At its core, pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an inert atmosphere. The process requires three fundamental conditions: a temperature high enough to break chemical bonds (typically above 300°C), the near-total absence of an oxidizing agent like oxygen, and a carbon-based feedstock to be decomposed.
The specific conditions for pyrolysis are not fixed; they are variables you control. Adjusting temperature, heating rate, and feedstock type allows you to precisely engineer the output, determining whether you primarily produce solid biochar, liquid bio-oil, or combustible syngas.
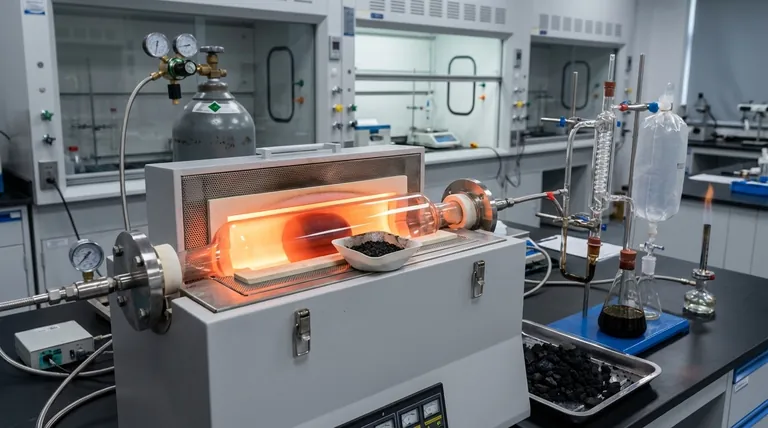

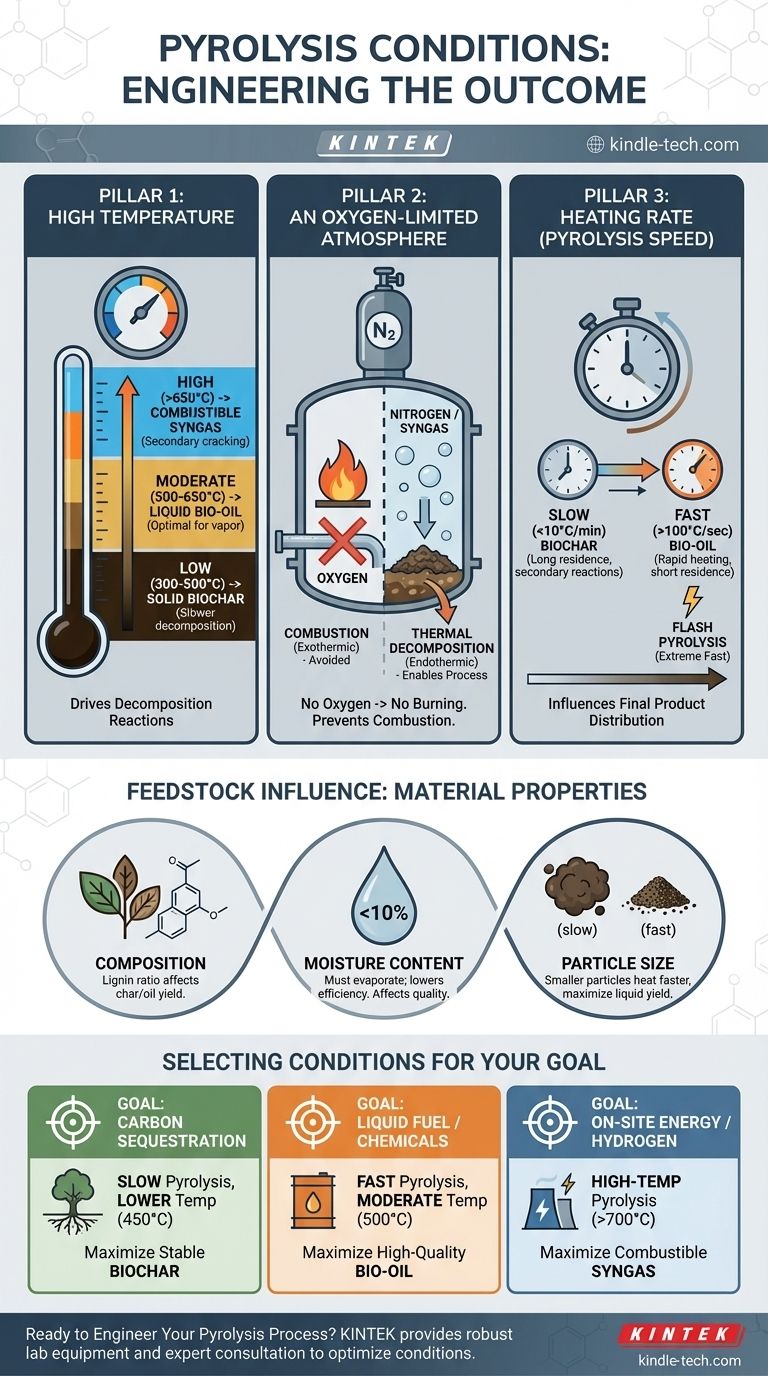
The Three Pillars of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is fundamentally a balancing act between three key process parameters. Mastering these variables is essential for achieving a desired outcome.
Pillar 1: High Temperature
Temperature is the primary driver of the decomposition reactions. Different temperature ranges favor the formation of different products.
- Low Temperatures (300-500°C): This range promotes slower decomposition, maximizing the yield of solid biochar. The complex organic structures don't have enough energy to fully break down into gases.
- Moderate Temperatures (500-650°C): This is the optimal range for producing liquid bio-oil. The heat is sufficient to break down the feedstock into smaller, volatile vapor molecules, which are then rapidly cooled and condensed into a liquid.
- High Temperatures (>650°C): At these temperatures, secondary cracking of the heavier vapor molecules occurs, breaking them down further into the simplest, non-condensable gaseous compounds, maximizing the yield of syngas.
Pillar 2: An Oxygen-Limited Atmosphere
This is the single most important condition that distinguishes pyrolysis from combustion or gasification. The process must occur in an environment with very little to no oxygen.
Without oxygen, the feedstock cannot burn. Instead of combustion, which is an exothermic oxidation reaction that releases heat, you get thermal decomposition—an endothermic process where heat energy is used to break molecules apart. This inert atmosphere is typically achieved by using nitrogen or by using the recycled syngas produced by the process itself.
Pillar 3: Heating Rate (Pyrolysis Speed)
The speed at which the feedstock is heated to the target temperature dramatically influences the final product distribution.
- Slow Pyrolysis: Involves very slow heating rates (e.g., <10°C per minute). Long residence times in the reactor allow for secondary reactions that favor the formation of stable, solid biochar. This is the traditional method for making charcoal.
- Fast Pyrolysis: Uses very rapid heating rates (e.g., >100°C per second). The goal is to quickly turn the solid feedstock into vapor and remove it from the hot zone before it can further react into gas or char. This method is optimized to produce up to 75% bio-oil by weight.
- Flash Pyrolysis: An extreme version of fast pyrolysis with even higher heating rates and shorter vapor residence times, often used to target specific high-value chemical compounds.
How Feedstock Influences the Process
The ideal conditions also depend on what you are putting into the reactor. The physical and chemical properties of the feedstock are a critical part of the equation.
Material Composition
The chemical makeup of the feedstock, particularly the ratio of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin in biomass, dictates the natural tendency of the material. Lignin, for example, is a complex polymer that tends to produce more biochar and phenolic compounds in the bio-oil.
Moisture Content
Water in the feedstock must be evaporated before pyrolysis can begin. This consumes a significant amount of energy, lowering the overall thermal efficiency of the process. High moisture can also increase the water content of the final bio-oil, reducing its quality and heating value. Most systems require feedstock to be dried to below 10% moisture.
Particle Size
Smaller particles have a higher surface-area-to-volume ratio. This allows them to heat up much more quickly and uniformly, which is essential for fast pyrolysis and maximizing liquid yields. Larger particles will have significant temperature gradients, leading to slower, less efficient decomposition.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right conditions is an exercise in engineering trade-offs, balancing desired output with operational reality.
Energy Balance: Yield vs. Input
Achieving higher temperatures to maximize syngas production requires a substantial energy input. This can negatively impact the net energy balance of the system, where you might consume a large fraction of the energy you produce just to run the process.
Product Quality vs. System Complexity
Producing high-quality, stable bio-oil requires more than just fast pyrolysis; it demands rapid and effective quenching of the vapors. This adds complexity and cost to the reactor and condensation system design. Lower-quality, acidic, or unstable oils are easier to make but harder to use.
Feedstock Preparation vs. Throughput
The ideal conditions for fast pyrolysis—very dry and very small particles—necessitate significant pre-processing. The energy and capital costs of industrial-scale dryers and grinders must be weighed against the value of the final products.
Selecting Conditions for Your Goal
Your choice of pyrolysis conditions should be driven by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration or soil amendment: Use slow pyrolysis at lower temperatures (around 450°C) with longer residence times to maximize the yield of stable biochar.
- If your primary focus is producing a liquid fuel or chemical feedstock: Use fast pyrolysis with moderate temperatures (around 500°C), extremely high heating rates, and rapid vapor quenching to maximize the yield of bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is generating on-site energy or producing hydrogen: Use high-temperature pyrolysis (above 700°C) to maximize the conversion of feedstock into combustible syngas.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is a versatile thermochemical tool that can be precisely adapted to meet specific engineering and commercial goals.
Summary Table:
| Condition | Key Role | Typical Range / State | Primary Product Influence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Drives decomposition reactions | 300°C to >700°C | Low: Biochar, Moderate: Bio-oil, High: Syngas |
| Atmosphere | Prevents combustion; enables decomposition | Inert (e.g., Nitrogen) | Essential for all pyrolysis processes |
| Heating Rate | Controls reaction speed & product distribution | Slow (<10°C/min) to Fast (>100°C/sec) | Slow: Biochar, Fast: Bio-oil |
| Feedstock Moisture | Affects energy efficiency | Ideally <10% | High moisture reduces bio-oil quality & yield |
Ready to Engineer Your Pyrolysis Process?
Whether your goal is to maximize biochar for carbon sequestration, produce high-quality bio-oil for fuel, or generate syngas for energy, precise control over your pyrolysis conditions is critical. KINTEK specializes in providing the robust lab equipment and expert consultation needed to optimize temperature, atmosphere, and heating rates for your specific feedstock and objectives.
Contact our pyrolysis experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve your target product yields and process efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What is the difference between a tubular furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Application
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness



















