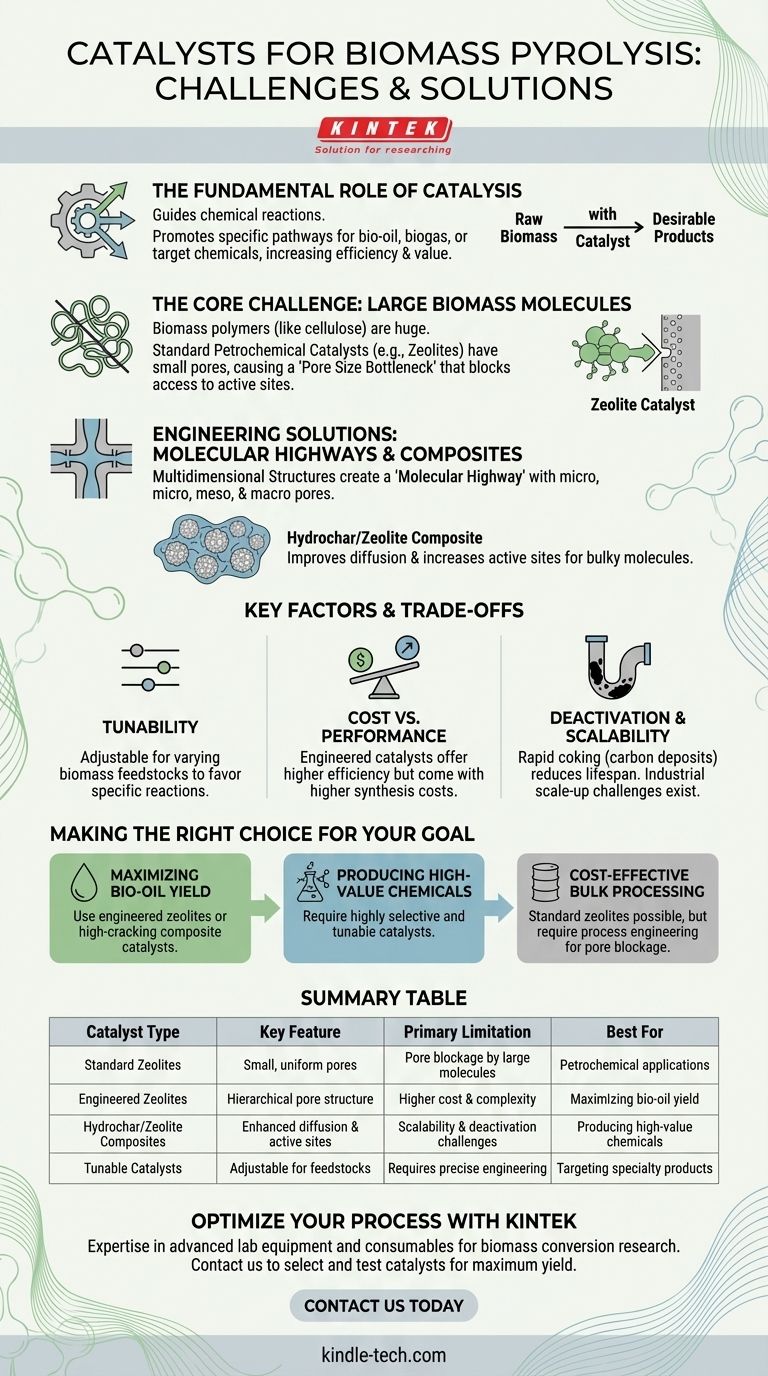
In biomass pyrolysis, catalysts serve to guide the chemical reactions, but conventional options face significant challenges. The most common commercial catalysts are silicon and zeolite-based, but their small pore structures are often incompatible with the large molecules found in biomass. This has led to the development of advanced materials, like hydrochar/zeolite composites, designed specifically to handle these complex feedstocks.
The core challenge in biomass pyrolysis is not simply finding a catalyst, but engineering one that can accommodate the bulky nature of biomass polymers while providing the control needed to target specific, high-value end products.

The Fundamental Role of Catalysis in Pyrolysis
Guiding Chemical Reactions
A catalyst's primary function in pyrolysis is to promote specific chemical reactions. Without one, thermal decomposition is less controlled, producing a wide mixture of compounds.
By introducing a catalyst, operators can steer the process toward converting biomass into desirable products like bio-oil, biogas, or specific chemicals, increasing the efficiency and value of the entire system.
Why It's More Complex Than Petrochemicals
The molecules in biomass, such as cellulose and lignin, are natural polymers that are significantly larger and more complex than the molecules found in crude oil.
This size difference is the central reason why catalysts designed for the petrochemical industry often fail or perform poorly in biomass applications.
Common Catalysts and Their Core Limitation
Standard Commercial Options
The most widely used catalysts in thermal and chemical conversion processes are zeolites. These are crystalline materials with a highly ordered, porous structure.
Their well-defined pores and acidic sites are excellent for cracking small hydrocarbon molecules, making them a default choice in many industries.
The "Pore Size" Bottleneck
The effectiveness of a zeolite catalyst depends on molecules entering its internal pores to reach the "active sites" where reactions occur.
However, the narrow pores of conventional zeolites physically block the large polymers found in biomass. This prevents the most critical reactions from ever taking place inside the catalyst.
Engineering Solutions for Better Performance
Creating a "Molecular Highway"
To solve the pore size problem, researchers are engineering catalysts with a multidimensional structure. This involves creating a network of micro, meso, and macro pores.
This hierarchical system acts like a molecular highway, allowing large biomass molecules to enter the catalyst through wide channels and then break down into smaller pieces that can access the highly active micropores.
The Promise of Composite Catalysts
A leading example of this new approach is the hydrochar/zeolite composite catalyst. This material combines the proven catalytic power of zeolites with the unique properties of hydrochar.
This composite structure improves the diffusion of molecules inside the catalyst and dramatically increases the number of accessible active sites, making it highly suitable for producing advanced biofuels.
The Need for Tunability
Biomass is not a uniform feedstock; its properties vary widely depending on the source (e.g., wood, agricultural waste).
This variability requires tunable catalysts that can be adjusted to favor specific reactions, allowing producers to target desirable compounds based on the unique characteristics of the input material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Cost vs. Performance
Engineered composite catalysts with hierarchical pore structures are significantly more complex and expensive to synthesize than standard commercial zeolites. This creates a trade-off between higher efficiency and upfront investment.
Catalyst Deactivation
The complex nature of biomass-derived vapors can lead to rapid catalyst deactivation. This often occurs through "coking," where carbon deposits build up and block the catalyst's pores and active sites, reducing its lifespan and effectiveness over time.
Scalability Challenges
A catalyst that performs exceptionally well in a controlled lab environment may face significant hurdles when scaled up to an industrial pyrolysis plant. Ensuring durability, stability, and consistent performance at a commercial scale remains a key engineering challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a catalytic strategy depends entirely on your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximizing bio-oil yield: An engineered zeolite or a composite catalyst with high cracking activity and tailored porosity is essential for efficiently breaking down large molecules.
- If your primary focus is producing high-value specialty chemicals: A highly selective and tunable catalyst is critical to favor specific reaction pathways and minimize the creation of unwanted byproducts.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective bulk processing: While standard zeolites may seem economical, you must engineer the process to manage the inevitable issues of pore blockage and lower efficiency with bulky biomass feedstock.
Ultimately, the right catalyst transforms biomass pyrolysis from a simple thermal process into a precise chemical engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Catalyst Type | Key Feature | Primary Limitation | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Zeolites | Small, uniform pores | Pore blockage by large biomass molecules | Petrochemical applications |
| Engineered Zeolites | Hierarchical pore structure | Higher cost and complexity | Maximizing bio-oil yield |
| Hydrochar/Zeolite Composites | Enhanced diffusion & active sites | Scalability and deactivation challenges | Producing high-value chemicals |
| Tunable Catalysts | Adjustable for specific feedstocks | Requires precise engineering | Targeting specialty products |
Ready to optimize your biomass pyrolysis process? The right catalyst is key to transforming your feedstock into high-value bio-oil or specialty chemicals. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored for biomass conversion research and development. Our expertise helps you select and test catalysts that overcome pore size limitations and maximize yield. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your pyrolysis efficiency and target your desired products!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Etching Flower Basket ITO FTO Developing Glue Removal
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Magnetic Stirring Bar
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
People Also Ask
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- Why are PTFE laboratory consumables required when testing stainless steel against organic acids? Ensure Data Integrity
- Why is PTFE wire used for hanging metal specimens in biodiesel corrosion tests? Ensure Pure Experimental Results
- How are PTFE gaskets utilized for POEGMA electrolyte conductivity? Ensure Precision in Electrochemical Measurements
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type



















