation. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve precise temperature control, uniform mixing, and reliable performance for your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What is the production of biochar through pyrolysis? Optimize for Soil Health & Carbon Sequestration
- What are the different types of pyrolysis oil? Choosing the Right Process for Your Fuel or Chemical Needs
- What is the chemical reaction of pyrolysis? A Guide to Controlled Thermal Decomposition
- What is a fluidized bed reactor used for? Unlock Superior Solid-to-Gas and Liquid Conversion
- What is the most suitable temperature for burning of cement in rotary kiln? Achieve Perfect Clinker at 1450°C
- How does the calcination process work? Master Thermal Decomposition for Material Purification
- What is a carbon regeneration kiln? Reuse Spent Carbon to Cut Costs & Waste



















