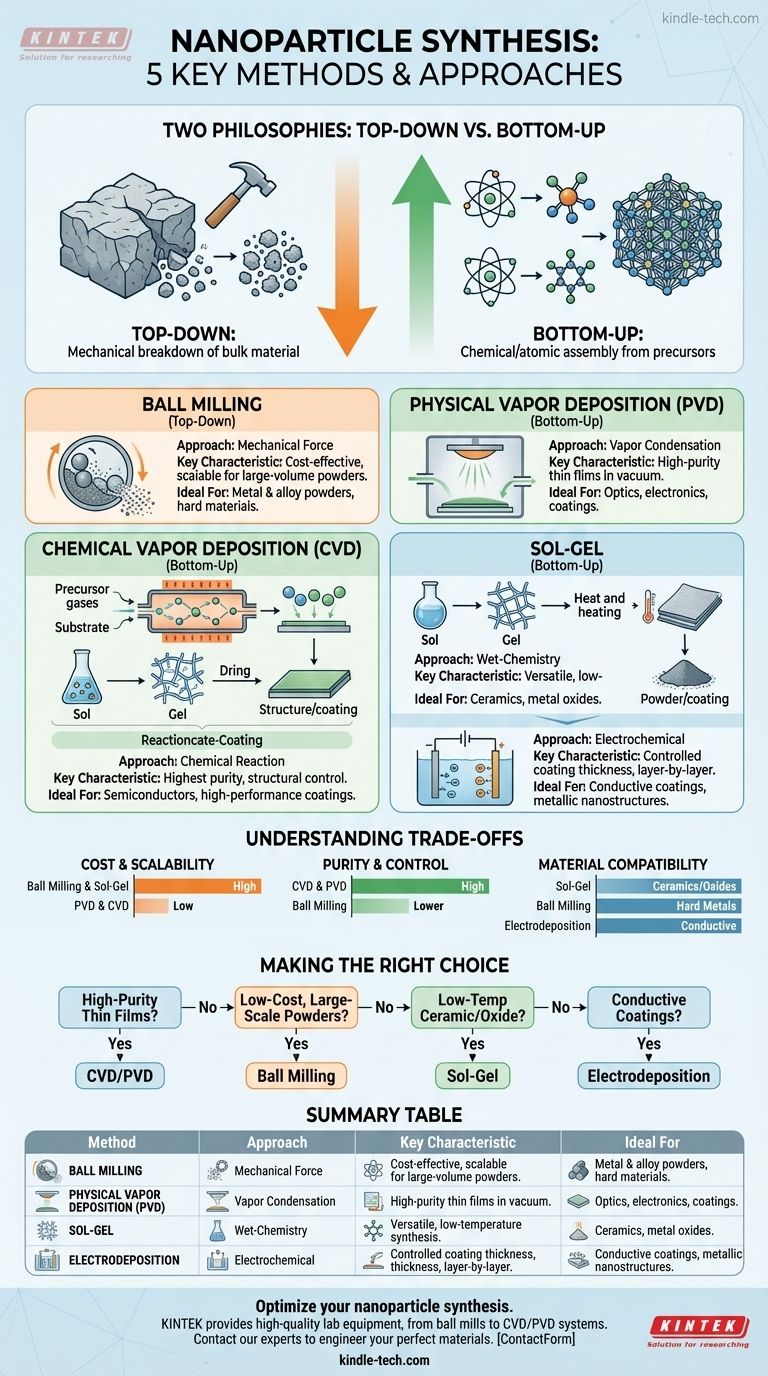
In nanoparticle synthesis, there are five commonly cited methods for producing nanomaterials. These are broadly categorized as either "top-down" or "bottom-up" approaches and include Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), Sol-Gel synthesis, Electrodeposition, and Ball Milling. Each method offers a distinct pathway to creating materials at the nanoscale.
The core distinction in nanoparticle synthesis is not just the method, but the fundamental approach: are you breaking down a larger material (top-down), or are you building nanoparticles from individual atoms and molecules (bottom-up)? This choice dictates the cost, purity, and ultimate properties of the final material.
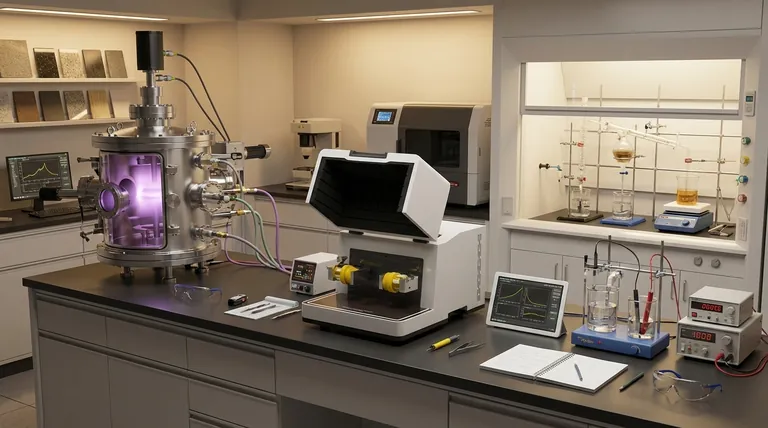

Top-Down vs. Bottom-Up: Two Philosophies of Creation
Understanding nanoparticle synthesis begins with its two guiding principles. These are not specific techniques but rather the overarching strategies that all methods follow.
The Top-Down Approach
This is the mechanical strategy. You start with a large, bulk material and break it down into smaller and smaller pieces until you reach the nanoscale. It is conceptually simple, like a sculptor carving a statue from a block of marble.
The Bottom-Up Approach
This is the chemical or atomic strategy. You start with atomic or molecular precursors and systematically build them up into a more complex nanoparticle. This is like a bricklayer constructing a wall one brick at a time, offering greater control over the final structure.
A Closer Look at Synthesis Methods
The five methods fall into one of these two categories. Ball Milling is a classic top-down method, while the other four are examples of bottom-up construction.
Ball Milling: The Mechanical Force Method (Top-Down)
Ball milling is a mechanical attrition process. A bulk material is placed in a container with heavy, hard milling balls. The container is then rotated at high speed, causing the balls to collide with and grind the material down into nanosized particles.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): The Condensation Method (Bottom-Up)
PVD involves vaporizing a solid source material in a vacuum. The resulting atoms or molecules travel through the vacuum chamber and condense onto a substrate, forming a thin film of nanoparticles. Think of it like water vapor condensing on a cold mirror.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The Reaction Method (Bottom-Up)
CVD is similar to PVD but adds a layer of chemistry. Precursor gases are introduced into a reaction chamber where they react or decompose on a heated substrate. This chemical reaction forms a high-purity solid film on the substrate's surface, offering exceptional control over the material's composition.
Sol-Gel: The Wet-Chemistry Method (Bottom-Up)
This method begins with a chemical solution, or "sol," containing molecular precursors. Through a series of chemical reactions, these molecules link together to form a gel-like network. After drying and heat treatment, this gel is converted into a high-purity nanopowder or coating.
Electrodeposition: The Electrochemical Method (Bottom-Up)
Also known as electroplating, this process uses an electric current passed through a solution containing ions of the desired material. The current causes these ions to deposit onto a conductive surface (the cathode), building up a thin film or coating of nanomaterial layer by layer.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Method vs. Outcome
No single synthesis method is universally superior. The optimal choice is always dictated by the desired properties of the final nanoparticle and the constraints of the project.
Cost and Scalability
Ball milling and sol-gel processes are often more cost-effective and easier to scale for large-volume production of nanopowders. In contrast, PVD and CVD require expensive vacuum equipment, making them better suited for high-value, high-performance coatings.
Purity and Structural Control
CVD offers the highest level of control over purity and crystal structure, making it ideal for electronics and semiconductors. PVD also provides high purity. Methods like ball milling can introduce impurities from the milling media and produce a wider range of particle sizes.
Material Compatibility
The choice of method is heavily dependent on the material. Sol-gel is excellent for creating metal oxides and ceramics at low temperatures. Ball milling is effective for hard metals and alloys. Electrodeposition is limited to conductive materials that can be plated from a solution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a synthesis method requires matching the technique's strengths to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-purity thin films for optics or electronics: CVD and PVD provide the atomic-level control necessary for these demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, large-scale production of metal or alloy powders: Ball milling is a straightforward and industrially scalable top-down approach.
- If your primary focus is versatile, low-temperature synthesis of ceramic or oxide nanoparticles: The sol-gel method offers excellent chemical flexibility and control over particle properties.
- If your primary focus is creating conductive coatings or metallic nanostructures on a surface: Electrodeposition is a highly effective and controlled bottom-up method.
Ultimately, mastering nanoparticle synthesis means understanding that the process you choose directly engineers the properties you get.
Summary Table:
| Method | Approach | Key Characteristic | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ball Milling | Top-Down | Mechanical grinding of bulk material | Cost-effective, large-scale metal/alloy powders |
| Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Bottom-Up | Vapor condensation in a vacuum | High-purity thin films for optics/electronics |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Bottom-Up | Chemical reaction of gases on a substrate | Highest purity & structural control (e.g., semiconductors) |
| Sol-Gel | Bottom-Up | Chemical solution forming a gel network | Versatile, low-temperature synthesis of ceramics/oxides |
| Electrodeposition | Bottom-Up | Electric current deposits ions from solution | Conductive coatings & metallic nanostructures |
Need to choose the right nanoparticle synthesis method for your research or production? The method you select directly impacts the cost, purity, and performance of your final nanomaterial. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for these advanced synthesis techniques, from robust ball mills to precision CVD/PVD systems. Let our experts help you engineer the perfect material properties for your application. Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and find the optimal solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Laboratory Jar Ball Mill with Alumina Zirconia Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory High Throughput Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- Hybrid High Energy Vibratory Ball Mill for Lab Use
- Low-Temperature Water-Cooled Touchscreen Vibratory Ultrafine Pulverizer
People Also Ask
- Why is grinding important in sample preparation? Ensure Accurate & Reliable Analytical Results
- Why grinding is important in laboratory techniques? Ensure Accurate & Reproducible Results
- How full should a ball mill be? Achieve Peak Grinding Efficiency with the 50% Rule
- How much balls should be loaded in a ball mill for working? Optimize Grinding with the Correct Ball Charge
- How does particle size affect XRF? Achieve Accurate and Repeatable Elemental Analysis



















