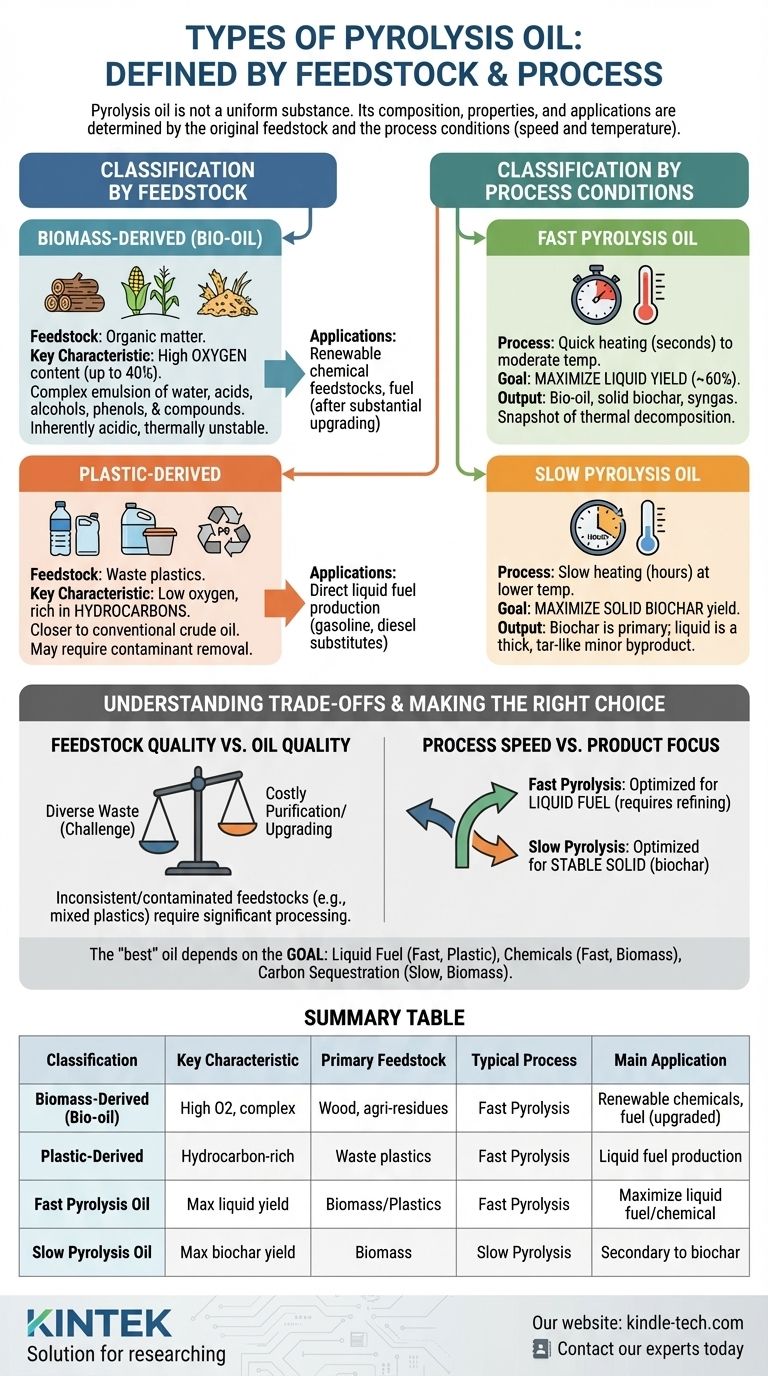
The primary types of pyrolysis oil are defined by two key factors: the original material used as feedstock (such as biomass or plastic) and the process conditions under which it was created (primarily fast or slow pyrolysis). These factors fundamentally determine the oil's chemical composition, physical properties, and potential applications.
The term "pyrolysis oil" does not refer to a single, uniform substance. Instead, think of it as a broad category of liquids whose characteristics are a direct reflection of what they were made from and how they were made. Understanding the source material and the process is essential to understanding the oil itself.

Classification by Feedstock
The single most important factor determining the nature of pyrolysis oil is the feedstock—the raw material that is heated in the absence of oxygen. The two main categories are biomass and plastic waste.
Biomass-Derived Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-oil)
This is the most common type, produced from organic matter like wood, agricultural residues, or other plant-based materials.
Its defining characteristic is a high oxygen content, which can be up to 40% by weight. This is because the original biomass itself contains a significant amount of oxygen.
This high oxygen level means bio-oil is not a simple hydrocarbon. It is a complex emulsion containing water, acids, alcohols, phenols, and hundreds of other oxygenated organic compounds.
Plastic-Derived Pyrolysis Oil
This type is produced from waste plastics, such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene.
Because plastics are primarily made of carbon and hydrogen, the resulting oil is much closer in composition to conventional crude oil. It has a low oxygen content and consists mainly of hydrocarbons.
This makes it a more direct candidate for refining into traditional liquid fuels like gasoline and diesel, though it may still require cleaning to remove contaminants from the original plastic waste.
Classification by Process Conditions
The speed and temperature of the pyrolysis process dramatically alter the final products. For oil production, fast pyrolysis is the dominant method.
Fast Pyrolysis Oil
This process involves heating the feedstock very quickly (in seconds) to moderate temperatures. It is designed to maximize the liquid yield.
A typical output from fast pyrolysis is approximately 60% liquid bio-oil, 20% solid biochar, and 20% synthesis gas (syngas). The resulting oil is a snapshot of the initial thermal decomposition products.
Slow Pyrolysis Oil
This process takes place over several hours at lower temperatures. Its primary goal is to maximize the solid biochar yield, which is a stable form of carbon.
Liquid oil is only a minor byproduct of slow pyrolysis and is often a thick, tar-like substance with a different chemical profile than fast pyrolysis oil due to the longer reaction times.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a feedstock and process involves critical trade-offs that impact the final product's viability and use.
Feedstock Quality vs. Oil Quality
The great advantage of pyrolysis is its ability to process diverse waste streams. However, this is also a challenge.
Inconsistent or contaminated feedstocks (like mixed plastic waste) will produce an oil that requires significant, and often costly, purification and upgrading before it can be used. Biomass creates a highly oxygenated oil that is inherently acidic, corrosive, and thermally unstable, requiring substantial processing to become a drop-in fuel.
Process Speed vs. Product Focus
The choice between fast and slow pyrolysis is a choice of primary product.
Fast pyrolysis is optimized for liquid fuel production, but this liquid is chemically complex and requires further refining. Slow pyrolysis is optimized for creating a stable solid (biochar), treating the liquid and gas as secondary energy products.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" type of pyrolysis oil depends entirely on the intended application.
- If your primary focus is producing a liquid fuel substitute: Fast pyrolysis of waste plastics is the most direct pathway to a hydrocarbon-rich oil that resembles conventional fossil fuels.
- If your primary focus is creating renewable chemical feedstocks: Fast pyrolysis of biomass generates bio-oil rich in valuable oxygenated compounds that can be extracted, though this is a complex chemical engineering challenge.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration or soil improvement: Slow pyrolysis is the superior process, as its main product is stable biochar, with oil being a secondary byproduct.
Ultimately, navigating the world of pyrolysis requires seeing the final oil not as a single product, but as the direct outcome of deliberate feedstock and process choices.
Summary Table:
| Classification | Key Characteristic | Primary Feedstock | Typical Process | Main Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomass-Derived (Bio-oil) | High oxygen content, complex mixture | Wood, agricultural residues | Fast Pyrolysis | Renewable chemicals, fuel (after upgrading) |
| Plastic-Derived | Hydrocarbon-rich, resembles crude oil | Waste plastics (PE, PP, PS) | Fast Pyrolysis | Liquid fuel production |
| Fast Pyrolysis Oil | Maximizes liquid yield (~60%) | Biomass or Plastics | Fast Pyrolysis | Maximizing liquid fuel/chemical output |
| Slow Pyrolysis Oil | Byproduct, maximizes biochar yield | Biomass | Slow Pyrolysis | Secondary to biochar production |
Ready to select the ideal pyrolysis process for your lab's research or production goals? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis applications. Whether you are developing biofuels from biomass, converting plastic waste, or optimizing biochar production, our expertise and reliable equipment can help you achieve precise and reproducible results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and drive your projects forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
- Laboratory High Throughput Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
People Also Ask
- How does a rotary extractor work? Master Continuous High-Volume Solid Processing
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- What is the meaning of rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- What is the drying zone in a rotary kiln? Boost Efficiency with Modern Drying Solutions
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker















