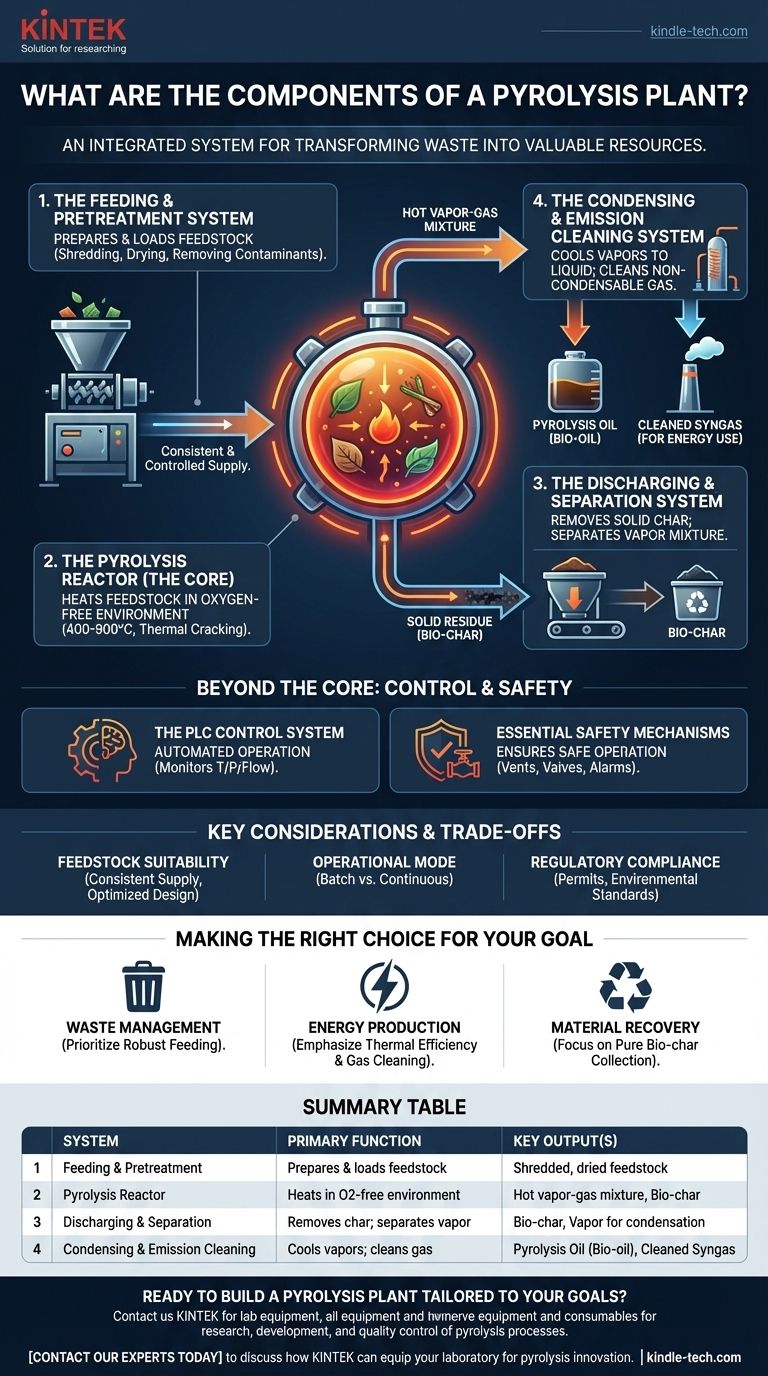
At its core, a pyrolysis plant is not a single machine but an integrated system with four primary components working in sequence: a feeding system, a pyrolysis reactor, a product discharging system, and an emission cleaning system. These components work together to thermally decompose organic materials like biomass, tires, or plastic in an oxygen-free environment, transforming them into valuable outputs.
A pyrolysis plant is best understood as a complete processing line. Its purpose is to break down complex organic waste in a high-temperature reactor at the center, supported by critical systems for feeding raw material, separating the valuable products, and ensuring clean emissions.

The Four Core Systems of a Pyrolysis Plant
Each part of the plant performs a distinct and essential function in the overall process of converting waste into resources. Understanding these systems is key to evaluating the technology.
1. The Feeding and Pretreatment System
The process begins with preparing and loading the raw material, or feedstock. This system ensures a consistent and controlled supply into the reactor.
For many plants, especially continuous models, this stage also includes pretreatment, which may involve shredding, drying, or removing contaminants to optimize the pyrolysis process.
2. The Pyrolysis Reactor (The Core)
The reactor is the heart of the plant. It is an airtight chamber, typically made from robust materials like Q245R boiler plate or stainless steel, designed to withstand extreme heat.
Inside the reactor, the feedstock is heated to very high temperatures (400-900°C) in the complete absence of oxygen. This prevents combustion and instead causes thermal cracking, where large organic molecules are broken down into smaller, energy-rich compounds.
The output from this stage is a hot vapor-gas mixture and a solid residue known as bio-char or fine coke.
3. The Discharging and Separation System
Once the reaction is complete, this system safely removes the solid bio-char from the reactor. In continuous plants, this is an automated process designed to maintain the oxygen-free environment.
Simultaneously, the hot vapor-gas mixture is piped out of the reactor to be cooled and separated. This is where the other primary products are collected.
4. The Condensing and Emission Cleaning System
The hot vapor-gas mixture first enters a condensing system. As it cools, the condensable vapors turn into a liquid known as pyrolysis oil or bio-oil, which is collected.
The remaining non-condensable gases, often called syngas, are directed to an emission cleaning line. This system scrubs out any harmful particulates or compounds before the cleaned gas is either flared, used to heat the reactor, or collected for other energy applications.
Beyond the Core: Control and Safety
A modern pyrolysis plant relies on more than just the four main processing systems. Its operational efficiency and safety depend on a central control network.
The PLC Control System
Most automated and continuous plants are managed by a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) system. This central brain monitors temperatures, pressures, and flow rates, automating the feeding and discharging systems to ensure stable and efficient operation.
Essential Safety Mechanisms
Given the high temperatures and flammable gases involved, safety systems are non-negotiable. These include emergency vents, pressure release valves, and monitoring alarms to ensure the plant operates within safe parameters.
Key Considerations and Trade-offs
Simply knowing the components is not enough. The design and feasibility of a plant depend heavily on its intended purpose and operational context.
Feedstock Suitability
The type and availability of feedstock are critical. A feasibility study is essential to ensure a consistent supply of suitable material, as the plant's design must be optimized for a specific type of waste (e.g., tires, plastic, or biomass).
Operational Mode: Batch vs. Continuous
Plants can be designed for batch processing, where one load is processed at a time, or as a fully continuous system. Continuous plants offer higher throughput and automation but require a more significant initial investment and a highly consistent feedstock.
Regulatory Compliance
Building and operating a pyrolysis plant requires strict adherence to local environmental regulations. Obtaining the necessary permits and consulting with authorities is a crucial step in the planning process to ensure safe and legal operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal plant configuration depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Prioritize a robust and flexible feeding and pretreatment system that can handle variability in the incoming waste stream.
- If your primary focus is energy production: Emphasize the reactor's thermal efficiency and the quality of the condensing and gas cleaning systems to maximize the yield of high-grade bio-oil and syngas.
- If your primary focus is material recovery: Focus on the discharging and separation systems to ensure you can collect pure, high-quality bio-char for use as a soil amendment or for activated carbon production.
Ultimately, viewing the pyrolysis plant as an interconnected system is the key to harnessing its full potential.
Summary Table:
| System | Primary Function | Key Output(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Feeding & Pretreatment | Prepares and loads raw material (feedstock) | Shredded, dried feedstock |
| Pyrolysis Reactor | Heats feedstock in oxygen-free environment | Hot vapor-gas mixture, Bio-char |
| Discharging & Separation | Removes solid char; separates vapor mixture | Bio-char, Vapor for condensation |
| Condensing & Emission Cleaning | Cools vapors to liquid; cleans non-condensable gas | Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-oil), Cleaned Syngas |
Ready to build a pyrolysis plant tailored to your waste management or energy production goals?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for the research, development, and quality control of pyrolysis processes. Whether you are testing feedstock suitability, analyzing bio-oil quality, or ensuring your plant meets environmental standards, our products support your success from lab to pilot scale.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can equip your laboratory for pyrolysis innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products



















