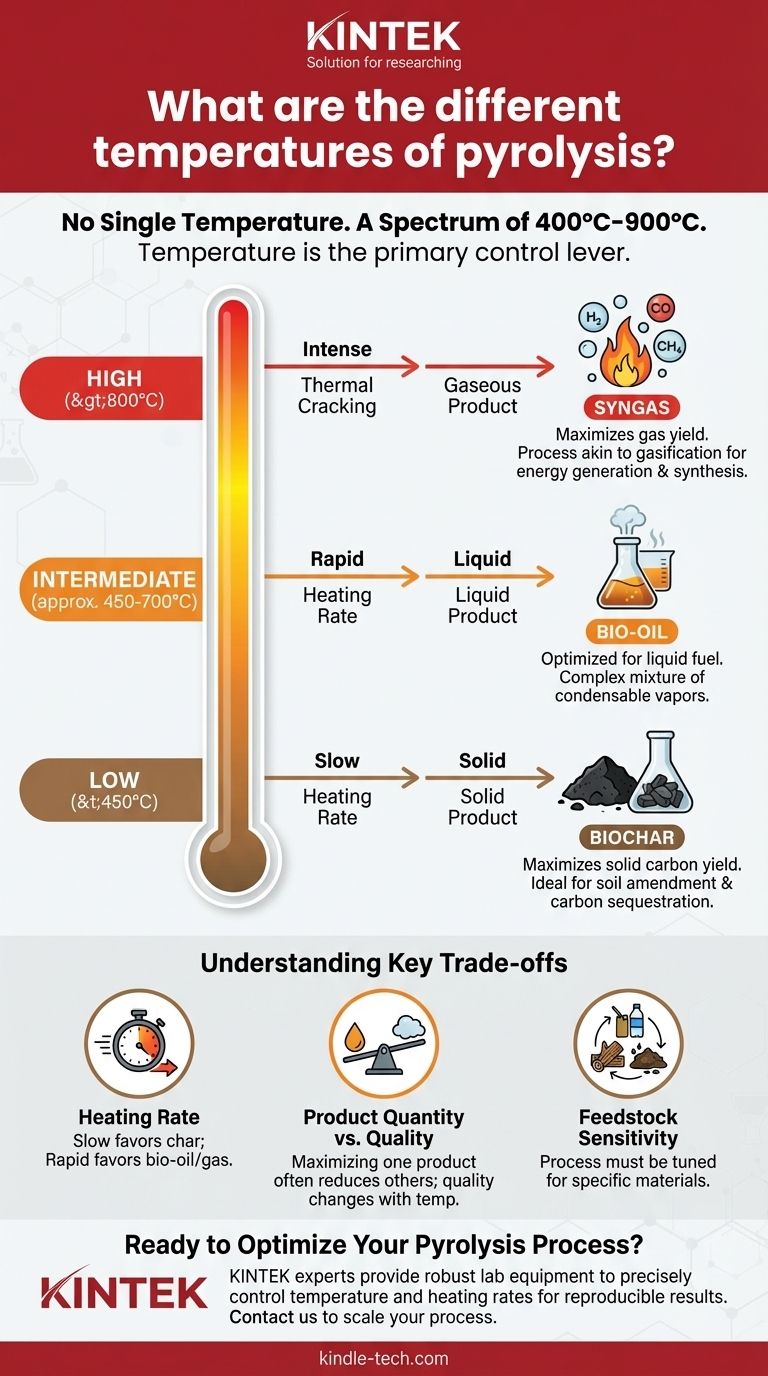
In pyrolysis, there is no single temperature. The process operates across a wide spectrum, typically between 400°C and 900°C. The specific temperature is carefully chosen based on the desired end-product, as it is the primary factor that determines the output.
The core principle to understand is that temperature acts as a control lever. Lower temperatures favor solid products (biochar), intermediate temperatures favor liquids (bio-oil), and high temperatures favor gases (syngas).

How Temperature Dictates Pyrolysis Products
The final temperature reached during pyrolysis, combined with the rate of heating, directly influences the chemical breakdown of the feedstock. This dictates the proportion of solid, liquid, and gaseous products that are created.
Low-Temperature Pyrolysis (<450°C): Maximizing Biochar
At lower temperatures, especially when combined with slow heating rates, the process favors the creation of a solid carbon-rich product.
This product is known as biochar. The slower process allows larger carbon structures to remain intact rather than breaking down into smaller volatile compounds.
Intermediate-Temperature Pyrolysis (approx. 450-700°C): The Bio-Oil Sweet Spot
This range, particularly with relatively high heating rates, is optimized for producing liquid fuel.
At these temperatures, the feedstock breaks down into a complex mixture of condensable vapors. When cooled, these vapors form a liquid commonly known as bio-oil. The reference range of 600-700°C falls squarely within this category.
High-Temperature Pyrolysis (>800°C): Prioritizing Gas Production
When temperatures exceed 800°C, the thermal cracking is far more intense. This breaks down even the heavier organic molecules into very simple, non-condensable gaseous compounds.
The primary output here is syngas, a mixture of gases like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane. This process is often referred to as gasification.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing a temperature is not just about the primary product; it involves balancing several interconnected factors. Understanding these trade-offs is critical for any successful application.
The Critical Role of Heating Rate
Temperature does not work in isolation. A slow heating rate gives the material time to form char, even at higher temperatures.
Conversely, a rapid heating rate quickly vaporizes the material, minimizing char formation and favoring the production of bio-oil or gas, depending on the final temperature.
Product Quantity vs. Quality
Maximizing the yield of one product often comes at the expense of others. For example, running the process at a high temperature to get the most gas means you will produce very little bio-oil or biochar.
Furthermore, the quality of each product also changes. The chemical composition of bio-oil produced at 500°C will be different from that produced at 650°C.
Feedstock Sensitivity
The ideal temperature range can also shift depending on the specific material being processed. Lignocellulosic biomass like wood will behave differently than waste plastic or sewage sludge, requiring process conditions to be tuned accordingly.
Matching Temperature to Your Goal
To select the right temperature, you must first define your primary objective. Each outcome requires a distinct approach.
- If your primary focus is producing biochar for soil amendment or carbon sequestration: Use low-temperature pyrolysis (below 450°C) with a slow heating rate.
- If your primary focus is generating liquid bio-oil for fuel or chemical feedstocks: Use intermediate-temperature pyrolysis (around 450-700°C) with a rapid heating rate.
- If your primary focus is creating syngas for energy generation or synthesis: Use high-temperature pyrolysis (above 800°C) to maximize gas yield.
Ultimately, mastering pyrolysis is about precisely controlling thermal conditions to transform raw materials into valuable products.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Primary Product | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Low (< 450°C) | Biochar | Maximizes solid carbon yield; ideal for soil amendment and carbon sequestration. |
| Intermediate (450-700°C) | Bio-Oil | Optimized for liquid fuel production; requires rapid heating rates. |
| High (> 800°C) | Syngas | Maximizes gas yield (H₂, CO, CH₄); process is akin to gasification. |
Ready to Optimize Your Pyrolysis Process?
Selecting the precise temperature and heating rate is critical to achieving your target product yield and quality. The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing robust lab equipment and consumables to help you master thermal processes like pyrolysis.
We can help you:
- Precisely control temperature and heating rates for reproducible results.
- Select the right equipment for your specific feedstock and desired output (biochar, bio-oil, or syngas).
- Scale your process from R&D to production with reliable and durable solutions.
Contact our thermal processing specialists today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the range of pyrolysis? Master Temperature Control for Optimal Bio-Product Yields
- What temperature is needed for pyrolysis waste? A Guide to Optimizing Your Waste-to-Value Process
- What are the main types of biomass conversion processes? Unlock the Best Pathway for Your Energy Needs
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity
- How is a high-temperature calcination furnace utilized in BZY20 Sol-gel? Achieve Pure Cubic Perovskite Phases



















