At its core, a pyrolysis reactor is a sealed vessel designed for thermal decomposition in the absence of oxygen, but its specific components vary significantly based on its intended function. The most basic configuration includes a reaction chamber with inlets and outlets, a heating system, and a system for collecting the resulting gas, liquid (bio-oil), and solid (char) products. More advanced designs incorporate specialized components to control processing speed and heat transfer.
The specific components of a pyrolysis reactor are not universal; they are dictated by the reactor's fundamental design. Understanding the goal—such as slow versus fast pyrolysis—is key to understanding why certain components like augers or fluidized beds are used.

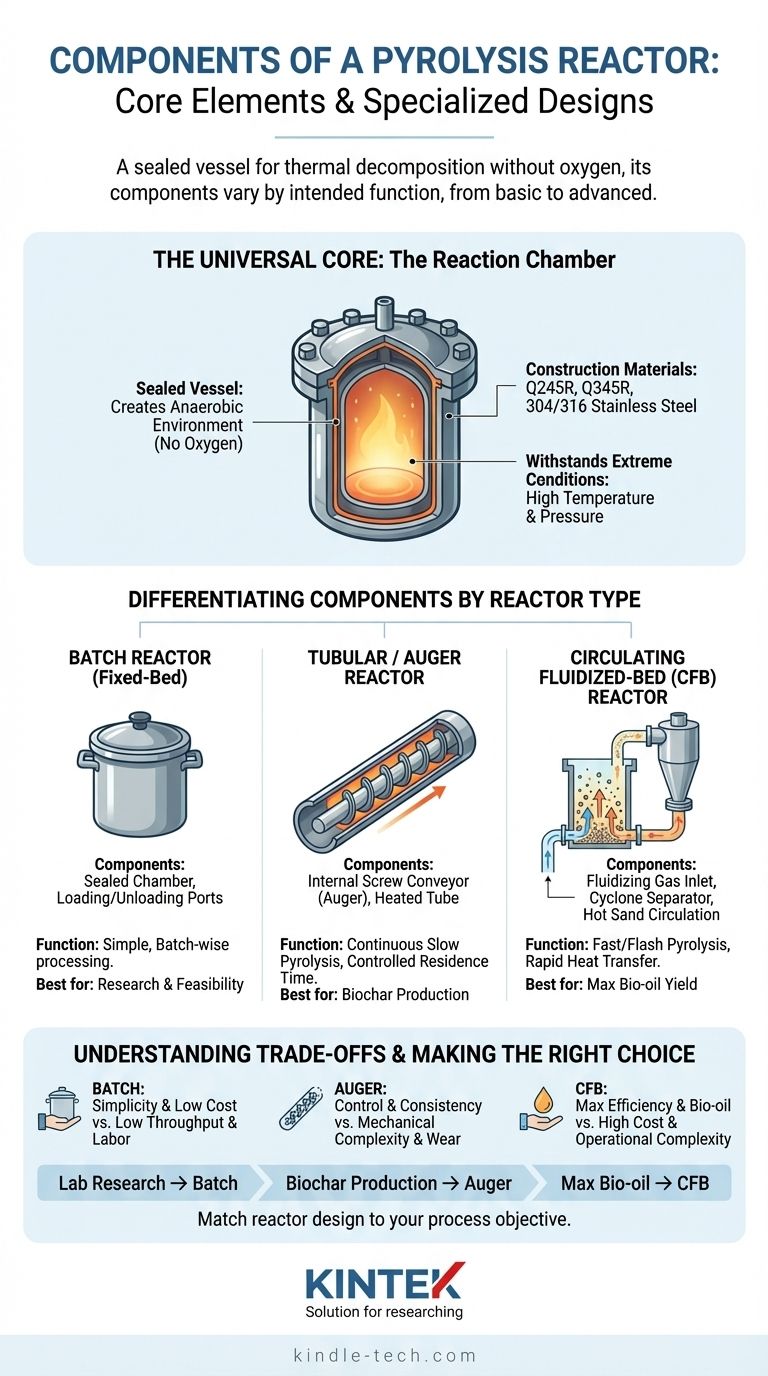
The Universal Core: The Reaction Chamber
Every pyrolysis reactor is built around a central reaction chamber, which is the heart of the system. This component is non-negotiable, regardless of the reactor's complexity.
The Sealed Vessel
The primary component is the sealed vessel itself. Its fundamental purpose is to create and maintain an anaerobic (oxygen-free) environment.
This is critical because the presence of oxygen would lead to combustion (burning) rather than pyrolysis, fundamentally changing the chemical process and its outputs.
Construction Materials
The vessel must withstand extreme conditions. Materials like Q245R and Q345R boiler plates or higher-grade 304 and 316 stainless steel are used.
These materials are chosen for their high-temperature strength and resistance to corrosion and pressure, ensuring the integrity and safety of the reaction.
Differentiating Components by Reactor Type
Beyond the basic vessel, the components diverge based on the reactor's operational mode. The method of loading material, applying heat, and processing speed dictates the design.
Batch Reactor Components
A batch reactor (or fixed-bed reactor) is the simplest design, loaded with a fixed amount of material for each run.
Its key components are a sealed chamber with ports for loading feedstock and outlets for pyrolysis products. Heat is typically applied externally to the vessel walls. This design is often used for lab-scale research and for investigating process stability.
Tubular / Auger Reactor Components
A tubular reactor, often using a screw or auger conveyor, is designed for continuous processing.
The defining component is the internal auger. This rotating screw moves feedstock from the inlet to the outlet through a heated tube. This mechanism provides excellent control over residence time, making it well-suited for slow pyrolysis operations where material needs to be heated gradually over a longer period.
Circulating Fluidized-Bed (CFB) Reactor Components
A CFB reactor is engineered for extremely rapid heat transfer, which is essential for fast and flash pyrolysis.
Its key components include an inlet for a fluidizing gas (like nitrogen), which suspends the feedstock particles. A cyclone separator is crucial for separating the hot char and vapors. Most importantly, it features a system for circulating a hot, inert material (like sand) between the reactor and a heater, ensuring the feedstock is heated almost instantaneously.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of components and reactor type involves significant trade-offs between simplicity, efficiency, and cost. There is no single "best" design.
Batch: Simplicity vs. Scale
The primary advantage of a batch reactor is its simplicity and low construction cost.
However, it is not suitable for large-scale, continuous industrial production due to its low throughput and the labor required for loading and unloading each batch.
Tubular/Auger: Control vs. Mechanical Complexity
An auger reactor offers excellent control over temperature and processing time, enabling consistent results for slow pyrolysis.
The main drawback is its mechanical complexity. The internal screw conveyor is a moving part that is subject to wear, potential blockages, and high maintenance, especially when processing non-uniform feedstock.
Fluidized-Bed: Speed vs. High Cost
The CFB design offers unmatched heat transfer efficiency, making it the superior choice for maximizing liquid bio-oil yield through fast pyrolysis.
This performance comes at the cost of high complexity and operational expense. It requires precise control over particle size, gas flow rates, and temperature, making it the most sophisticated and expensive option.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The components you need depend entirely on what you want to achieve with the pyrolysis process.
- If your primary focus is lab-scale research or initial feasibility tests: A simple batch reactor provides a cost-effective and straightforward platform.
- If your primary focus is the continuous, controlled production of biochar via slow pyrolysis: An auger or tubular reactor offers the necessary control over residence time.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid bio-oil yield from biomass through fast pyrolysis: A circulating fluidized-bed reactor is the industry standard due to its superior heat transfer capabilities.
Ultimately, selecting the right components means matching the reactor's engineering design to your specific process objective.
Summary Table:
| Reactor Type | Key Components | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Batch / Fixed-Bed | Sealed chamber, loading/unloading ports | Simple, batch-wise processing for research |
| Tubular / Auger | Internal screw conveyor, heated tube | Continuous slow pyrolysis with controlled residence time |
| Circulating Fluidized-Bed (CFB) | Fluidizing gas inlet, cyclone separator, hot sand circulation | Fast/Flash pyrolysis for maximum bio-oil yield |
Ready to select the right pyrolysis reactor for your application? The optimal design depends entirely on your process goals—whether it's research, biochar production, or maximizing bio-oil yield. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing robust solutions for all your laboratory needs. Our experts can help you choose a reactor with the right components to ensure efficiency and success. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success



















