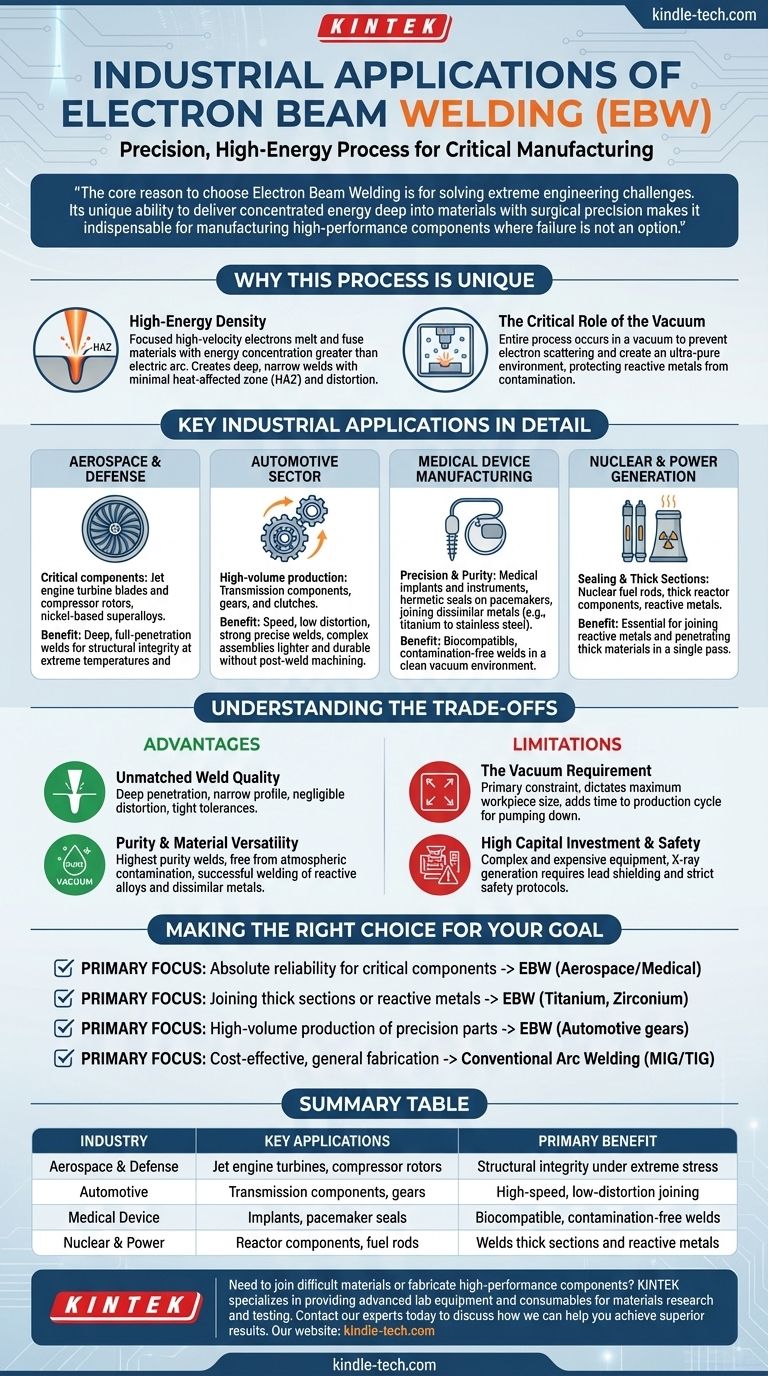
In short, Electron Beam Welding (EBW) is a high-energy, precision process used for critical applications in the aerospace, automotive, medical, and nuclear industries. It excels where deep welds, minimal distortion, and the joining of difficult-to-weld or dissimilar materials are required, leveraging a focused beam of electrons in a vacuum to produce superior quality joints.
The core reason to choose Electron Beam Welding is not for general fabrication, but for solving extreme engineering challenges. Its unique ability to deliver concentrated energy deep into materials with surgical precision makes it indispensable for manufacturing high-performance components where failure is not an option.

Why This Process is Unique
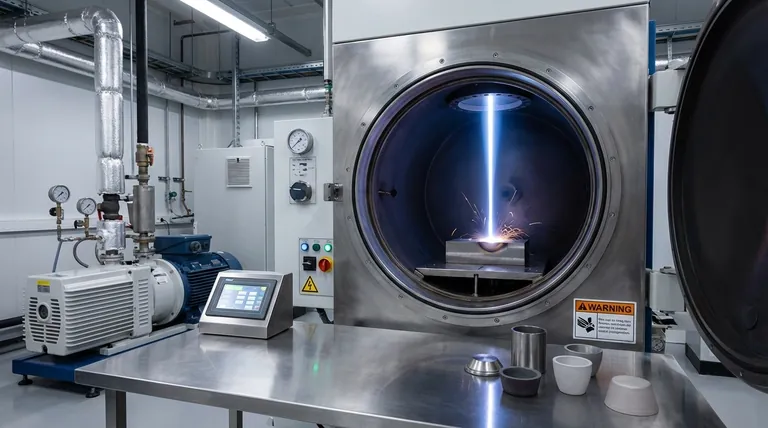
Electron Beam Welding operates on a principle fundamentally different from conventional welding methods. Understanding this is key to grasping its applications.
The Power of High-Energy Density
EBW uses a focused beam of high-velocity electrons to melt and fuse materials. This concentration of energy is far greater than an electric arc, allowing it to create deep, narrow welds with a very small heat-affected zone (HAZ). This minimizes distortion and preserves the properties of the parent material.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
The entire process must occur in a vacuum chamber. This is not a drawback but a defining feature. The vacuum prevents the electrons from scattering off air molecules, ensuring the beam remains focused. It also creates an ultra-pure environment, protecting reactive metals like titanium and zirconium from contamination by oxygen or nitrogen.
Key Industrial Applications in Detail
The unique characteristics of EBW make it the go-to solution in several demanding fields.
Aerospace and Defense
This is the quintessential application for EBW. It is used for fabricating critical jet engine components like turbine blades and compressor rotors, often made from nickel-based superalloys. The process ensures the deep, full-penetration welds needed for structural integrity at extreme temperatures and stresses.
Automotive Sector
In high-volume automotive production, EBW is valued for its speed and low distortion. It is commonly used to weld transmission components, gears, and clutches. By creating strong, precise welds with minimal heat input, manufacturers can produce complex assemblies that are lighter and more durable without the need for post-weld machining.
Medical Device Manufacturing
The precision and purity of EBW are vital for medical implants and instruments. It can create hermetic seals on pacemakers and join dissimilar metals, such as a titanium implant to a stainless steel component. The clean vacuum environment ensures no contaminants are trapped in the weld, which is critical for biocompatibility.
Nuclear and Power Generation
EBW is used for sealing nuclear fuel rods and welding thick sections of reactor components. The vacuum is essential for joining reactive metals common in the nuclear industry, and its ability to penetrate thick materials in a single pass is a significant advantage over other methods that would require multiple passes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, EBW is a specialized tool with clear limitations. Choosing it requires understanding its specific costs and benefits.
Advantage: Unmatched Weld Quality
The deep penetration and narrow profile of an electron beam weld are structurally superior to most other methods. The extremely low heat input results in negligible distortion, which is critical for maintaining tight tolerances in complex assemblies.
Advantage: Purity and Material Versatility
The vacuum environment produces welds of the highest purity, free from atmospheric contamination. This allows for the successful welding of reactive alloys and dissimilar metals that are impossible to join with conventional arc welding.
Limitation: The Vacuum Requirement
The need for a vacuum chamber is the process's primary constraint. It dictates the maximum size of the workpiece and adds significant time to the production cycle for pumping the chamber down. This makes it less flexible than processes like TIG or laser welding.
Limitation: High Capital Investment and Safety
EBW equipment is complex and expensive. Furthermore, the electron beam's interaction with the workpiece generates X-rays, which necessitates extensive lead shielding for the chamber and strict safety protocols for operators.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to use Electron Beam Welding depends entirely on the specific demands of your component and production environment.
- If your primary focus is absolute reliability for critical components: EBW is the superior choice for parts in aerospace or medical devices where weld failure would be catastrophic.
- If your primary focus is joining thick sections or reactive metals: The deep penetration and pure vacuum environment of EBW make it a leading solution for materials like titanium, zirconium, or thick steel sections.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of precision parts: For components like automotive gears, EBW offers a fast, repeatable, and low-distortion process that justifies the capital investment.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, general fabrication: Conventional arc welding processes like MIG or TIG are far more practical, flexible, and economical for less demanding applications.
Ultimately, Electron Beam Welding is a powerful, specialized tool designed to solve the most challenging material joining problems in modern engineering.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Jet engine turbines, compressor rotors | Structural integrity under extreme stress |
| Automotive | Transmission components, gears | High-speed, low-distortion joining |
| Medical Device | Implants, pacemaker seals | Biocompatible, contamination-free welds |
| Nuclear & Power | Reactor components, fuel rods | Welds thick sections and reactive metals |
Need to join difficult materials or fabricate high-performance components? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for materials research and testing. If your project involves developing or qualifying welds for critical applications in aerospace, medical, or energy sectors, our solutions can support your R&D and quality control processes. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Head Tweezers with Pointed Elbow Zirconia Ceramic Tip
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Precision Wire Saw Laboratory Cutting Machine with 800mm x 800mm Workbench for Diamond Single Wire Circular Small Cutting
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is sputtering in plasma treatment? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is called sputtering? The Ultimate Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the container that holds the metal source material called in e-beam evaporation? Ensure Purity and Quality in Your Thin-Film Deposition
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is a magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition



















