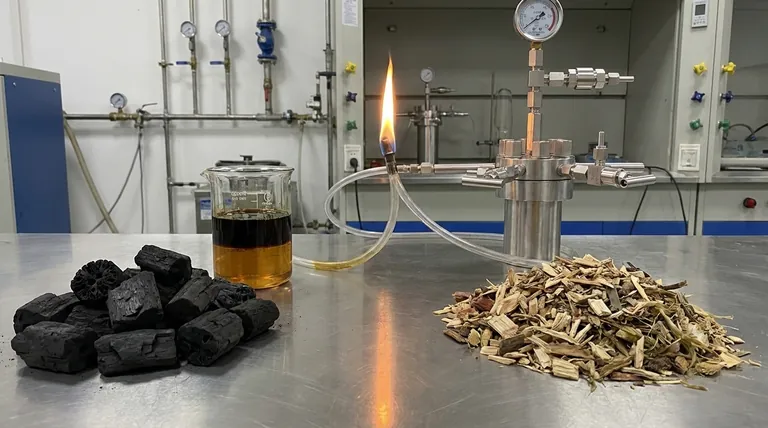
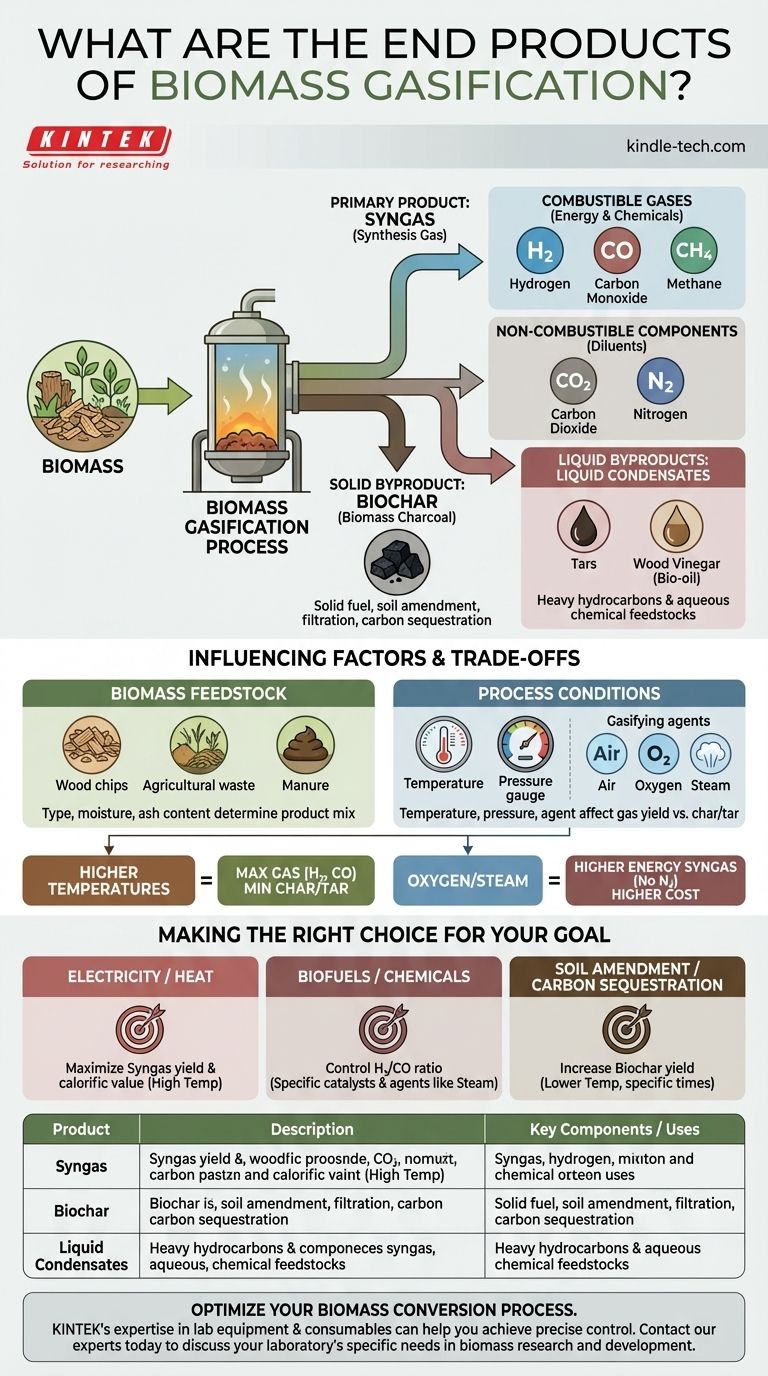
The primary end products of biomass gasification are a combustible fuel gas mixture known as syngas, a solid carbon-rich residue called biochar, and liquid condensates including tar and wood vinegar. The specific composition and ratio of these products are not fixed; they are a direct result of the type of biomass used and the precise conditions of the gasification process.
Biomass gasification is not a single-output process but a thermochemical conversion that yields a portfolio of products. The true value lies in understanding how to control the process to optimize the desired output—whether it's high-quality fuel gas, valuable solid charcoal, or other chemical feedstocks.

The Primary Product: Syngas
Syngas (synthesis gas) is the main gaseous output and the primary target for most energy-focused gasification systems. Its composition is a mix of valuable and inert components.
Combustible Gases (H₂, CO, CH₄)
The energy value of syngas comes from its combustible components.
- Hydrogen (H₂): A clean-burning, high-energy fuel and a critical feedstock for producing chemicals like ammonia and methanol.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): A combustible gas that also serves as a key building block in chemical synthesis.
- Methane (CH₄): The principal component of natural gas. Its presence increases the heating value of the syngas.
Non-Combustible Components (CO₂, N₂)
These gases are also present and act as diluents, affecting the overall energy density of the syngas.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): An unavoidable byproduct of combustion and gasification reactions.
- Nitrogen (N₂): If air is used as the gasifying agent (the cheapest and most common method), nitrogen will make up a significant portion of the syngas, lowering its energy content per unit of volume.
Solid and Liquid Byproducts
While syngas is often the focus, the solid and liquid outputs have significant value and potential applications of their own.
Biochar (Biomass Charcoal)
Biochar is the stable, carbon-rich solid that remains after the volatile components of the biomass have been vaporized. It is not waste; it can be used as a solid fuel, a filtration medium, or a powerful soil amendment that improves water retention and sequesters carbon in the ground.
Tars and Wood Vinegar (Bio-oil)
As the hot syngas cools, various organic compounds condense into a complex liquid mixture, often separated into tar and pyroligneous acid (wood vinegar). Tars are heavy hydrocarbons, while wood vinegar is an aqueous solution containing acetic acid, methanol, and other chemicals.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Influencing Factors
You cannot get maximum yields of all products simultaneously. The output is a direct result of a series of trade-offs controlled by the process conditions.
The Impact of Biomass Feedstock
The type of biomass used—whether it's wood chips, agricultural waste, or manure—directly influences the product mix. Factors like moisture content, ash content, and chemical makeup determine how efficiently the material will convert to gas versus char.
The Critical Role of Process Conditions
The operator's main levers for controlling the output are temperature, pressure, and the gasifying agent (air, oxygen, or steam).
- Higher temperatures generally favor the production of H₂ and CO, maximizing gas yield while minimizing char and tar.
- Using pure oxygen or steam instead of air eliminates nitrogen dilution, producing a higher-energy syngas, but at a significantly higher operational cost.
The Challenge of Tars
Tars are a notorious operational challenge in biomass gasification. This sticky, complex substance can condense in pipes and on equipment, causing blockages and requiring costly and complex gas cleanup systems before the syngas can be used in engines or turbines.
Economic Viability
A key challenge for biomass gasification is achieving cost-effective operation at smaller, decentralized scales. Unlike massive fossil-fuel refineries, biomass systems must be economically viable while processing local, often variable, feedstocks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal product mix depends entirely on your end-use application. You must define your primary objective to optimize the process correctly.
- If your primary focus is generating electricity or heat: You should aim to maximize the yield and calorific value of the syngas, which typically involves operating at high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid biofuels or chemicals: You need to carefully control the H₂/CO ratio within the syngas, which often requires specific catalysts and gasifying agents like steam.
- If your primary focus is soil amendment and carbon sequestration: You would operate at lower temperatures and with specific residence times to increase the yield of stable, high-quality biochar.
By understanding these variables, you can transform biomass from a simple material into a targeted source of energy and valuable products.
Summary Table:
| Product | Description | Key Components / Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Syngas | Main gaseous fuel mixture | H₂, CO, CH₄ (for energy/chemicals) |
| Biochar | Solid carbon-rich residue | Solid fuel, soil amendment, filtration |
| Liquid Condensates | Tar and wood vinegar (bio-oil) | Chemical feedstocks |
Ready to optimize your biomass conversion process? Whether your goal is to maximize syngas for energy, produce high-quality biochar, or develop a system for chemical feedstocks, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables can help you achieve precise control over your gasification parameters. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs in biomass research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a constant temperature hydrothermal reactor? Master Coal Fly Ash Activation
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature hydrothermal reactor? Enhance Iodine@Activated Carbon Cathode Synthesis
- How does a high-pressure reactor demonstrate its value in accelerated aging? Predict Catalyst Durability Fast
- Why are high-pressure autoclaves essential for preparing bio-based polyamide curing agents from dimeric acid?
- What is the purpose of using high-purity argon gas in a high-pressure reactor? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Data


















