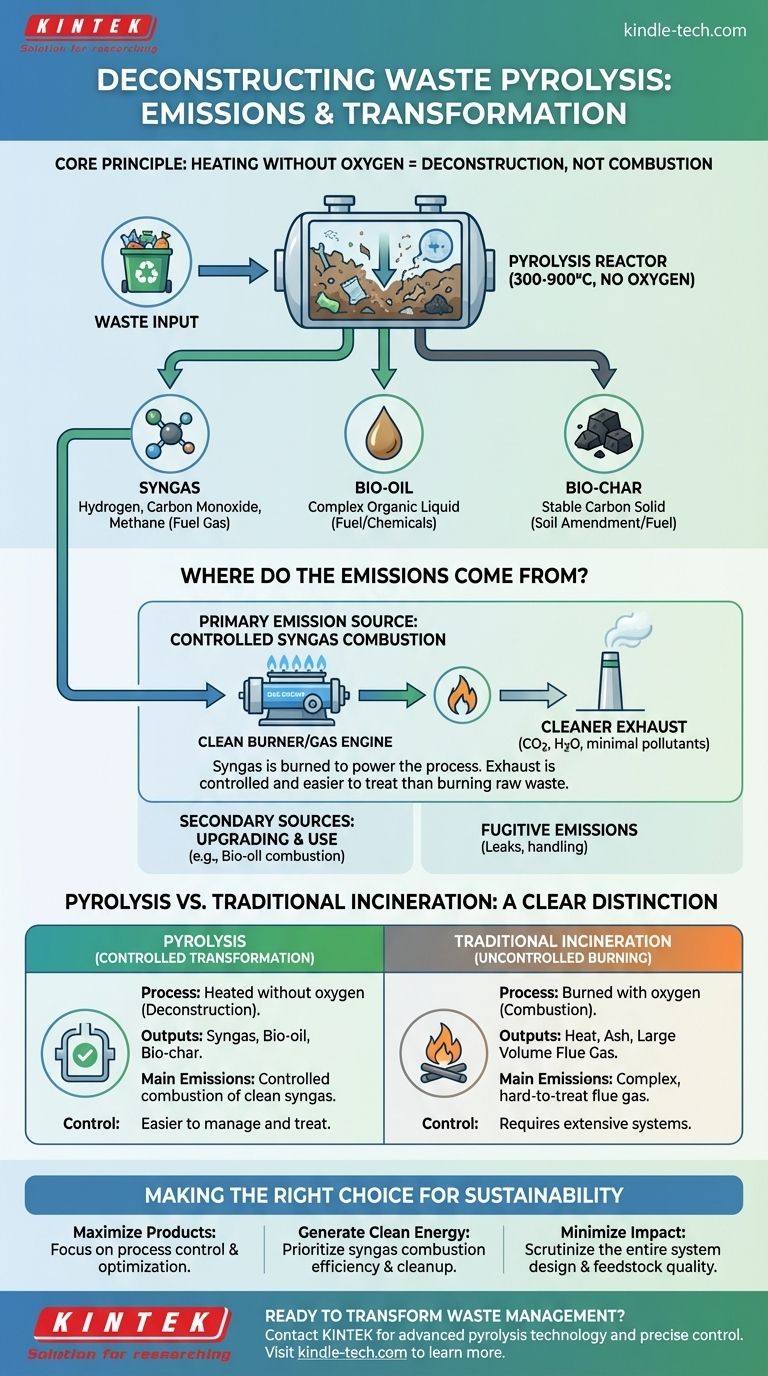
In essence, waste pyrolysis does not produce "emissions" in the traditional sense of smoke or flue gas from combustion. Instead, it is a thermochemical process that operates without oxygen, breaking down waste into three distinct, valuable products: a solid biochar, a liquid bio-oil, and a combustible gas called syngas. The actual atmospheric emissions depend entirely on how these captured products, particularly the syngas, are subsequently used or processed.
The critical distinction to understand is that pyrolysis transforms waste into controlled, usable outputs, whereas incineration burns waste to produce ash and a large volume of flue gas that must be treated. The "emissions" from a pyrolysis plant are primarily from the controlled combustion of its own clean syngas to power the process itself.

Deconstructing Pyrolysis: Transformation, Not Combustion
To understand the emissions profile of pyrolysis, you must first understand that its goal is fundamentally different from burning. It doesn't destroy waste; it deconstructs it at a molecular level.
The Core Principle: Heating Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis involves heating waste materials to high temperatures (typically 300-900°C) in a sealed, oxygen-free reactor. The absence of oxygen is crucial because it prevents combustion from occurring.
Instead of burning and releasing pollutants, the heat breaks the complex molecules in the waste into simpler, more stable components.
The Three Primary Product Streams
The process consistently separates the input waste into three distinct streams, each with its own properties and potential uses.
- Solid (Biochar): This stable, carbon-rich solid is similar to charcoal. It can be used as an agricultural soil amendment, for filtration, or pressed into briquettes for fuel.
- Liquid (Bio-oil): This dense, dark liquid is a complex mixture of organic compounds. It can be refined into transportation fuels like biodiesel or used directly as an industrial heating oil.
- Gas (Syngas): This is a mix of non-condensable, flammable gases, primarily composed of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane. This gas is rarely released into the atmosphere.
So, Where Do the Actual Emissions Come From?
While the core pyrolysis process is enclosed, a modern pyrolysis facility does have emission points. These are almost always related to the subsequent use of the products it creates.
The Primary Source: Internal Combustion of Syngas
The most significant feature of a modern pyrolysis plant is that it is often self-sustaining. The syngas produced during the process is captured and piped to a burner or gas engine.
The combustion of this syngas generates the heat required to run the pyrolysis reactor. The exhaust from this controlled combustion is the plant's main emission point, but it is far cleaner and easier to manage than the exhaust from burning raw, unsorted waste.
Secondary Sources: Upgrading and Use
If the bio-oil is combusted on-site for additional energy or transported for use as a fuel in an external boiler or engine, its combustion will produce emissions, similar to those from heavy fuel oil.
Additionally, small "fugitive emissions" can occur from minor leaks or during the handling and transport of the raw waste and finished products.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Pyrolysis is not a magic bullet. Its environmental performance is highly dependent on design, operation, and the material being processed.
Feedstock Quality is Paramount
The composition of the input waste directly affects the quality of the outputs. Contaminants like heavy metals, chlorine from plastics (PVC), and sulfur can become concentrated in the biochar or bio-oil. A "clean" feedstock like untreated wood will yield a much cleaner set of products than mixed municipal solid waste.
Process Control Defines Performance
The efficiency of the gas capture system and the precision of temperature control are critical. A well-designed, state-of-the-art facility will have minimal fugitive emissions and highly efficient syngas combustion with post-treatment. A poorly operated plant could have a significantly worse environmental footprint.
Pyrolysis vs. Incineration: A Clear Distinction
The key difference lies in control. Incineration combines thousands of different materials in an oxygen-rich environment, creating a complex and difficult-to-treat flue gas. Pyrolysis first separates the waste into three simpler, more uniform streams, allowing for much cleaner and more controlled energy generation from the gas stream.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating pyrolysis, your primary objective will determine what you need to focus on.
- If your primary focus is creating valuable products from waste: Prioritize a process that allows for precise temperature control to optimize the yield and quality of either the bio-oil or biochar.
- If your primary focus is generating clean energy: The most important factor is the efficiency of the syngas combustion system and the associated flue gas treatment technology.
- If your primary focus is minimizing environmental impact: Scrutinize the entire system, from feedstock pre-sorting to remove contaminants to the design of the sealed reactor and the quality of the syngas cleanup and combustion process.
Ultimately, pyrolysis shifts the paradigm from waste "disposal" to resource "recovery," with its environmental performance depending directly on the quality of the system's engineering and operation.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Pyrolysis | Traditional Incineration |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Heated without oxygen (deconstruction) | Burned with oxygen (combustion) |
| Primary Outputs | Syngas, Bio-oil, Bio-char | Heat, Ash, Flue Gas |
| Main Emission Source | Controlled combustion of clean syngas | Complex, hard-to-treat flue gas |
| Emissions Control | Easier to manage and treat | Requires extensive gas cleaning systems |
Ready to transform your laboratory's waste management with advanced pyrolysis technology?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including pyrolysis systems, that enable precise control and efficient resource recovery. Our solutions help you minimize environmental impact while creating valuable products from waste streams.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how KINTEK's expertise can support your laboratory's sustainability and research goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy



















