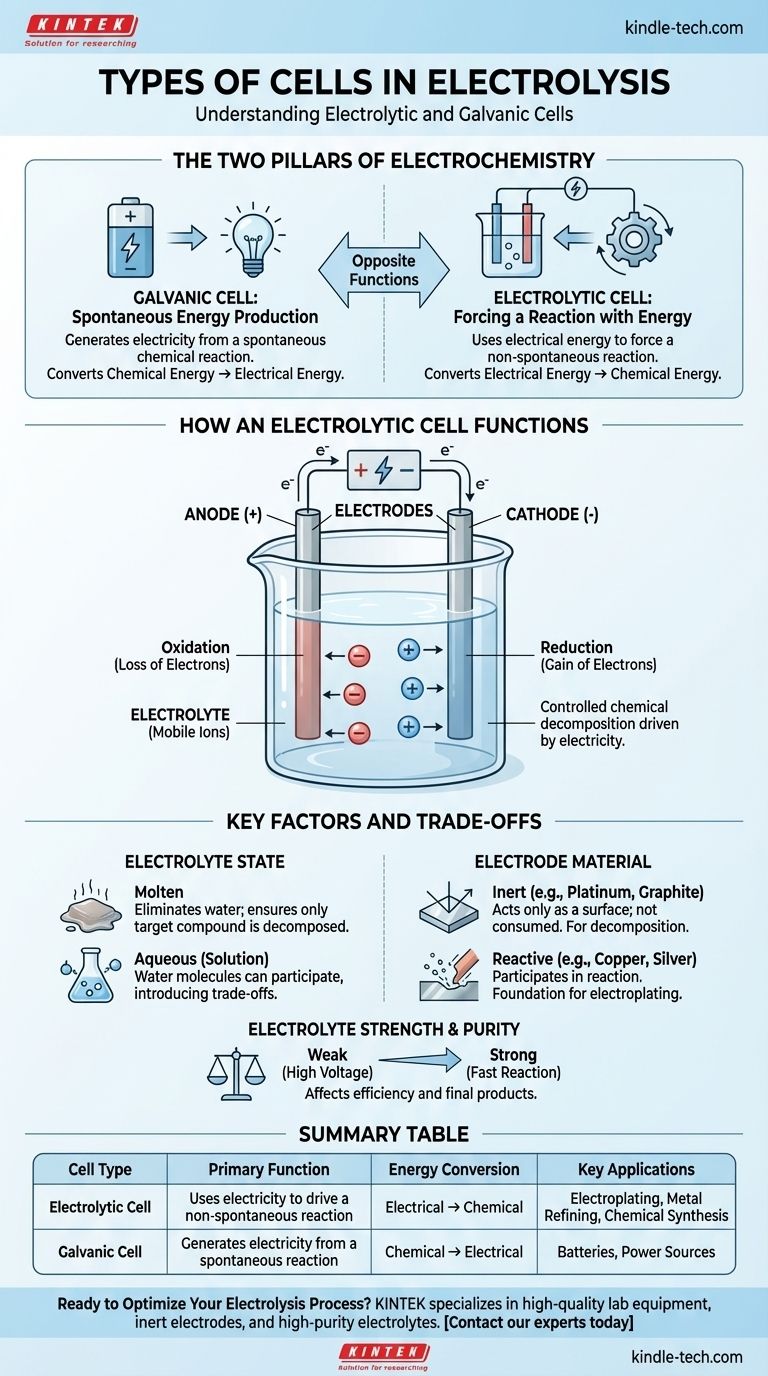
At its core, electrolysis occurs within a specific type of electrochemical cell known as an electrolytic cell. This cell is one of two fundamental types of electrochemical cells, the other being a galvanic cell. An electrolytic cell uses electrical energy to force a non-spontaneous chemical reaction, while a galvanic cell does the opposite, generating electricity from a spontaneous chemical reaction.
The critical distinction is purpose. A galvanic cell (like a battery) produces electricity from a chemical reaction. An electrolytic cell uses electricity to drive a chemical reaction that would not happen on its own.

The Two Pillars of Electrochemistry
To understand the cell used for electrolysis, you must first understand its counterpart. Both cell types are fundamental to electrochemistry, but they serve opposite functions.
The Galvanic Cell: Spontaneous Energy Production
A galvanic cell is what we commonly know as a battery. It harnesses a spontaneous chemical reaction that naturally wants to occur.
As this reaction proceeds, it releases energy in the form of an electric current. It directly converts stored chemical energy into electrical energy.
The Electrolytic Cell: Forcing a Reaction with Energy
An electrolytic cell is the engine of electrolysis. It is designed to make a non-spontaneous chemical reaction happen by supplying external energy.
You apply an electric current from an outside source (like a power supply) to the cell. This forces the decomposition of a substance, effectively converting electrical energy back into chemical energy by creating new substances.
How an Electrolytic Cell Functions
The process of electrolysis is a controlled chemical decomposition driven by electricity. This requires a few key components working in concert.
The Core Components
An electrolytic cell consists of two electrodes (a positive anode and a negative cathode) submerged in an electrolyte. An external power source is connected to these electrodes, creating a circuit.
The Role of the Electrolyte
The electrolyte is the substance that will be broken down. It is typically an ionic compound, either in a molten state or dissolved in a solution (aqueous).
This substance must contain mobile ions that are free to move and carry a charge. Electrolytes are generally solutions of acids, bases, or salts.
The Function of the Electrodes
The electrodes are the conductors through which electricity enters and leaves the electrolyte.
- Anode: The positive electrode. It attracts negative ions (anions), where oxidation (loss of electrons) occurs.
- Cathode: The negative electrode. It attracts positive ions (cations), where reduction (gain of electrons) occurs.
The external power source is what maintains this charge separation and drives the entire process.
Understanding the Key Factors and Trade-offs
The outcome of electrolysis is not automatic. The specific products you create depend entirely on the materials and conditions you choose.
Electrolyte State: Molten vs. Aqueous
The state of the electrolyte is a critical decision. If you use an aqueous solution (dissolved in water), the water molecules themselves can participate in the reaction.
This introduces a trade-off, as the electricity may split the water instead of the dissolved compound, depending on which reaction is easier to drive. Using a molten electrolyte eliminates water from the equation, ensuring only the target compound is decomposed.
Electrode Material: Inert vs. Reactive
Electrodes can be either passive participants or active players in the reaction.
- Inert Electrodes (e.g., Platinum, Graphite): These act only as a surface for the reaction to happen. They do not get consumed and are used when you want to decompose the electrolyte itself, such as splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Reactive Electrodes (e.g., Copper, Silver): These can dissolve or participate in the chemical reaction. This is the principle behind electroplating, where the anode dissolves and its metal ions are deposited onto the object at the cathode.
Electrolyte Strength and Purity
The efficiency of electrolysis is also influenced by the electrolyte. Strong electrolytes, which dissociate completely into ions, conduct electricity well and allow for a faster reaction.
Weak electrolytes require more energy (a higher voltage) to initiate and sustain the reaction. The presence of other oxidizing or reducing agents in the electrolyte can also alter the final products.
Applying This to Your Goal
Understanding the function of an electrolytic cell allows you to control chemical reactions for specific industrial and scientific purposes.
- If your primary focus is to produce a pure substance: Select an inert electrode and a high-purity electrolyte (molten or aqueous) to ensure you decompose the target compound, such as when producing aluminum from bauxite ore.
- If your primary focus is to coat or purify a metal: Use a reactive anode made of the coating material and an electrolyte containing ions of that same metal. This is the foundation of electroplating and electrorefining.
- If your primary focus is to generate electricity: You need a galvanic cell, not an electrolytic one, as its function is to release energy from a spontaneous reaction.
Ultimately, electrolysis provides a powerful method for using electrical energy to precisely control and drive chemical change.
Summary Table:
| Cell Type | Primary Function | Energy Conversion | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrolytic Cell | Uses electricity to drive a non-spontaneous reaction | Electrical → Chemical | Electroplating, Metal Refining, Chemical Synthesis |
| Galvanic Cell | Generates electricity from a spontaneous reaction | Chemical → Electrical | Batteries, Power Sources |
Ready to Optimize Your Electrolysis Process?
Understanding the right cell type and components is crucial for efficient electroplating, metal refining, or chemical synthesis. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including inert electrodes and high-purity electrolytes, to ensure your electrolytic processes are precise and effective.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover how our solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
- PTFE Electrolytic Cell Electrochemical Cell Corrosion-Resistant Sealed and Non-Sealed
People Also Ask
- How should the body of an electrolytic cell be maintained for longevity? Extend Your Equipment's Lifespan
- What is the proper way to handle a five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Ensure Accurate and Safe Electrochemical Experiments
- How should the five-port water bath electrolytic cell be operated during an experiment? Master Precise Control for Reliable Results
- How should the five-port water bath electrolytic cell be cleaned for maintenance? A Step-by-Step Guide to Reliable Results
- What are the proper storage procedures for the multifunctional electrolytic cell? Protect Your Investment and Ensure Data Accuracy