In short, PVD coatings are categorized by their primary function and resulting properties. The main types include general-purpose performance coatings for enhancing durability, decorative coatings for combining aesthetic appeal with toughness, and highly specialized films like Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) for extreme hardness and low friction. These are applied through various physical deposition processes in a vacuum, not to be confused with chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Choosing the right PVD coating is not about the coating itself, but about the problem you need to solve. The "best" type is the one whose specific properties—like hardness, lubricity, or color—directly address your application's demands for performance, longevity, or aesthetics.

What is PVD? A Foundational Overview
The Core Principle: Physical Deposition
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a vacuum coating process where a solid material is vaporized into a plasma of atoms or molecules. This vapor is then transported and deposited, atom by atom, onto a substrate, forming a thin, tightly bonded film.
This process is fundamentally different from Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which uses chemical reactions on the substrate surface to form a film. PVD is a physical line-of-sight process, while CVD can often coat more complex geometries.
Why PVD is Chosen
PVD coatings are selected for their exceptional physical properties. They are inherently hard, dense, and durable, offering significant resistance to wear, scratches, and corrosion. This unique combination of toughness and a thin application makes them ideal for improving the surface of a vast range of products without altering their underlying dimensions.
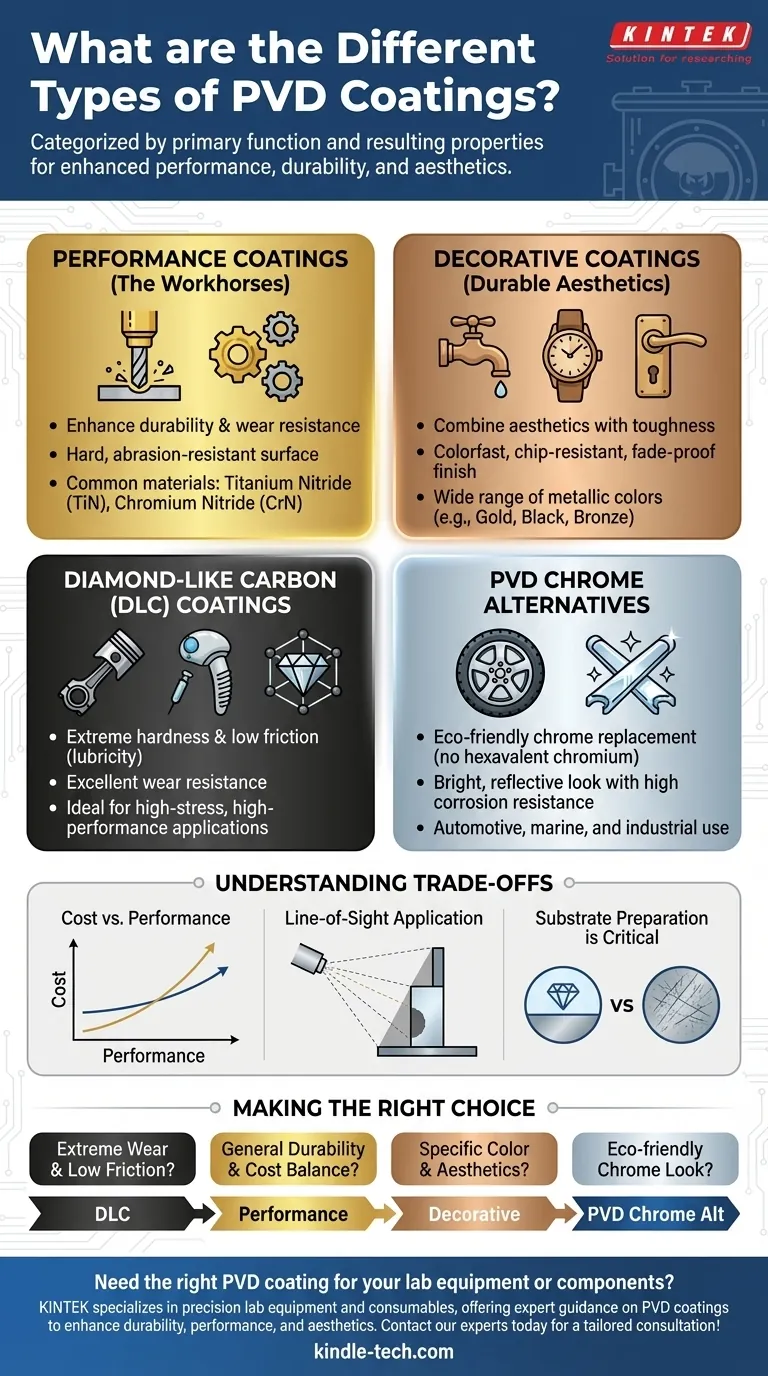
A Functional Guide to PVD Coating Types
The "type" of PVD coating is best understood by its intended function. The specific material used—such as Titanium Nitride or Chromium—determines the coating's final characteristics.
Performance Coatings (The Workhorses)
These are the most common PVD coatings, designed primarily to increase the service life of tools and components. They provide a hard, wear-resistant surface that protects against abrasion and corrosion.
Common applications include cutting tools, drills, molds, and engine components. Materials like Titanium Nitride (TiN) and Chromium Nitride (CrN) are staples in this category, offering a superb balance of cost and enhanced performance.
Decorative Coatings (Durable Aesthetics)
Often called durable-decorative coatings, this category focuses on achieving a specific color and finish while providing superior durability compared to paint or traditional plating.
These coatings can produce a wide range of metallic finishes, including brass, gold, black, and bronze. Because the color is an integral part of the coating's structure, it will not chip, fade, or tarnish. This makes it ideal for high-touch consumer products like faucets, watches, and architectural hardware.
Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) Coatings
DLC is a class of PVD coating that stands out for its extreme hardness, lubricity (low friction), and wear resistance, properties that approach those of natural diamond.
This makes DLC the go-to solution for high-performance applications where reducing friction and preventing wear are critical. You will find it on professional motorsport engine parts, high-end medical implants, and advanced cutting tools that operate under extreme stress.
PVD Chrome Alternatives
This category serves as a modern, environmentally friendly alternative to traditional electroplated hard chrome. Hexavalent chromium plating involves hazardous chemicals, which PVD processes eliminate entirely.
PVD chrome coatings provide the bright, reflective look of chrome but with superior hardness and corrosion resistance. It is an excellent choice for automotive, marine, and industrial applications seeking high performance and sustainability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a PVD coating requires balancing performance needs with practical constraints.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between a coating's performance level and its cost. A standard TiN performance coating is highly effective and economical. A more advanced DLC coating offers superior lubricity and hardness but at a significantly higher price point.
Line-of-Sight Application
Most PVD processes are "line-of-sight," meaning the coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This can make it challenging to achieve a uniform coating on parts with complex internal geometries or deep, narrow holes.
Substrate Preparation is Critical
A PVD coating is only as good as the surface it is applied to. The substrate must be impeccably clean and have the desired surface finish before coating. The process will not hide or fix underlying scratches, tool marks, or other surface imperfections.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal should dictate your choice. Use this as a guide to narrow down the best functional category for your needs.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear resistance and low friction: A Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coating is the superior choice for high-performance components.
- If your primary focus is improving tool life and general durability: A standard Performance Coating like TiN or CrN offers the best balance of cost and function.
- If your primary focus is a specific color with high durability: A Decorative PVD coating will provide the desired aesthetic without the risk of chipping or fading.
- If your primary focus is replacing traditional hard chrome: A PVD chrome alternative provides a similar look with enhanced performance and a better environmental profile.
Ultimately, understanding these categories empowers you to select a coating not just as a feature, but as a strategic solution to your engineering or design challenge.
Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Primary Function | Common Materials | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance Coatings | Enhance durability & wear resistance | TiN, CrN | Hard, abrasion-resistant, cost-effective |
| Decorative Coatings | Combine aesthetics with toughness | Various (gold, black, bronze) | Colorfast, chip-resistant, durable finish |
| Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) | Extreme hardness & low friction | Carbon-based | Ultra-hard, low friction, wear-resistant |
| PVD Chrome Alternatives | Eco-friendly chrome replacement | Chromium-based | Bright finish, high corrosion resistance |
Need the right PVD coating for your lab equipment or components? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance on PVD coatings to enhance durability, performance, and aesthetics for your laboratory applications. Let us help you select the ideal coating solution to extend the life of your tools and improve your results. Contact our experts today for a tailored consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Adjustable Height Flower Basket
People Also Ask
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- Is diamond coating permanent? The Truth About Its Long-Lasting Durability
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance













