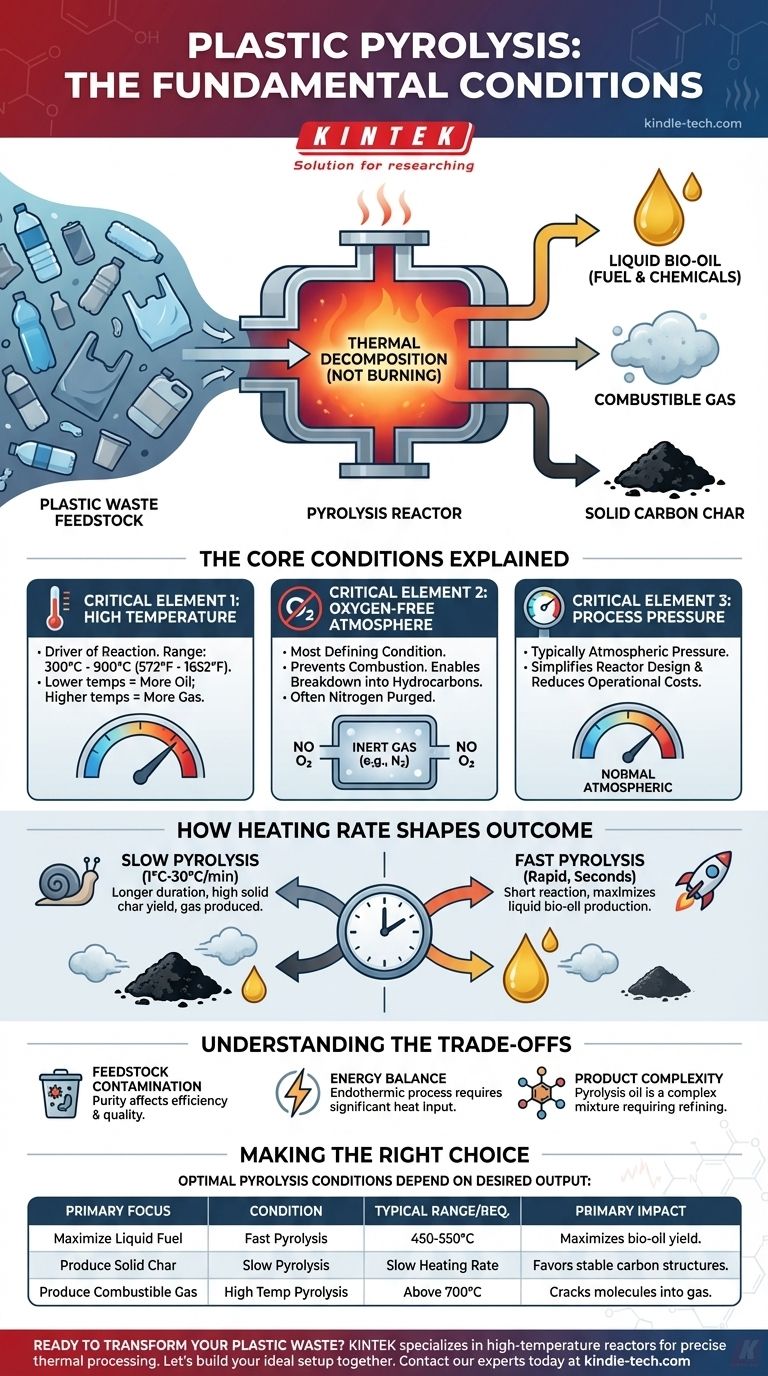
The fundamental conditions for plastic pyrolysis are high heat and the near-total absence of oxygen. This process is not burning; it is the thermal decomposition of long polymer chains into smaller, more valuable molecules like oils, gases, and a solid carbon residue called char.
Pyrolysis is a chemical recycling process that uses an oxygen-free, high-temperature environment to break down plastic waste into valuable fuel and chemical feedstocks, rather than combusting it.

The Core Conditions Explained
To successfully initiate pyrolysis, three primary environmental parameters must be precisely controlled: temperature, atmospheric composition, and pressure. Each plays a distinct role in the decomposition process.
Critical Element 1: High Temperature
The temperature is the primary driver of the reaction, providing the energy needed to break the strong chemical bonds within plastic polymers.
Typical temperature ranges for plastic pyrolysis are between 300°C and 900°C (572°F to 1652°F). Lower temperatures tend to yield more liquid oil, while higher temperatures can favor gas production.
Critical Element 2: An Oxygen-Free Atmosphere
This is the most defining condition of pyrolysis. The process must occur in an inert or oxygen-limited environment, often by purging the reactor with nitrogen gas.
The absence of oxygen is crucial because it prevents combustion (burning). Instead of reacting with oxygen to produce ash, CO2, and water, the plastic molecules break down into smaller hydrocarbons.
Critical Element 3: Process Pressure
For most applications, plastic pyrolysis is conducted at or near normal atmospheric pressure. This simplifies reactor design and reduces operational costs and complexity compared to high-pressure systems.
How Heating Rate Shapes the Outcome
Beyond the core conditions, the speed at which the plastic is heated (the heating rate) has a significant impact on the final products. This is the primary distinction between the two main types of pyrolysis.
Slow Pyrolysis
As the name implies, this method uses a slow heating rate, typically between 1°C and 30°C per minute. The plastic is exposed to the target temperature for a longer duration.
This slower process tends to produce a higher yield of solid char (a form of carbon black) and gas, with a lower yield of liquid oil.
Fast Pyrolysis
Fast pyrolysis uses a very high heating rate and a much shorter reaction time (often just a few seconds).
This rapid decomposition is optimized to maximize the production of liquid bio-oil (also known as pyrolysis oil), which is often the most desired product for use as a fuel or chemical feedstock.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, pyrolysis is a complex process with inherent challenges that must be considered for any practical application.
Feedstock Contamination
Real-world plastic waste is rarely pure. Contaminants like food residue, paper labels, and other materials can affect the efficiency of the reaction and the quality of the end products.
Energy Balance
Pyrolysis is an endothermic process, meaning it requires a significant energy input to maintain the high temperatures needed to break down the plastic. A portion of the gas produced during the process is often combusted to provide this necessary heat.
Product Complexity
The resulting pyrolysis oil is not a finished fuel. It is a complex mixture of dozens or hundreds of different hydrocarbon compounds and may require further refining or upgrading before it can be used in engines or chemical processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal pyrolysis conditions depend entirely on your desired output.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid fuel (pyrolysis oil): Fast pyrolysis at moderate temperatures (around 450-550°C) is the most effective approach.
- If your primary focus is producing solid carbon char: Slow pyrolysis is the ideal method, as the longer reaction time favors the formation of stable carbon structures.
- If your primary focus is producing combustible gas: Pyrolysis at very high temperatures (above 700°C) will crack the larger molecules into smaller, gaseous hydrocarbons.
Ultimately, controlling these core conditions allows you to transform plastic waste into a targeted and valuable resource.
Summary Table:
| Condition | Typical Range / Requirement | Primary Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 300°C to 900°C (572°F to 1652°F) | Drives polymer breakdown; lower temps favor liquid oil, higher temps favor gas. |
| Atmosphere | Oxygen-free (inert, e.g., nitrogen) | Prevents combustion; enables thermal decomposition into hydrocarbons. |
| Pressure | Atmospheric pressure | Simplifies reactor design and operation. |
| Heating Rate | Slow (1-30°C/min) or Fast (rapid, seconds) | Slow pyrolysis yields more char; fast pyrolysis maximizes liquid oil. |
Ready to transform your plastic waste into valuable resources? The right lab equipment is crucial for researching and optimizing pyrolysis conditions. KINTEK specializes in high-temperature reactors and laboratory systems designed for precise thermal processing. Whether you're developing fast pyrolysis for bio-oil or studying slow pyrolysis for char production, our solutions provide the control and reliability you need.
Let's build your ideal pyrolysis setup together. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and how KINTEK can support your recycling and energy recovery goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
















