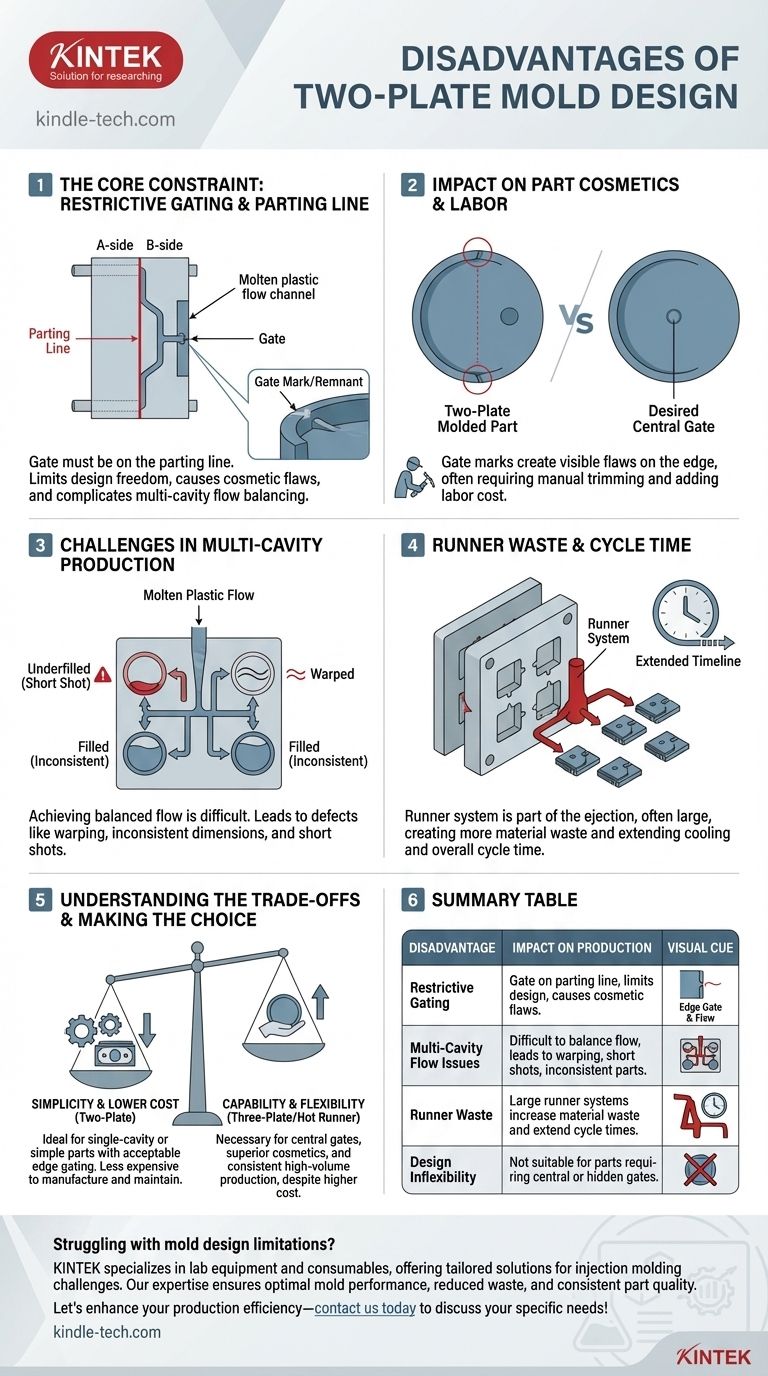
The primary disadvantages of a two-plate mold are its restrictive gating options and the significant challenges it creates for multi-cavity layouts. Because the gate must be located on the mold's parting line, it limits design freedom, can create cosmetic blemishes on the part, and makes it difficult to achieve balanced plastic flow across multiple cavities.
While valued for its simplicity and lower initial cost, a two-plate mold's design is inherently inflexible. This simplicity comes at the cost of control over gate location and runner efficiency, which can compromise part quality and production consistency, especially in complex applications.

The Core Constraint: Gating and the Parting Line
A two-plate mold is the most basic form of injection mold, consisting of two main plates, the A-side and B-side, that meet at a single parting line. The simplicity of this design is its greatest strength and the source of its main limitations.
The Inflexible Gate Location
In a two-plate mold, the channel that allows molten plastic to enter the part cavity, known as the gate, must be located directly on this parting line.
This means the gate can only be placed on the outer perimeter or edge of the molded part. There is no design freedom to place the gate in the center or on a non-visible surface away from the edge.
Impact on Part Cosmetics
The point where the gate connects to the part leaves a small mark or remnant after it is removed.
Because a two-plate mold forces this gate mark onto the edge of the part, it can create a cosmetic flaw. This often requires a secondary manual trimming operation, which adds labor cost and time to the manufacturing process.
Challenges in Multi-Cavity Production
These limitations are magnified when producing multiple parts in a single cycle (a multi-cavity mold). The runner system, which distributes plastic to each cavity, is also confined to the parting line.
Difficulty in Balancing Flow
In a multi-cavity layout, achieving a balanced flow—where all cavities fill at the same time and pressure—is a critical design challenge.
With the runners restricted to the parting line, the path to some cavities is often longer than to others. This imbalance can cause a host of molding defects, including warping, inconsistent dimensions, and short shots (incomplete parts).
Runner Waste and Cycle Time
The runner system is ejected from the mold along with the parts after each cycle.
In a two-plate design, especially with multiple cavities, this runner can be large and complex. This not only creates more wasted material but can also extend the cooling time required, thereby increasing the overall production cycle time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision to use a two-plate mold is a classic engineering trade-off between simplicity and capability. Its limitations do not make it a poor choice, but they must be weighed against the project's specific requirements.
Where Simplicity Wins
For single-cavity molds, or for parts where an edge gate is cosmetically and functionally acceptable, the two-plate design is ideal. Its construction is simpler, making it less expensive to manufacture and easier to maintain than more complex alternatives.
The Cost of Inflexibility
If your part requires a central gate for structural integrity or cosmetic reasons (e.g., a pin-point gate on a round part), a two-plate mold is simply not a viable option. The design does not allow for it.
The Three-Plate Mold Alternative
The primary alternative is a three-plate mold. By introducing a third plate and a second parting line, this design allows the gate to be located almost anywhere on the part's surface. This solves the cosmetic and flow issues but comes at the cost of higher mold complexity and expense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct mold type requires aligning the design's capabilities with your project's priorities.
- If your primary focus is minimizing upfront tooling cost: A two-plate mold is often the most economical choice, especially for simpler parts where edge gating is acceptable.
- If your primary focus is superior part cosmetics: A three-plate or hot runner mold is necessary to position the gate on a non-visible surface, away from the parting line.
- If your primary focus is consistent, high-volume production: Carefully weigh the flow-balancing challenges of a two-plate design; a more complex mold often provides better part-to-part consistency and may prove more economical in the long run.
Understanding these fundamental trade-offs empowers you to select a mold design that aligns with your part's specific functional, cosmetic, and production requirements.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Impact on Production |
|---|---|
| Restrictive Gating | Gate must be on parting line, limiting design freedom and causing cosmetic flaws. |
| Multi-Cavity Flow Issues | Difficult to balance plastic flow, leading to warping, short shots, and inconsistent parts. |
| Runner Waste | Large runner systems increase material waste and extend cycle times. |
| Design Inflexibility | Not suitable for parts requiring central or hidden gates. |
Struggling with mold design limitations? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering tailored solutions for injection molding challenges. Our expertise ensures optimal mold performance, reduced waste, and consistent part quality. Let’s enhance your production efficiency—contact us today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Cylindrical Press Mold for Lab Applications
- No Demolding Lab Infrared Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Stirring Bar Recovery Rod
People Also Ask
- What is the function of high-strength pressure molds for nanostructured copper powders? Achieve High Purity Densification
- How do steel molds and hydraulic equipment collaborate for high-density molding? Optimize WC/Cu FGM Green Body Prep
- How does a Hot Isostatic Press (HIP) improve W-Cu densification? Achieve Near-Theoretical Density with High Pressure
- How do high-precision molds contribute to Li6PS5Cl electrolyte membrane formation? Achieve Perfect Density and Thickness
- What are the factors affecting molding? Master the 4 Keys to Perfect Plastic Parts
















