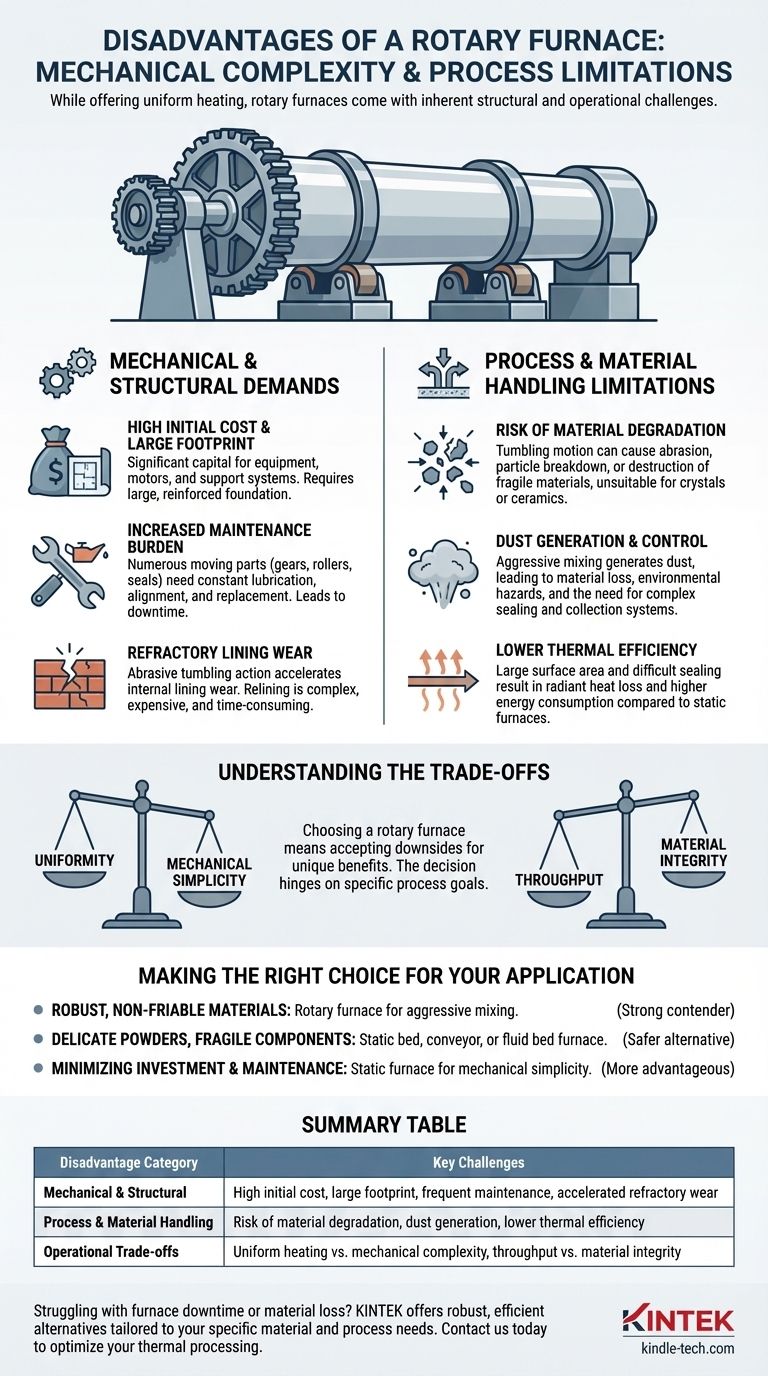
While rotary furnaces excel at uniform heating, their primary disadvantages stem directly from their mechanical complexity and the dynamic nature of their operation. These challenges manifest as higher maintenance demands, potential for material degradation, and significant operational costs compared to simpler, static furnace designs.
The core trade-off of a rotary furnace is clear: you gain superior material mixing and temperature uniformity at the cost of increased mechanical complexity, higher maintenance, and the risk of damaging the material being processed.

The Mechanical and Structural Demands
The design of a rotary furnace introduces several inherent structural and maintenance challenges that are not present in static alternatives.
High Initial Cost and Large Footprint
A rotary furnace is a significant piece of capital equipment. Its long cylindrical body, coupled with the motors, gears, and support wheel systems required for rotation, results in a high initial purchase and installation cost.
These systems also demand a substantial physical footprint, requiring a large, reinforced foundation to support the weight and dynamic loads of the rotating vessel.
Increased Maintenance Burden
Unlike a static furnace, a rotary furnace contains numerous moving parts. The drive gear, support rollers, and seals at the feed and discharge ends are all subject to constant mechanical stress and wear.
This necessitates a rigorous preventative maintenance schedule to manage lubrication, alignment, and component replacement, leading to increased downtime and operational costs over the furnace's lifespan.
Refractory Lining Wear
The constant tumbling of material inside the furnace creates an abrasive environment. This action accelerates the wear and tear on the internal refractory lining far more than in a static furnace.
Relining a rotary furnace is a complex, time-consuming, and expensive procedure that represents a significant long-term operational cost.
Process and Material Handling Limitations
The very action that provides uniform heating—the tumbling motion—can be a major drawback for certain materials and processes.
Risk of Material Degradation
The tumbling motion is not suitable for all materials. It can easily cause abrasion, particle breakdown, or outright destruction of fragile or friable substances.
This makes rotary furnaces a poor choice for delicate crystals, certain ceramic components, or any material where maintaining a specific particle size and shape is critical.
Dust Generation and Control
The aggressive mixing action inevitably generates dust, especially when processing powders or granular materials.
This creates several problems, including material loss, potential environmental and safety hazards, and the need for complex sealing and dust collection systems, which add to the furnace's cost and complexity.
Lower Thermal Efficiency
The large, rotating shell of the furnace has a massive surface area, leading to significant radiant heat loss. Furthermore, achieving a perfect, gas-tight seal at the inlet and outlet of a rotating tube is notoriously difficult.
These factors often result in lower overall thermal efficiency and higher energy consumption compared to a well-sealed and insulated static furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a rotary furnace means consciously accepting its downsides to gain its unique benefits. The decision is not about which furnace is "best," but which presents the right set of compromises for your specific goal.
Uniformity vs. Mechanical Simplicity
The primary benefit of a rotary furnace is unparalleled temperature uniformity and material mixing. However, this is achieved through a complex mechanical system. A static box or conveyor furnace offers mechanical simplicity and lower maintenance but cannot match the mixing intensity.
Throughput vs. Material Integrity
A continuous rotary furnace can offer high throughput for bulk materials. The trade-off is the constant risk of abrasion and particle degradation. If preserving the physical integrity of your material is the top priority, the potential for damage during processing may be an unacceptable risk.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your material properties and process goals are the ultimate guide to selecting the appropriate thermal processing equipment.
- If your primary focus is processing robust, non-friable materials that require aggressive mixing: A rotary furnace is likely a strong contender, as its core strength aligns perfectly with your needs.
- If your primary focus is processing delicate powders, fragile components, or materials sensitive to abrasion: The risk of material degradation makes a static bed, conveyor, or fluid bed furnace a much safer alternative.
- If your primary focus is minimizing capital investment, maintenance costs, and operational complexity: The mechanical simplicity and lower upkeep of a static furnace design will be more advantageous.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace requires a clear understanding of the trade-offs inherent in its design and how they align with your specific process requirements.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Challenges |
|---|---|
| Mechanical & Structural | High initial cost, large footprint, frequent maintenance, accelerated refractory wear |
| Process & Material Handling | Risk of material degradation, dust generation, lower thermal efficiency |
| Operational Trade-offs | Uniform heating vs. mechanical complexity, throughput vs. material integrity |
Struggling with furnace downtime or material loss? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering robust, efficient alternatives tailored to your specific material and process needs. Whether you require gentle handling for delicate materials or a low-maintenance static furnace solution, our experts can help you optimize your thermal processing. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's productivity and reduce operational costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a rotary kiln reactor? A Guide to Industrial Thermal Processing
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the meaning of rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding



















